Great crested grebe
The great crested grebe (Podiceps cristatus) is a member of the grebe family of water birds noted for its elaborate mating display. Its scientific name comes from Latin: the genus name Podiceps is from podicis, "vent" and pes, "foot", and is a reference to the placement of a grebe's legs towards the rear of its body; the species name, cristatus, means "crested".[2]
| Great crested grebe | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Podicipediformes |
| Family: | Podicipedidae |
| Genus: | Podiceps |
| Species: | P. cristatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Podiceps cristatus | |
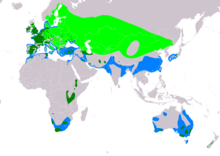 | |
| Range of P. cristatus
Breeding Resident Non-breeding | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Colymbus cristatus Linnaeus, 1758 | |
Description
The great crested grebe is the largest member of the grebe family found in the Old World, with some larger species residing in the Americas. They measure 46–51 cm (18–20 in) long with a 59–73 cm (23–29 in) wingspan and weigh 0.9 to 1.5 kg (2.0 to 3.3 lb).[3][4] It is an excellent swimmer and diver, and pursues its fish prey underwater. The adults are unmistakable in summer with head and neck decorations. In winter, this is whiter than most grebes, with white above the eye, and a pink bill.
The young are distinctive because their heads are striped black and white. They lose these markings when they become adults.
Distribution
The great crested grebe breeds in vegetated areas of freshwater lakes. The subspecies P. c. cristatus is found across Europe and east across the Palearctic. It is resident in the milder west of its range, but migrates from the colder regions. It winters on freshwater lakes and reservoirs or the coast. The African subspecies P. c. infuscatus and the Australasian subspecies P. c. australis are mainly sedentary.
Behaviour
The great crested grebe has an elaborate mating display. Like all grebes, it nests on the water's edge, since its legs are set relatively far back and it is thus unable to walk very well. Usually two eggs are laid, and the fluffy, striped young grebes are often carried on the adult's back. In a clutch of two or more hatchlings, male and female grebes will each identify their 'favourites', which they alone will care for and teach.
Unusually, young grebes are capable of swimming and diving almost at hatching. The adults teach these skills to their young by carrying them on their back and diving, leaving the chicks to float on the surface; they then re-emerge a few feet away so that the chicks may swim back onto them.
The great crested grebe feeds mainly on fish, but also small crustaceans, insects small frogs and newts.
This species was hunted almost to extinction in the United Kingdom in the 19th century for its head plumes, which were used to decorate hats and ladies' undergarments. The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds was set up to help protect this species, which is again a common sight.
The great crested grebe and its behaviour was the subject of one of the landmark publications in avian ethology: Julian Huxley's 1914 paper on The Courtship‐habits of the Great Crested Grebe (Podiceps cristatus).[5][6]
Gallery
 A flock at high altitude marsh at 5,600 ft: Khecheopalri Lake in Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve, West Sikkim in India
A flock at high altitude marsh at 5,600 ft: Khecheopalri Lake in Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve, West Sikkim in India- Juvenile with adult
 Head of juvenile with characteristic stripes
Head of juvenile with characteristic stripes.jpg) Adult ready to feed its young in Scotland
Adult ready to feed its young in Scotland.jpg) Mating ritual, Otmoor, Oxfordshire
Mating ritual, Otmoor, Oxfordshire.jpg) Male displaying during mating ritual, Otmoor, Oxfordshire
Male displaying during mating ritual, Otmoor, Oxfordshire- Great Crested Grebe courtship display at Hyde Park, London, UK
 Podiceps cristatus with nest and eggs, Sweden 2013
Podiceps cristatus with nest and eggs, Sweden 2013 Podiceps cristatus family at nest, Sweden 2013
Podiceps cristatus family at nest, Sweden 2013 Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015
Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015 Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015
Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015 Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015
Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015 Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015
Podiceps Cristatus Sweden 2015 Museum specimen
Museum specimen.jpg) Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019
Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019.jpg) Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019
Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019.jpg) Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019
Podiceps cristatus, Serbia 2019 A great crested grebe in Thunersee in Spiez in Switzerland
A great crested grebe in Thunersee in Spiez in Switzerland
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Podiceps cristatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 122, 341. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- "Great crested grebe videos, photos and facts – Podiceps cristatus". ARKive. Archived from the original on 2012-08-23. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- Burnie, D.; Wilson, D.E., eds. (2005). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. DK Adult. ISBN 0789477645.
- Burkhardt Jr, R.W. (1992). Huxley and the rise of ethology. Julian Huxley. Biologist and statesman of science. Houston, Texas: Rice University Press. pp. 127–149.
- Huxley, J.S. (September 1914). "33 The Courtship‐habits* of the Great Crested Grebe (Podiceps cristatus); with an addition to the Theory of Sexual Selection" (PDF). Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. 84 (3): 491–562. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1914.tb07052.x.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Podiceps cristatus. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Podiceps cristatus |
- Ageing and sexing (PDF) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze
- "Great crested grebe media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Great Crested Grebe Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
- Podiceps cristatus in the Flickr: Field Guide Birds of the World
- "Podiceps cristatus". Avibase.

- BTO BirdFacts – Great-crested Grebe
- BirdLife species factsheet for Podiceps cristatus
- Great crested grebe photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Audio recordings of Great crested grebe on Xeno-canto.
