Ian Bremmer
Ian Arthur Bremmer (born November 12, 1969) is an American political scientist and author with a focus on global political risk. He is the president and founder of Eurasia Group, a political risk research and consulting firm with principal offices in New York City.
Ian Bremmer | |
|---|---|
 Bremmer in 2017 | |
| Born | November 12, 1969 Chelsea, Massachusetts, United States |
| Occupation | Political scientist, author, entrepreneur, lecturer |
| Nationality | American |
| Education | BA, Tulane University PhD, Stanford University |
| Website | |
| ianbremmer | |
Early life and education
Bremmer is of Armenian and German descent. His father, Arthur, served in the Korean War and died at the age of 46 when Bremmer was four. He grew up in housing projects in Chelsea, Massachusetts, near Boston.[1] Bremmer went to St. Dominic Savio High School in East Boston.[2] He later earned a BA in international relations, magna cum laude, from Tulane University in 1989 and a PhD in political science from Stanford University in 1994, writing "The politics of ethnicity: Russians in the Ukraine".[3][4]
Career
Eurasia Group
Bremmer founded the political risk research and consulting firm Eurasia Group in 1998 in the offices of the World Policy Institute in New York City.[5] The firm opened a London office in 2000, a Washington, DC office in 2005, a Tokyo office in 2015, San Francisco and São Paulo offices in 2016, and Brasilia and Singapore offices in 2017.
Writing
Bremmer has published ten books on global affairs. In addition, Bremmer is the foreign affairs columnist and editor-at-large for Time and a contributor for the Financial Times A-List,[6].
Appointments
Bremmer has held research and faculty positions at New York University, Columbia University, the EastWest Institute, the World Policy Institute, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and the Asia Society Policy Institute, where he has served as the first Harold J. Newman Distinguished Fellow in Geopolitics since 2015.
In 2013, he was named Global Research Professor at New York University.[7] and in 2019, Columbia University's School of International and Public Affairs announced that Bremmer would teach an Applied Geopolitics course at the school.[8]
Bremmer serves on the President's Council of the Near East Foundation, the Leadership Council for the Concordia Summit, and the board of trustees of Intelligence Squared. In 2007, he was named as a "Young Global Leader" of the World Economic Forum, and in 2010, founded and was appointed Chair of the Forum's Global Agenda Council for Geopolitical Risk. In December 2015, Bremmer was knighted by the government of Italy.
Key concepts
Bremmer's research fields include: international political economy, geoeconomics and geopolitics, states in transition and global emerging markets, and US foreign policy.
J-Curve
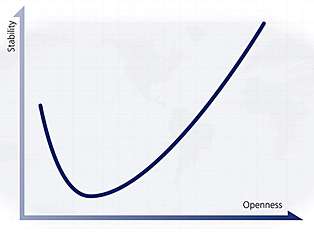
Bremmer's J curve[9] outlines the link between a country's openness and its stability. While many countries are stable because they are open (the United States, France, Japan), others are stable because they are closed (North Korea, Cuba, Iraq under Saddam Hussein). States can travel both forward (right) and backward (left) along this J curve, so stability and openness are never secure. The J is steeper on the left-hand side, as it is easier for a leader in a failed state to create stability by closing the country than to build a civil society and establish accountable institutions; the curve is higher on the far right because states that prevail in opening their societies (Eastern Europe, for example) ultimately become more stable than authoritarian regimes.
State capitalism
Ian Bremmer describes state capitalism as a system in which the state dominates markets primarily for political gain. In his 2010 book The End of the Free Market: Who Wins the War Between States and Corporations ), Bremmer describes China as the primary driver for the rise of state capitalism as a challenge to the free market economies of the developed world, particularly in the aftermath of the financial crisis.[10]
G-Zero
The term G-Zero world refers to a breakdown in global leadership brought about by a decline of Western influence and the inability of other nations to fill the void.[11][12] It is a reference to a perceived shift away from the pre-eminence of the ["G7"] ("Group of Seven") industrialized countries and the expanded Group of Twenty, which includes major emerging powers like China, India, Brazil, Turkey, and others. In his book, Every Nation for Itself: Winners and Losers in a G-Zero World (New York: Portfolio, 2012), Bremmer explains that, in the G-Zero, no country or group of countries has the political and economic leverage to drive an international agenda or provide global public goods.[13][14]
Weaponization of finance
The term weaponization of finance refers to the foreign policy strategy of using incentives (access to capital markets) and penalties (varied types of sanctions) as tools of coercive diplomacy. In his Eurasia Group Top Risks 2015 report,[15] Bremmer coins the term weaponization of finance to describe the ways in which the United States is using its influence to affect global outcomes. Rather than rely on traditional elements of America's security advantage – including US-led alliances such as NATO and multi-lateral institutions such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund – Bremmer argues that the US is now 'weaponizing finance' by limiting access to the American marketplace and to US banks as an instrument of its foreign and security policy.
Pivot state
Bremmer uses pivot state to describe a nation that is able to build profitable relationships with multiple other major powers without becoming overly reliant on any one of them.[16] This ability to hedge allows a pivot state to avoid capture—in terms of security or economy—at the hands of a single country. In his book, Every Nation for Itself: Winners and Losers in a G-Zero World (New York: Portfolio, 2012),[17] Bremmer explains how, in a volatile G-Zero world, the ability to pivot will take on increased importance. At the opposite end of the spectrum are shadow states frozen within the influence of a single power. For example, with significant trade ties with both the United States and Asia and formal security ties with NATO, Canada is an example of a pivot state hedged against a slowdown in or conflict with any single major power. Mexico, on the other hand, is a shadow state due to its overwhelming reliance on the US economy.
Geopolitical recession
Bremmer has coined the term “geopolitical recession” to describe the current geopolitical environment, one defined by an unwind of the former US-led global order. Unlike economic recessions, linked to frequent boom and bust cycles, Bremmer see geopolitical recessions as much longer cycles, and accordingly are less likely to be recognized.[18] He see the present geopolitical recession as defined by deteriorating relations between the US and its traditional allies—particularly the Europeans—as China is rising but creating alternative international political and economic architecture. Bremmer argues that the overall result is a more fragmented approach to global governance, an increase in geopolitical tail risks, and a reduced ability to respond effectively to major international crises when they do hit.
World Data Organization
Bremmer proposed creating a “World Data Organization” to forestall a division in technology ecosystems due to conflict between the United States and China. He described it as a digital version of the World Trade Organization, arguing that the United States, Europe, Japan, and other “governments that believe in online openness and transparency” should collaborate to set standards for artificial intelligence, data, privacy, citizens’ rights, and intellectual property.[19] 2020 Democratic party presidential nominee candidate Andrew Yang expressed his support for such an organization during his campaign.[20][21]
Other organizations
In 2016, Bremmer founded the Eurasia Group Foundation (EGF), a 501(c)3 public charity. EGF created its first social media campaign to raise awareness in American voters about the foreign policy issues informing the presidential election. In 2019, it launched "Independent America", a multi-year project exploring what a more restrained US foreign policy would look like to Americans and elsewhere. Bremmer currently serves as the Eurasia Group Foundation’s board president.
Controversies
In March 2016, Bremmer sent a weekly note to clients where he unintentionally came up with the “America First” slogan used by Donald Trump. The note described then-candidate Trump's foreign policy as not isolationist but "America First," a transactional, unilateralist perspective that was more a Chinese than American framework for foreign policy. Bremmer used the term to help explain Trump’s foreign policy views and not as a campaign slogan.
A few weeks later New York Times reporters David Sanger and Maggie Haberman, both of whom receive Bremmer's weekly note, conducted Trump’s first foreign policy interview and asked him if he would describe himself as an isolationist. He said no. They then asked Trump if he considered himself America First. Trump said yes[22] and liked the term so much he started using it himself. Haberman later credited Bremmer with coming up with “America First” to describe Trump’s foreign policy.[23]
In July 2017, Bremmer broke news of a second, previously undisclosed meeting between Presidents Trump and Putin during the G20 heads of state dinner in Hamburg. He wrote about the meeting in his weekly client note and later appeared on Charlie Rose to discuss the meeting’s implications. The news was quickly picked up by other major media outlets. Newsweek profiled Bremmer in an article titled "Who is Eurasia Group’s Ian Bremmer, the risk consultant who exposed the second Trump-Putin meeting?"[24] Trump initially denied that his second meeting with Putin happened and called Bremmer "fake news."[25] However, then-White House Press Secretary Sarah Sanders later held a press conference and admitted the second meeting indeed happened.[26]
In 2019, Bremmer was criticized on Twitter[27] for posting a tweet that appeared to quote Trump. The tweet read: "President Trump in Tokyo: 'Kim Jong Un is smarter and would make a better President than Sleepy Joe Biden.'" After the tweet went viral, Bremmer acknowledged on Twitter that President Trump did not in fact say that quote and apologized on Twitter.[28] President Trump used the incident to call for stronger libel laws.[29]
Selected bibliography
- Soviet Nationalities Problems. (edited with Norman Naimark), (Stanford: Stanford Center for Russian and East European Studies: 1990). ISBN 0-87725-195-9
- Nations and Politics in the Soviet Successor States. (edited with Raymond Taras), (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993). ISBN 0-521-43860-8
- New States, New Politics: Building the Post-Soviet Nations. (edited with Raymond Taras), (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997). ISBN 0-521-57799-3
- The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall. (Simon & Schuster, 2006; revised paperback, 2007). ISBN 0-7432-7471-7
- 'Managing Strategic Surprise: Lessons from Risk Management & Risk Assessment. (edited with Paul Bracken and David Gordon), (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008). ISBN 0-521-88315-6
- The Fat Tail: The Power of Political Knowledge for Strategic Investing. (with Preston Keat), (New York: Oxford University Press, 2009; revised paperback, 2010). ISBN 0-19-532855-8
- The End of the Free Market: Who Wins the War Between States and Corporations. (New York: Portfolio, 2010; revised paperback 2011). ISBN 978-1-59184-301-6
- Every Nation for Itself: Winners and Losers in a G-Zero World. (New York: Portfolio, May 2012; revised paperback 2013). ISBN 978-1-59184-468-6
- Superpower: Three Choices for America's Role in the World. (New York: Portfolio, May 2015). ISBN 978-1591847472
- Us vs Them: The Failure of Globalism. (New York: Portfolio, April 2018). ISBN 978-0525533184
References
- Thompson, Damian (September 30, 2006). "Here's how the world works". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved August 1, 2008.
- ""Superpower" Excerpt by Ian Bremmer". MSNBC. May 19, 2015.
- "Ian Bremmer | World Policy Institute". Worldpolicy.org. Retrieved January 30, 2016.
- "The politics of ethnicity : Russians in the Ukraine". Stanford University. Archived from the original on March 27, 2017. Retrieved March 27, 2017.
- Harding, Luke (February 3, 2018). "Why Carter Page Was Worth Watching: There's plenty of evidence that the former Trump campaign adviser, for all his quirks, was on suspiciously good terms with Russia". Politico. Retrieved October 8, 2018.
- "The A-List". The Financial Times. June 2011.
- "Ian Bremmer, President of Eurasia Group, Named NYU Global Research Professor". Nyu.edu. Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- "Eurasia Group | Ian Bremmer returns to Columbia University Faculty". eurasiagroup.net. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- Bremmer, Ian. 2006. The J Curve: A New Way to Understand Why Nations Rise and Fall. Simon and Schuster.
- "State capitalism: China's 'market-Leninism' has yet to face biggest test". Ft.com. Retrieved July 19, 2017. (subscription required)
- "Eurasia Group Top 10 Risks of 2011". Eurasiagroup.net. Archived from the original on January 31, 2011. Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- Gregory Scoblete. Will Free Markets Give Way to State Capitalism?, RealClearPolitics, May 28, 2010.
- Ian Bremmer and David Gordon.G-Zero Archived September 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Foreign Policy, January 7, 2011.
- Ian Bremmer and Nouriel Roubini. A G-Zero World, Foreign Affairs, March/April 2011.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 28, 2015. Retrieved April 27, 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "The Future Belongs to the Flexible". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- Bremmer, Ian. Every Nation for Itself, New York: Portfolio, 2012, ISBN 978-0670921041
- Tan, Weizhen (October 10, 2018). "A 'geopolitical recession' has arrived and the US-led world order is ending, Ian Bremmer says". CNBC. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- "Why we need a World Data Organization. Now". GZERO Media. November 25, 2019. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- Yang 🧢, Andrew (November 25, 2019). "You heard me talk about my support for a World Data Organization in last week's debate. I got the idea from @ianbremmer. Thanks Ian https://www.gzeromedia.com/why-we-need-a-world-data-organization-now …". @AndrewYang. Retrieved December 4, 2019. External link in
|title=(help) - Everything Andrew Yang Said at the Democratic Debate in Atlanta | NBC New York, retrieved December 4, 2019
- "Transcript: Donald Trump Expounds on His Foreign Policy Views". The New York Times. March 26, 2016. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- Haberman, Maggie (March 26, 2016). ".@ianbremmer was one who identified Trump's view as "America First" a few months ago". @maggieNYT. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- EDT, Tom Porter On 7/19/17 at 9:09 AM (July 19, 2017). "Who is Ian Bremmer, the political risk consultant who broke the story of the second Trump-Putin meeting?". Newsweek. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- "Russian lawmaker: Reports of 'secret' Putin-Trump meeting 'sick'". USA TODAY. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- "Trump, Putin had second, previously undisclosed meeting at G-20 summit". NBC News. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- "NYU Professor Panned For Tweeting Out Fake Trump Quote". Mediaite. May 26, 2019. Retrieved May 26, 2019.
- bremmer, ian (May 27, 2019). "My tweet yesterday about Trump preferring Kim Jong Un to Biden as President was meant in jest. The President correctly quoted me as saying it was a "completely ludicrous" statement. I should have been clearer. My apologies". @ianbremmer. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- Rosenberg, Eli (May 27, 2019). "A political scientist caused confusion when he made up a Trump quote. The president noticed". The Washington Post. Washington DC. Retrieved May 27, 2019.
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Ian Bremmer |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ian Bremmer. |
- Official website
- Profile at Eurasia Group
- A Second Look... by Ian Bremmer
- The End of the American International Order: What Comes Next? by Ian Bremmer