Nakasongola Airport
Nakasongola Airport (IATA: n/a, ICAO: n/a) is an airport in Uganda. As of 2013, it was one of the 47 airports in the country.[1] It is the intended headquarters of the Air Wing of the Uganda People's Defense Force and, along with Entebbe Airport, Gulu Airport, Jinja Airport and Soroti Airport, is one of the five national military airports.[2]
Nakasongola Airport | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Military | ||||||||||
| Owner | Uganda People's Defence Force | ||||||||||
| Operator | UPDF | ||||||||||
| Serves | Nakasongola, Uganda | ||||||||||
| Location | Nakasongola, Uganda | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 3,710 ft / 1,130 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 01°25′12″N 32°28′12″E | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
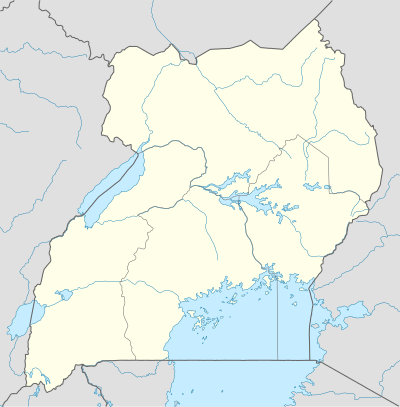 Nakasongola Location of Nakasongola Airport in Uganda Placement on map is approximate | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Location
Nakasongola Airport is located in the neighborhood known as Wabisi, approximately 12 kilometres (7 mi), north of the town of Nakasongola, Nakasongola District, in the Central Region of Uganda.[3] It is located on the campus of Nakasongola Air Force Base, approximately 152 kilometres (94 mi), by air, directly north of Entebbe International Airport, the country’s largest civilian and military airport.[4] The geographic coordinates of Nakasongola Airport are:1°25′12″N 32°28′12″E.[5]
Overview
Nakasongola Airport is a medium-sized military airport that serves the town of Nakasongola. It is the largest stand-alone military airport in Uganda. Nakasongola Airport is approximately 1,130 metres (3,710 ft) above sea level.[6] The airport has a single asphalt runway and taxiway that measure approximately 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) in length.[7]
The airport and the air base on which it is located were constructed by an Israeli company in the 1970s. In 2014, after several years of disuse, the Ugandan government began a renovation of the airport projected to last six months and cost US$11 million (UGX:28 billion) , following which the headquarters of the UPDF Air Force were to be relocated to Nakasongola to decongest Entebbe Air Force Base.[7][8][9] However, in 2016 the construction of a radar system on the site was still incomplete and threatened by a land-use dispute.[10] As of 2019 the relocation of the Air Force had reportedly still not occurred.[11]
See also
References
- CIA (2018). "Uganda: Transportation: Airports". Washington, DC: CIA Factbook. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- Defenceweb (1 March 2014). "Uganda moving combat aircraft out of Entebbe". Johannesburg: Defenceweb.co.za. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Globefeed.com (11 June 2018). "Distance between Post Bank, Nakasongola, Uganda and Nakasongola Airforce Base, Uganda". Globefeed.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Globefeed.com (11 June 2018). "Air Distance between Entebbe International Airport, Entebbe, Uganda and Nakasongola Airforce Base, Uganda". Globefeed.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Google (11 June 2018). "Location of Nakasongola Airport" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Floodmap (11 June 2018). "Elevation of Nakasongola, Uganda". Floodmap.net. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Binnie, Jeremy (25 February 2014). "UPDF Air Wing to move main base". London: Jane's Defence Weekly. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Kasasira, Risdel (5 April 2014). "Works on Nakasongola UPDF Air Base Begin". Daily Monitor. Kampala. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Candia, Steven (23 February 2014). "UPDF's Air Force To Move To Nakasongola". New Vision. Kampala. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Luwaga, Brian (12 August 2016). "Bickering Threatens Radar Project in Nakasongola". Uganda Radio Network. pp. Nakasongola, Uganda. Retrieved 7 November 2019.
- "Museveni rejects CAA proposal to use Nakasongala airport as Entebbe's alternative". The Independent. Kampala, Uganda. 24 April 2019. Retrieved 7 November 2019.