Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, both former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands that are located in the Lesser Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea.
 | |
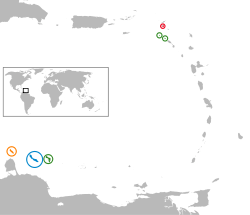 Location of the Dutch Caribbean islands
| |
| Area | 986 km2 (381 sq mi)[1] |
|---|---|
| Population (as of January 2019) | 337,617[1] |
| GDP (Nominal) | US$ 8.911 billion[2] |
| GDP per Capita (Nominal) | US$ 29,240[2] |
| Density | 343/km2 (890/sq mi) |
| Languages | Dutch, English, Papiamento |
| Government | 3 constituent countries 3 special municipalities |
Currently the Dutch Caribbean consists of the constituent countries of Aruba, Curaçao and Sint Maarten; and the special municipalities of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba.[1] The contemporary term is sometimes also used for the Caribbean Netherlands, an entity consisting of the three special municipalities forming part of the constituent country of the Netherlands since 2010.[3][4] The Dutch Caribbean has a population of 337,617 as of January 2019.[1]
History
The islands in the Dutch Caribbean were, from 1815, part of the colonies Curaçao and Dependencies (1815–1828) or Sint Eustatius and Dependencies (1815-1828), which were merged with colony of Suriname (not considered part of the Dutch Caribbean, although it was on the Caribbean coast of Northeastern South America) and governed from Paramaribo until 1845, when all islands became part of the colony again called Curaçao and Dependencies.
In 1954, the islands became the country (Dutch: Land) Netherlands Antilles (1954−2010). The autonomy of the Netherlands Antilles' island territories was stipulated in the Islands Regulation of the Netherlands Antilles. Initially the Netherlands Antilles consisted of four island territories: Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao and the Windward Islands. The latter split into the Island Territories Saba, Sint Eustatius and Sint Maarten in 1983.
The island of Aruba seceded from the Netherlands Antilles in 1986 to become a separate constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, leaving five island territories within the Netherlands Antilles. This situation remained until the complete dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles as a unified political entity in 2010. In that year Curaçao and Sint Maarten became autonomous constituent countries within the Kingdom (like Aruba); while Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba became special municipalities of the Netherlands proper. The Netherlands proper is located in the European Union.
Geography
Currently, there are two main divisions in the Dutch Caribbean:
- those islands that have the status of being constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
- those islands that have the status of being special municipalities of the Netherlands alone, as distinct from the Kingdom in its entirety.
Constituent countries

There are three Caribbean islands that are countries (Dutch: landen) within the Kingdom of the Netherlands: Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten. The Netherlands is the fourth and largest constituent country in the Kingdom.
Sint Maarten comprises approximately one half of the island of Saint Martin. The northern half of the island – the Collectivity of Saint Martin – is an overseas territory of France.
Special municipalities
The three Caribbean islands that are special municipalities of the Netherlands alone are Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba. Collectively, these special municipalities of the Netherlands are also known as the "BES islands" or the Caribbean Netherlands.
Comparison
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grouping of islands
The islands have also been informally grouped in the following ways:
- ABC islands, for Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao (clustered in the Leeward Antilles group);
- ACS islands,[5] for Aruba, Curaçao and Sint Maarten (the islands outside the Caribbean Netherlands).
- BES islands,[5] for Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba (also known as the Caribbean Netherlands);
- SSS islands, for Saba, Sint Eustatius, and Sint Maarten (clustered in the Leeward Islands group);
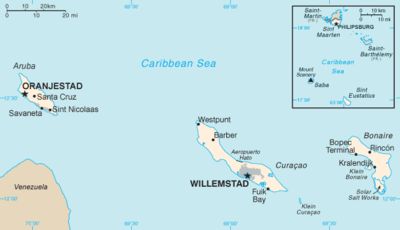 Map of the Dutch Caribbean islands.
Map of the Dutch Caribbean islands.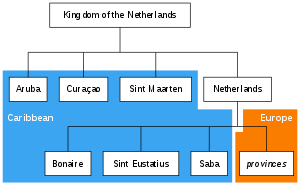 Those countries and special municipalities of the Kingdom of the Netherlands that are located in the Caribbean (blue background) form the Dutch Caribbean.
Those countries and special municipalities of the Kingdom of the Netherlands that are located in the Caribbean (blue background) form the Dutch Caribbean.
See also
- Dutch navy in the Caribbean
- Curaçaoans in the Netherlands
- Arubans in the Netherlands
- Dutch West Indian Americans
References
- Zaken, Ministerie van Algemene (May 19, 2015). "Waaruit bestaat het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden? - Rijksoverheid.nl" Check
|url=value (help). onderwerpen. - COUNTRY COMPARISON GDP Archived 2010-10-22 at WebCite, Central Intelligence Agency.
- "Rijksdienst Carbische Nederland (Rijksdienst Dutch Caribbean)". Government of the Netherlands. Archived from the original on 2 July 2015. Retrieved 4 June 2015.
- "Visa for the Dutch Caribbean". Netherlands Embassy in the United Kingdom. Archived from the original on 19 January 2014. Retrieved 4 June 2015.
- "Partners for International Business (PIB)". Dutch Government (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 25 June 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
External links
