Electric vehicle industry in India
This article is about the electric vehicle landscape in India. The central and state governments have launched schemes and incentives to promote electric mobility in the country and some regulations and standards are also in place. While the country stands to benefit in a large way by switching its transport from IC engines to electric motor-powered, there are challenges like lack of charging infrastructure, high initial cost and lack of electricity produced from renewable energy. Still, e-commerce companies, car manufacturers, app-based transportation network companies and mobility solution providers have entered the sector and are slowly building up electric car capacity and visibility.[1][2]

Government policies
India unveiled the 'National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020' in 2013 to address the issues of National energy security, vehicular pollution and growth of domestic manufacturing capabilities.[3][4] Reiterating its commitment to the Paris Agreement, the Government of India has plans to make a major shift to electric vehicles by 2030.[5][6][7]
Central government
Recently, the Government released a two-pronged strategy aimed at both buyers and manufacturers, in which it offers $1.4 billion in subsidies to buyers while imposing a hike on import tariffs to increase manufacturing of these vehicles by domestic companies.[8] The Government is mainly focusing to electrify public transportation as the subsidies, mainly available for two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and buses. This policy also earmarks $140 million to develop charging infrastructure which should further help the development of the EV industry in India.[8] On 14 December 2018, the government also released a document which outlines the standard and guidelines for EV Charging infrastructure. Beyond the specifications of the charging infrastructure, the guidelines also required a charging station to be present every 25 km along a road/highway.[9]
Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL) is procuring 10,000 nos. of Electric Vehicles from reputed manufacturers for distribution to Government Departments on rental model and upfront sale model. EESL's tender of 10,000 nos. of EV's has reduced the cost of EV's substantially.
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020
The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020 was launched by the Government of India in 2020 with the aim of improving the national fuel security through the promotion of hybrid and electric vehicles.[10]
Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric vehicles (FAME)
The Government started Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric vehicles (FAME) scheme which provides incentives for purchasing electric vehicles.[11] Phase I of the scheme lasted from 2015 to 2019,[12] while Phase II began in 2019 and is planned to be completed in 2022.[13][14]
Government is releasing tenders to increase charging infrastructure in the country.[15] The scheme offers incentives to the electric and hybrid vehicles ranging from Rs.1,800 to Rs.29,000 for scooters and motorcycles and Rs.1.38 Lac for cars. FAME is a part of National Electric Mobility Mission Plan by Government of India.[16]
Delhi
The Delhi Government recently approved 1000 Electric buses to be used in Delhi’s public transport system.[17]
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu chief minister Edappadi K Palaniswami on Friday launched in Chennai, Mauto Electric mobility’s electric autorickshaws - touted as India’s first retrofit electric autos in India in 2019.
Dubai-based KMC group and Mauto Electric Mobility will convert petrol-run autorickshaws into electric vehicles with an investment of Rs 100 crore and offer job opportunities to 5,000 people. KMC group and Mauto Electric Mobility signed a memorandum of understanding during chief minister’s stopover in Dubai during his three-nation trip in September. The MoUs were signed at an event hosted by the Business Leaders Forum (BLF), an initiative of UAE’s ministry of economy and the Indian Embassy in the UAE. The state government recently gave necessary clearances for the units to start the venture.
“The driving range per full charge of three hours will be 100km. The aim is to introduce 4,000 electric rickshaws in the city, 100 by a month to reduce air pollution to a large extent. The autos are fitted with CCTV surveillance, panic button and television. It is highly safe for children going to school and women,” said Mansoor Ali Khan, chairman, Mauto group of companies. Mansoor,CEO of MAuto Group, said the petrol-driven autorickshaws would incur an expenditure of Rs 350-Rs 400 for every 100km while it is Rs 40 for electric autorickshaws. “The retrofitting of autorickshaws will cost only Rs 1.2 to Rs 1.5 lakh. We are ready to convert the vehicles registered after 2000,” he added.The company is planning to set up charging stations in each of the ten zones of the city. Charging on the go will be possible with the help of a mobile app. [18]
Karnataka
Karnataka approved Electric Vehicle and Energy Storage Policy 2017.[19]
Maharashtra
The Maharashtra Government is focusing on increasing EV use in the state by proposing to exempt EV’s from road tax and providing a 15% subsidy to the first lakh EV’s registered in the state. To improve suitable infrastructure, the government proposed to provide a maximum subsidy of Rs. 1 million (~$15,549) per charging station to the first 250 stations that are set up in Maharashtra.[20]
Uttarakhand
In 2018, the Uttrakhand Government introduced a new scheme to help the manufacturing and promote the use of EV’s as well.[21] The scheme would provide companies with loans ranging between Rs 10 crore and Rs 50 crore to build EV's and charging infrastructure. The scheme also doesn't charge motor tax for first lakh customers of EV’s for five years.
Regulatory framework

Charging
AC charging
IS:17017 specifies Bharat EV Charging standard AC001. It uses 15A, 230V, 3.3kW, and an IEC 60309 connector.
Electric vehicles can be charged using a regular 220V 15A household supply that delivers around 2.5kW power. There is no policy or standard defined for at-home EV charging. Bharat EV specifications recommend the installation of a Residual Current Circuit Breaker to ensure safety and using an IEC 60309 Industrial connector, but a 3-pin 15A plug could also be used.[22]
For higher power AC charging (~22kW), Type 2 connectors are specified.[23] The advantage of Type 2 connectors is that they can use three phase AC power for charging.
DC charging
The public DC Charging Standard is DC 001. It uses custom GB/T for EV-EVSE communication over CAN mode.[22] It uses 200A, 15kW, and a GB/T 20234 connector.
The IS:17017-1 published by BIS in August 2018 recommends CCS-2 (Combined Charging System) and CHAdeMO protocols for high power fast charging.[22][24]
The advantage of CCS over CHAdeMO and GB/T is that it uses Power Line Carrier Communications (PLCC) for EV-EVSE communication while CHAdeMO and GB/T use CAN. PLC allows secure communication using encrypted messages and the link can support higher data-rate as compared to that by CAN.[25]
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)
The IS:17017 standard published by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) covers general requirements and safety norms for EVSEs.[22]
Central Management System (CMS)
The Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) 1.5 or higher over the internet is to be used.[26]
Benefits of electric vehicles
- Electric vehicles are around 3-5 times more efficient than internal combustion vehicles in utilising energy. Even if electric vehicles run on electricity produced from fossil fuels, the overall efficiency of electric vehicles is still higher and the pollution is less, because large thermal power plants are much more efficient than IC engines, and it is easier to control emissions from power plants than vehicle engines.
- Electric vehicles save energy by regenerative braking. Around 30-70% of the energy used for propulsion can be recovered, with higher percentages applicable to stop-and-go city driving.[27]
- Air quality indices related to India[28][29][30] indicate that the air in many cities of India is no longer healthy. Automobile related pollution has been one of the causes for this.
- Aspects related to global warming needs a shift to automobile solutions that reduce / do not produce greenhouse gas emissions. If electric vehicles run on electricity produced from non-polluting sources of energy like hydro, solar, wind, tidal and nuclear, they reduce emissions due to vehicles almost to zero.
- The need to reduce dependency on a fossil-fuel based economy. India's crude oil imports for 2014-15 was 112 billion dollars[31] (approximately 7,00,000 crore rupees). For comparison, the allocation for the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme, in budget 2017-18, is 48,000 crore rupees.[32]
- India can become a global provider for clean mobility solutions and processes that are affordable and scalable.
- People living in some Indian cities are being affected by noise pollution.[33] Some of the Indian cities have the worst noise pollution levels in the world.[34][35] Electric vehicles are much quieter and may contribute to a reduction in noise pollution levels in the cities.[36]
- Energy efficiency and emission reduction has improved in automobiles. Yet, the growth in total number of vehicles on road, and the resulting total pollution and total energy consumption removed all gains made by betterment in energy efficiency and emission reduction by automobiles. Energy efficiency measures and pollution control measures did not keep pace with the sales growth in vehicles. The total number of vehicles registered in India has been 5.4 million,[37] 11 million,[38] 33 million,[38] 40 million[39] and 210 million[37] in the years 1981, 1986, 1996, 2000 and 2015. This indicates a 3500+ percentage growth in the total number of vehicles between 1981 and 2015. The total number of vehicles sold in India increased between 1,54,81,381 in 2010-11 and 2,04,69,385 in 2015-16 [40] indicating a 30+ percentage growth in this five year period.
- Through smart charging, electric vehicles can help to balance the balance-supply variations in the electricity grid, and provide a buffer against electricity supply failures.
- Electric vehicles have much fewer moving parts as compared to vehicles with IC engines. Thus, being simpler, they are cheaper and easier to maintain.[41][42]
- Electric motors can deliver high torque at low speeds. As a result, electric vehicles deliver much better performance while starting off and on slopes than IC engine-powered vehicles.[43]
Challenges faced
Lack of charging infrastructure
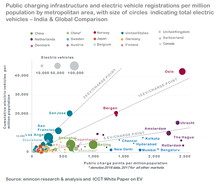
The charging infrastructure for electric vehicles in India has not been fully developed yet. For more details, see the section 'Charging Infrastructure' below.
Cost
The cost of EVs is very high mainly due to the cost of Li-ion cells. The battery packs are imported and cost a lot, about $275/KWh in India. This combined with the GST of 28% and the lack of lithium in India, further increase the cost of batteries. Most EVs in India provide a range of 110 km and cost between Rs 6-8 lakhs which does not give a cost advantage compared to higher range cars in the same price range.[44]
Lack of renewable energy and grid infrastructure
In India electricity is mainly produced by burning coal, which produces a great amount of greenhouse emissions. With the introduction of EVs and charging infrastructure, the electricity demand will go up a lot and the whole point of introducing EVs to reduce GHG emissions would be ineffective, if all this electricity was produced by burning coal. Moreover, India’s Distribution companies hold debts and are unable to suffice the energy requirement of the whole country adequately. If EVs were to enter this equation, the sudden increase in electricity requirement would put extra load on these companies. Moreover, there are a lot of factors that would go into deciding pricing of the electricity as well the demand on the grid.[45]
Charging infrastructure
The Government of India has declared public charging stations and EV charging businesses as a de-licensed activity.[46][47] The government has laid down that there should be at least one charging station in a grid of 3km x 3km in cities and one station every 25 Km on both sides of highways. This coverage is to be achieved in cities with a population of more than 4 million and all existing expressways and important highways connected to these mega-cities by 2022. The second phase (3-5 years) will cover big cities like state capitals and UT headquarters.[48]
There have been initiatives to set up community charging stations, as in the case of Plugin India facilitated charging stations.[49] News reports have indicated about plans to provide solar-powered charging points at the existing fuel stations of the country.[50][51][52]
There are companies like Tata Power, Fortum and others which are engaged in the business of electric vehicle charging. They have already installed all varieties of chargers - rapid DC chargers and level 2 AC chargers for all kinds of applications - public access, workplace charging, fleet charging, residential communities, malls, highways etc and have large plans to scale up.
Charging infrastructure, mainly setting up of level 2 charging at public level shall be the toughest challenge in terms of service integration for India. For normal charging, the charging time poses a serious problem as it ranges from 6 to 8 hours whereas for fast DC charging; cost & high renewable energy are the biggest factors which could pose a problem. It is also assumed that 10% of the charging infrastructure required in India shall be composed of fast charging station and rest 90% shall come from level 2 public charging setups.[53]
On 22 May 2018 Ather Energy launched its charging infrastructure service in Bangalore called Ather Grid, with each charging station called 'Point'. The service is open to all electric vehicles but has been deployed where Ather plans to launch its own electric scooter.[54]
Industry associations
- Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers
- Society of Manufacturers of Electric Vehicles (SMEV)
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design
Electric vehicle manufacturers
Fully electric cars

The electric cars available in India are:
- Hyundai Kona Electric[55]
- Mahindra e-Verito[56]
- Mahindra e2o
- MG ZS EV
- Tata Tigor EV 2019 (Only for Commercial purposes)[57]
- Tata Nexon EV 2020
ISRO has tested a solar-powered hybrid car - modified Maruti Omni with a solar panel platform installed on top of the car. The installation of this solar platform on the car has been rated "awful" for its design.[58] The Hyundai Kona electric has the highest range of 452(as per ARAI) km in a single charge among the electric cars available in India.
Motorcycles
The following companies have launched electric motorcycles in India:
Scooters
Buses
.jpg)
India's first electric bus was launched in Bangalore in 2014.[69]
Ashok Leyland launched its electric bus in October 2016.[70]
Tata Motors launched its pure electric bus ‘Starbus Electric 9m’ and hybrid ‘StarBus Electric 12m’ in January 2017.[71]
Goldstone Infratech supplied Himachal Pradesh Transport Corporation with 25 electric buses in September 2017.[72]
25 Tata Starbus Hybrid electric buses were delivered in Maharashtra in March 2018.
India's first intercity electric bus was inaugurated on 5 September which is operated between Mumbai and Pune by MSRTC[73]
November 2019, 133 Electric buses have been deployed across Pune city in the first phase of its e-bus programme.
Mini pickup trucks
The following companies have launched electric pickup trucks in India:
Heavy duty trucks, semi-trailer and tractor trucks
A Gurgaon based company, Infraprime Logistics Technologies Pvt. Ltd. launched first heavy duty truck (tractor-tipper-trailer combination) in India in Sep 2019.[77]
No other case of manufacturing and use of electric heavy duty trucks, semi-trailers or tractor trucks in India has been reported.
Rickshaws

A Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill was passed by the Parliament in 2015, which established battery-powered e-rickshaws as a valid form of commercial transport in India.[78] With their small size and small turning radius, E-rickshaw is already a popular mode of transport in Delhi-NCR, particularly in small lanes and congested areas.
The following companies have launched electric auto rickshaws in India:
- MAuto Electric Mobility (First in India to introduce Retrofit EV Vehicles in Auto rickshaw category) [79]
- Entice Impex Pvt Ltd (Gatti E-rickshaw) [80]
- Mahindra[74]
- Kerala Neem G[81] from Kerala Automobiles Limited
Railways

Indian Railways has a long history of electric locomotives, with their first use in 1925. On 31 March 2017, government announced that the entire rail network in the country will be electrified by 2022.[82] Indian Railways has successfully tested solar-panel mounted trains.[83][84] Power generated from these solar panels will be used for the lights and fans inside the train.[85]
Solar-electric boat
- Aditya, from NavAlt
Conversion of old vehicles in to battery vehicles
- E-trio Automobiles for Maruti Alto and Maruti Wagon R[86]
Hybrid cars
Hybrid cars are available in various types depending upon its combination of power supply form battery and petrol.[87] Below are some of the hybrid cars available in India:[88]
- Toyota Prius
- Honda Accord Hybrid
- Toyota Camry
- MG Hector
- Maruti Suzuki Ciaz
- Maruti Suzuki Swift
- Maruti Suzuki Ertiga
- Mahindra Scorpio Intelli hybrid
- Maruti Suzuki Baleno (mild hybrid)
- Toyota Glanza (mild hybrid)
- Volvo XC90 T8 Excellence
- BMW i8
Mobility solution providers
In 2015, Bangalore based Lithium Technologies launched a fully electric taxi service for corporates.[89] In June 2017, Bangalore based logistic group Baghirathi Travel Solutions is one of the EV fleet Transport company.[90]
In January 2019, Blu-Smart mobility launched all-electric cab service in Delhi-NCR with a fleet of 70 Mahindra eVerito cars. It has plans of expansion to 400 cars by March 2019. Also, it has planned to set up a massive charging infrastructure comprising 65 stations. Each station will have the capacity to charge up to 20 vehicles at a time, with 20 charging points. The company has also ensured there will be a charging station within every five kilometre of radius. The company also has plans for Tata Tigor electric, Nissan Leaf, BMW i3 and Tesla 3 in their fleet. So far the company is running only 10 cars in Delhi NCR and not a single charging station has been installed. The promoters do not intent to increase number of fleets post automobile industry's massive losses that has hit market as well as production values. [91] The company raised funding from Deepika Padukone (Ka Enterprises), Micromax co-founder Rajesh Agarwal, Sanjiv Bajaj (Bajaj Capital MD), Rajat Gupta (former Global MD McKinsey) and Rohit Chanana (Ex-President Strategy, Hero Corporate Services) and various other VC firms.[92][93]
See also
- Automotive industry in India
- Bicycle-sharing system
- Bus lane
- Electric car use by country
- Electric truck
- Electric car use by country
- Electric vehicle industry in China
- Electric vehicle industry in Pakistan
- Plug-in electric vehicles in the United States
- Plug-in electric vehicles in Europe
- Energy efficiency in transport
- List of prototype solar-powered cars
- List of vehicle plants in India
- Pedestrian zone
- Solar car
- Solar vehicle
- Vehicular metrics
- Walkability
- Oil and gas industry in India
References
- "Ola readies big push for electric vehicles". The Times of India. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- "Marketers of Electric Vehicles in India". erickshawprice.com.
- "India Prime Minister today unveiled the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. Retrieved 15 August 2015.
- "Why the government is betting big on EVs, and why the gambit has automobile industry worried". The Economic Times. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "India Wants To Become First Country With 100 Percent Electric Vehicles". techtimes.com. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- "Germany and India Aim to Have All Cars Electric by 2030 (TSLA)". investopedia.com. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- "India is planning to reach 100% electric vehicles by 2030". horizons.gc.ca. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- Bahree, Megha. "India Offers $1.4 Billion In Subsidies To Support The Domestic Electric Vehicle Industry". Forbes. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- "Government to Install Electric Vehicle Charging Stations at Every 25 Km in India". News18. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- "National Electric Mobility Mission: 2020". Drishti IAS. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "FAME-India scheme launched to offer sops on hybrid, e-vehicles". Economic Times.
- "FAME India scheme - MANIFEST IAS". Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "FAME INDIA II Scheme.. : Department of Heavy Industry, Ministry of Heavy Industries & Public Enterprises, Government of India". Dhi.nic.in. 4 May 2020. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "National Automotive Board (NAB)". Fame2.heavyindustry.gov.in. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Govt. Invites Tenders For 10,000 Electric Vehicles & 4,000 Charging Stations In NCR". Inc42.
- "FAME India Scheme launched to offer sops on hybrid, e-vehicles". Economic Times.
- "Cabinet approves engagement of 1,000 Low Floor AC pure electric buses – Aam Aadmi Party". Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- "100 electric-autorickshaws mostly driven by women to hit roads".
- "Karnataka govt approves electric vehicle policy to reduce dependency on fossil fuels". Livemint.
- "Highlights of Maharashtra EV Policy (2018) – Incentives, Subsidies, Exemptions of Electric Vehicle Policy | India Renewable Energy Consulting - Solar, Biomass, Wind, Cleantech". eai.in. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- "Uttarakhand cabinet nod to new electric vehicle manufacturing policy to combat pollution". Hindustan Times. 28 September 2018. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- "A Guide to EV Charging and EV Standards in India • EVreporter". EVreporter. 13 September 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Bharat EV specifications for AC and DC charging". Pluginindia.com. 27 December 2017. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "EV charging station guidelines to support dual platforms". Team-BHP. 18 December 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Report of the committee on technical aspects of charging infrastructure for EVs" (PDF). Central Electricity Authority, Government of India. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Committee Report on Standardization of Public EV Chargers" (PDF). Department of Heavy Industry, Government of India. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- Martins, L. a. S. B.; Brito, J. M. O.; Rocha, A. M. D.; Martins, J. J. G. (8 July 2010). "Regenerative Braking Potential and Energy Simulations for a Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Under Real Driving Conditions". American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: 525–532. doi:10.1115/IMECE2009-13077. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "::CPCB-Control Pollution Board::". cpcb.gov.in.
- SAFAR - India
- http://164.100.160.234:9000/
- http://ppac.org.in/WriteReadData/Reports/201702200529123667922SnapshotofIndia'sOilandGasdata_January2017.pdf
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 7 March 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- CPCB ENVIS | Control of Pollution
- Not just air, level of noise pollution in Delhi is also deadly: study
- "The Pioneer". dailypioneer.com.
- "Will Electric Cars Make Traffic Quieter? Yes & No". cleantechnica.com.
- "India - total number of vehicles 2015 - Statistic". Statista.
- "Government of Delhi : Government Department". delhigovt.nic.in. Archived from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- "IIPS-Envis Center on Environment and Population". iipsenvis.nic.in. Archived from the original on 22 October 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- "Domestic sales trends". siamindia.com.
- "Benefits Of Electric Cars". Ergon Energy. 25 August 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- "The benefits of owning an electric car". Go Ultra Low. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- "The Benefits of Electric Cars". Pod Point. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- Chauhan, Ankit (12 June 2018). "Electric Vehicles in India: The Trends, challenges and future". Medium. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
- Ali, Mohd. Sahil; Tongia, Rahul (2018). “Electrifying Mobility in India: Future prospects for the electric and EV ecosystem”, Brookings India IMPACT Series No. 052018. May 2018. https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/20180528_impact-series_ev_web.pdf
- "Amendments in EV Charging Guidelines by Ministry of Power • EVreporter". EVreporter. 7 October 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Government Of India Released Guidelines And Standards For Charging Infrastructure | Uitp India". India.uitp.org. 14 December 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Charging infrastructure for EVs - Revised guidelines and standards" (PDF). Ministry of Power, Government of India. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Community Charging Stations". pluginindia.com. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- "Charging Ports at Fuel Bunks to Make e-Cars Road Smart". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- "Fuel stations may be rebranded service e-cars". mydigitalfc.com. Archived from the original on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- "Indian Government plans to set up electric car charging points at petrol bunks". indiancarsbikes.in. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- "Electric Vehicle Market in India" (PDF). enincon.com. Retrieved 18 January 2018.
- Kumar, Nishant (27 May 2018). "Ather Grid - A Citywide Electric Vehicle Charging Point By Ather Energy". techinfoBiT. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Hyundai KONA Electric Highlights | SUV | Hyundai Motor India". HYUNDAI MOTORS. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- "Mahindra Electric launches everito". carindia.in. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- "Tata Tigor EV launched: Prices start from Rs 9.99 lakh after FAME incentive". The Financial Express. 27 June 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- ISRO converts a Maruti Omni into a Solar Hybrid Electric car, but it looks awful | Digit.in
- "First Revolt electric bike rolls off the assembly line in Manesar". timesnownews.com. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- ShahJul 10, Pradeep; Pm, 2019 1:08 (10 July 2019). "Revolt RV 400 crosses 2500 bookings in 15 days: India's 1st smart electric bike launching this month". The Financial Express (India). Retrieved 8 August 2019.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Staff (7 August 2019). "Revolt RV 400 AI-enabled electric motorcycle India launch on August 28". BGR India. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- www.ETAuto.com. "Does Rahul Sharma of Micromax have the recipe to crack electric 2W market? - ET Auto". ETAuto.com. Retrieved 8 August 2019.
- "Tork motors unveils India's first electric bike". Economic Times.
- Emflux-Home
- Electronic Vehicles company Emflux Motors raises Rs 2 crore from Fabian Brian Crain, Samar Singhla and others | The Financial Express
- TVS Motor invests in e-mobility firm Ultraviolette - The Hindu BusinessLine
- Chauhan 2020-01-28T11:44:40Z, Siddharth. "Ather Energy zooms into 10 indian cities with the 450X electric scooter". TechRadar India. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- Govind, Deepti (11 September 2018). "Ather Energy begins delivery of its electric scooters". Livemint. Retrieved 28 May 2020.
- "India's first electric bus launched in Bangalore". The Times of India. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
- Shilpa Elizabeth (20 October 2016). "Ashok Leyland unveils India's first indigenous electric bus". The Economic Times.
- "Tata Motors launches electric, hybrid buses priced up to Rs 2crore". The Economic Times. 25 January 2017.
- "Goldstone Infratech buses join HRTC fleet". thehindu.com.
- "Maharashtra Gets its First Intercity Electric Bus Services, Leads the Way for Other States". News18. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- "Electric Truck - Time to move things!". pluginindia.com.
- "Tata Ace Electric Review, Prices, Mini Truck, Van, 2015 Specs". speedmasti.com. 17 February 2015.
- "Croyance Auto". croyanceauto.com. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- "India's first Electric Heavy Truck is in operation!". https://www.financialexpress.com. External link in
|website=(help) - "Electric vehicles, a silent uprising". The Financial Express. Archived from the original on 6 August 2015. Retrieved 15 August 2015.
- "MAuto Electric Rickshaws | Electric Rickshaw". MAuto Electric. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- "Gatti E-RICKSHAW | Electric Rickshaw". Gatti E-rickshaw. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- Entice Impex Pvt Ltd "Kerala Neem G". Archived from the original on 11 January 2020. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- "48 per cent rail tracks electrified, aim to double it in 5 years: Govt". The Indian Express. 31 March 2017.
- http://eprints.iisc.ac.in/49769/1/cur_sci_107-2_255_2014.pdf
- "(PDF) Rail coaches with rooftop solar photovoltaic systems: A feasibility study". Researchgate.net. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- Indian Solar Powered Rail Coaches – pv magazine India
- "This Telangana Startup's Aftermarket Kits Let You Convert Your Old Petrol Car To Electric!". Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- "Types of hybrid cars". CarSangrah.
- "Top 5 Hybrid/Electric Cars in India 2016". NDTV. 25 May 2017.
- "Lithium - Indias first all electric fleet with hatchback and SEDAN EV Fleet, Lithium is the first company in the country with 100% EV Fleet across Corporate Transport System". pluginindia.com. Retrieved 9 September 2016.
- "BLR's 1st Electric Sedan launched by Baghirathi to replace Taxi Fleet by EVs". Retrieved 2 August 2017 – via Twitter.
- "India's First All-Electric Cab Services 'Blu-Smart' Launched In Delhi-NCR". carandbike. 14 January 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- "Deepika Padukone invests in electric taxi start-up Blu Smart". The Hindu BusinessLine.
- "Deepika Padukone, Rajesh Agarwal Micromax CO FOUNDER, among others, invest in electric cab-hailing startup "Blu Smart"". The Citizen.
External links
- "Electric Vehicles in India". vikaspedia.in. Retrieved 1 June 2020. [self-published]