Lusophone
Lusophones (Portuguese: Lusófonos) are an ethnolinguistic group of peoples and nations that comprise an estimated 270 million people spread across 10 sovereign states and territories that recognize Portuguese as an official language. This area, known as the Lusofonia or Lusophone World (Mundo Lusófono), is the corresponding community of Lusophone nations which exist in Europe, the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
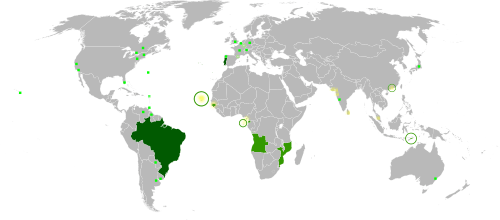
The history of the Lusophone World is intrinsically linked with the history of the Portuguese Empire, although Portuguese diaspora and Brazilian diaspora communities have also played a role in spreading the Portuguese language and Lusophone culture. Today, Portuguese-speaking nations of the world come together for cooperation in politics, culture, and the economy, through the Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth.
Etymology
The term Lusophone is a classical compound, whereby the combining form "Luso-" derives from the Latin term for an area roughly corresponding to modern Portugal, called Lusitania.[1] The suffix "-phone" derives from the Ancient Greek word φωνή (phōnē), meaning "voice". The use of the term Lusophone mirrors similar terms, such as Anglophone for English-speakers, Francophone for French-speakers, Hispanophone for Spanish-speakers, and Sinophone for Chinese-speakers. The term is sometimes used in reference to the Community of Portuguese Language Countries, similar to the Francophonie.
Officially Lusophone countries
| Country | Population (July 2017 est.)[2] | More information | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 207,353,391 | Portuguese in Brazil | Spoken by the vast majority as a native language | |
| 29,310,273 | Portuguese in Angola | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language, and by the majority as a second language | |
| 26,573,706 | Portuguese in Mozambique | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | |
| 10,839,514 | Portuguese in Portugal1 | Spoken by the vast majority as a native language | |
| 1,792,338 | Portuguese in Guinea-Bissau | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | |
| 1,291,358 | Portuguese in East Timor | Spoken by a minority as a second language | |
| 778,358 | Portuguese in Equatorial Guinea | Spoken by a significant minority as a native language | |
| 601,969 | Portuguese in Macau | Spoken by a small minority as a native language | |
| 560,899 | Portuguese in Cape Verde | Spoken by the majority as a second language | |
| 201,025 | Portuguese in São Tomé and Príncipe | Spoken by the vast majority as a native language | |
| Total | c. 279 million | Community of Portuguese Language Countries |
Notes:
- Some linguists such as Lindley Cintra and Teixeira de Pascoaes argue that Galician, spoken in Galicia, is merely a dialect of Portuguese rather than an independent language; this would make northwestern Spain a part of the Portuguese-speaking world.
- Macau is not a sovereign nation. It is one of the two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China (the other being Anglophone Hong Kong, a former British colony).
- Equatorial Guinea adopted Portuguese as one of its official languages in 2007, being admitted to CPLP in 2014. The use of the Portuguese language in this country is limited. However, a Portuguese-based creole language, Annobonese Creole, is used, mainly on islands of Annobon and Bioko.
- 15% of Uruguay's population speaks Portuguese (in the northern regions near Brazil) as a native language though it is not an official language.[3] This makes Portuguese the second most spoken language of the country. A number of Uruguayans living near the Brazilian border also speak a mixture of Spanish and Portuguese called Portuñol.[4] A similar blending of Portuguese, Spanish, and Guarani (Jopara) occurs along the border with Paraguay.
See also
- Geographic distribution of Portuguese
- Lusitanic
- Lusophobia
- Lusophone literature
- Lusophone music
- Lusophone name
References
- "lusophone, adj". OED Online. Oxford University Press. September 2014. Retrieved 18 November 2014.
- "The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population - CIA". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2015-03-07.
- The Portuguese Dialect of Uruguay (DPU) is spoken by circa 15% of the Uruguayan population according Juan Pedro Mir, director of education of the Ministry of Education and Culture of the country. pgl.gal (19 August 2017)
- O dialeto fronteiriço do Uruguai: origens, investigações e oportunidades Archived 27 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine Espaço acadêmico. Retrieved 17 December 2010
External links
| Look up Lusophone in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Words Without Borders explores Lusophone literature in translation
- Flavours of Lusophony (in Portuguese)