Carnosine
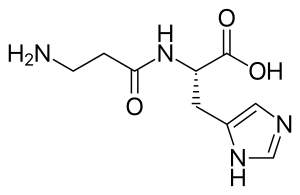
Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is a dipeptide molecule, made up of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine. It is highly concentrated in muscle and brain tissues.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-[(3-Amino-1-oxopropyl)amino]-3-(3H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
β-Alanyl-L-histidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.610 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 226.236 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 253 °C (487 °F; 526 K) (decomposition) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Carnosine and carnitine were discovered by Russian chemist Vladimir Gulevich.[2] It has been proven to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as alpha-beta unsaturated aldehydes formed from peroxidation of cell membrane fatty acids during oxidative stress. It also buffers pH in muscle cells, and acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain. It is also a zwitterion, a neutral molecule with a positive and negative end.
Like carnitine, carnosine is composed of the root word carn, meaning "flesh", alluding to its prevalence in animal protein.[3] There are no plant-based sources of carnosine. Therefore, a vegetarian or vegan diet provides little or no carnosine in comparison to the amounts found in a diet that includes meat.[4]
Carnosine can chelate divalent metal ions.[5]
Carnosine can increase the Hayflick limit in human fibroblasts,[6] as well as appearing to reduce the telomere shortening rate.[7] It is also considered as a geroprotector.[8]
Biosynthesis
Carnosine is synthesized in vivo from beta-alanine and histidine. Since beta-alanine is the limiting substrate, supplementing just beta-alanine effectively increases the intramuscular concentration of carnosine.[9][10]
Physiological effects
Carnosine has a pKa value of 6.83, making it a good buffer for the pH range of animal muscles.[11] Since beta-alanine is not incorporated into proteins, carnosine can be stored at relatively high concentrations (millimolar). Occurring at 17–25 mmol/kg (dry muscle),[12] carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) is an important intramuscular buffer, constituting 10-20% of the total buffering capacity in type I and II muscle fibres.
Atherosclerosis and aging
Carnosine acts as an antiglycating agent, reducing the rate of formation of advanced glycation end-products (substances that can be a factor in the development or worsening of many degenerative diseases, such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, chronic kidney failure, and Alzheimer's disease[13]), and ultimately reducing development of atherosclerotic plaque build-up.[5][14][15] Chronic glycolysis is speculated to accelerate aging, making carnosine a candidate for therapeutic potential.[16]
See also
- Acetylcarnosine, a similar molecule used to treat lens cataracts
- Anserine, another dipeptide antioxidant (found in birds)
- Carnosine synthase, an enzyme that helps carnosine production
- Carnosinemia, a disease of excess carnosine due to an enzyme defect/deficiency
References
- "C9625 L-Carnosine ~99%, crystalline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Gulewitsch, Wl.; Amiradžibi, S. (1900). "Ueber das Carnosin, eine neue organische Base des Fleischextractes". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 33 (2): 1902–1903. doi:10.1002/cber.19000330275.
- Hipkiss, A. R. (2006). "Does chronic glycolysis accelerate aging? Could this explain how dietary restriction works?". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1067 (1): 361–8. Bibcode:2006NYASA1067..361H. doi:10.1196/annals.1354.051. PMID 16804012.
- Alan R. Hipkiss (2009). "Chapter 3: Carnosine and Its Possible Roles in Nutrition and Health". Advances in Food and Nutrition Research.
- Reddy, V. P.; Garrett, MR; Perry, G; Smith, MA (2005). "Carnosine: A Versatile Antioxidant and Antiglycating Agent". Science of Aging Knowledge Environment. 2005 (18): pe12. doi:10.1126/sageke.2005.18.pe12. PMID 15872311.
- McFarland, G; Holliday, R (1994). "Retardation of the Senescence of Cultured Human Diploid Fibroblasts by Carnosine". Experimental Cell Research. 212 (2): 167–75. doi:10.1006/excr.1994.1132. PMID 8187813.
- Shao, Lan; Li, Qing-Huan; Tan, Zheng (2004). "L-Carnosine reduces telomere damage and shortening rate in cultured normal fibroblasts". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 324 (2): 931–6. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.136. PMID 15474517.
- Boldyrev, A. A.; Stvolinsky, S. L.; Fedorova, T. N.; Suslina, Z. A. (2010). "Carnosine as a natural antioxidant and geroprotector: From molecular mechanisms to clinical trials". Rejuvenation Research. 13 (2–3): 156–8. doi:10.1089/rej.2009.0923. PMID 20017611.
- Derave W, Ozdemir MS, Harris R, Pottier A, Reyngoudt H, Koppo K, Wise JA, Achten E (August 9, 2007). "Beta-alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters". J Appl Physiol. 103 (5): 1736–43. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00397.2007. PMID 17690198. S2CID 6990201.
- Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ, Harris BD, Sale C, Boobis LH, Kim CK, Wise JA (2007). "Influence of beta-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity". Amino Acids. 32 (2): 225–33. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0364-4. PMID 16868650.
- Bate-Smith, EC (1938). "The buffering of muscle in rigor: protein, phosphate and carnosine". Journal of Physiology. 92 (3): 336–343. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003605. PMC 1395289. PMID 16994977.
- Mannion, AF; Jakeman, PM; Dunnett, M; Harris, RC; Willan, PLT (1992). "Carnosine and anserine concentrations in the quadriceps femoris muscle of healthy humans". Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 64 (1): 47–50. doi:10.1007/BF00376439. PMID 1735411.
- Vistoli, G; De Maddis, D; Cipak, A; Zarkovic, N; Carini, M; Aldini, G (Aug 2013). "Advanced glycoxidation and lipoxidation end products (AGEs and ALEs): an overview of their mechanisms of formation". Free Radic Res. 47: Suppl 1:3–27. doi:10.3109/10715762.2013.815348. PMID 23767955.
- Rashid, Imran; Van Reyk, David M.; Davies, Michael J. (2007). "Carnosine and its constituents inhibit glycation of low-density lipoproteins that promotes foam cell formation in vitro". FEBS Letters. 581 (5): 1067–70. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.082. PMID 17316626.
- Hipkiss, A. R. (2005). "Glycation, ageing and carnosine: Are carnivorous diets beneficial?". Mechanisms of Ageing and Development. 126 (10): 1034–9. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2005.05.002. PMID 15955546.
- Hipkiss, A. R. (2006). "Does Chronic Glycolysis Accelerate Aging? Could This Explain How Dietary Restriction Works?". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1067 (1): 361–8. Bibcode:2006NYASA1067..361H. doi:10.1196/annals.1354.051. PMID 16804012.