CEMIP
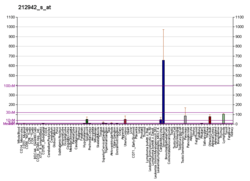
Cell migration-inducing and hyaluronan-binding protein (CEMIP), formerly known as KIAA1199, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEMIP gene.[5] CEMIP has been shown to bind hyaluronic acid and catalyze its depolymerization independently of CD44 and hyaluronidases.[6] Such function has been also been validated in mice.[7]
CEMIP is associated with nonsyndromic deafness,[8] as well as a variety of cancers.[9]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000103888 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052353 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: KIAA1199 KIAA1199".
- Yoshida, H.; Nagaoka, A.; Kusaka-Kikushima, A.; Tobiishi, M.; Kawabata, K.; Sayo, T.; Sakai, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Okada, Y.; Inoue, S. (18 March 2013). "KIAA1199, a deafness gene of unknown function, is a new hyaluronan binding protein involved in hyaluronan depolymerization". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (14): 5612–5617. doi:10.1073/pnas.1215432110. PMC 3619336. PMID 23509262.
- Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagaoka, Aya; Nakamura, Sachiko; Sugiyama, Yoshinori; Okada, Yasunori; Inoue, Shintaro (17 August 2013). "Murine homologue of the human KIAA1199 is implicated in hyaluronan binding and depolymerization". FEBS Open Bio. 3 (1): 352–356. doi:10.1016/j.fob.2013.08.003. PMC 3821019.
- Abe S, Usami S, Nakamura Y (Nov 2003). "Mutations in the gene encoding KIAA1199 protein, an inner-ear protein expressed in Deiters' cells and the fibrocytes, as the cause of nonsyndromic hearing loss". J Hum Genet. 48 (11): 564–70. doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0079-2. PMID 14577002.
- Zhang, Yongsheng; Jia, Shuqin; Jiang, Wen (20 February 2014). "KIAA1199 and its biological role in human cancer and cancer cells (Review)". Oncology Reports. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3038.
Further reading
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Kikuno R, et al. (2000). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 6 (5): 337–45. doi:10.1093/dnares/6.5.337. PMID 10574462.
- Wines ME, Lee L, Katari MS, et al. (2001). "Identification of mesoderm development (mesd) candidate genes by comparative mapping and genome sequence analysis". Genomics. 72 (1): 88–98. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6466. PMID 11247670.
- Nakayama M, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2003). "Protein–Protein Interactions Between Large Proteins: Two-Hybrid Screening Using a Functionally Classified Library Composed of Long cDNAs". Genome Res. 12 (11): 1773–84. doi:10.1101/gr.406902. PMC 187542. PMID 12421765.
- Abe S, Katagiri T, Saito-Hisaminato A, et al. (2003). "Identification of CRYM as a Candidate Responsible for Nonsyndromic Deafness, through cDNA Microarray Analysis of Human Cochlear and Vestibular Tissues". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72 (1): 73–82. doi:10.1086/345398. PMC 420014. PMID 12471561.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Guo J, Cheng H, Zhao S, Yu L (2006). "GG: a domain involved in phage LTF apparatus and implicated in human MEB and non-syndromic hearing loss diseases". FEBS Lett. 580 (2): 581–4. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.12.076. PMID 16406369.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.