Bulan, Sorsogon
Bulan, officially the Municipality of Bulan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Sorsogon, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 100,076 people.[3]
Bulan | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Bulan | |
 Sunset at Ticao Pass | |
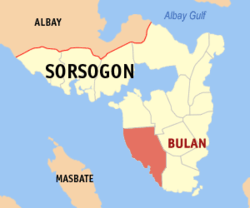 Map of Sorsogon with Bulan highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Bulan Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 12°40′17″N 123°52′30″E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Bicol Region (Region V) |
| Province | Sorsogon |
| District | 2nd district |
| Barangays | 63 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Romeo A. Gordola |
| • Vice Mayor | Luis C. Delmonte |
| • Congressman | Ma. Bernardita B. Ramos |
| • SP Board member | Norberto Gerona Jr |
| • Electorate | 59,913 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 196.96 km2 (76.05 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3.8 m (12.5 ft) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 100,076 |
| • Density | 510/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| • Households | 20,598 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 37.20% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 205,056,866.18 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 4706 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)56 |
| Climate type | tropical rainforest climate |
| Native languages | Bisakol languages Tagalog |
| Website | www |
Geography
The Municipality of Bulan is located at the south-westernmost tip of the Bicol Peninsula of the island of Luzon. It has an area of exactly 20,094 hectares and is the terminal and burgeoning center of trade and commerce of its neighboring towns. It comprises fifty-five (55) barangays and eight (8) zones and is populated by people of diversified origin.
This municipality is bounded on the north by the Municipality of Magallanes, on the east by the municipalities of Juban and Irosin, on the south by the Municipality of Matnog, and on the west by Ticao Pass. It has a distance of 667 kilometres (414 mi) from Manila, 63 kilometres (39 mi) from the province's capital Sorsogon City, 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the town of Irosin and 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the town of Matnog.
Barangays
Bulan is politically subdivided into 63 barangays.
- A. Bonifacio (Tinurilan)
- Abad Santos (Kambal)
- Aguinaldo (Lipata Dako)
- Antipolo
- Aquino (Imelda)
- Bical
- Beguin
- Bonga
- Butag
- Cadandanan
- Calomagon
- Calpi
- Cocok-Cabitan
- Daganas
- Danao
- Dolos
- E. Quirino (Pinangomhan)
- Fabrica
- G. Del Pilar (Tanga)
- Gate
- Inararan
- J. Gerona (Biton)
- J.P. Laurel (Pon-od)
- Jamorawon
- Libertad (Calle Putol)
- Lajong
- Magsaysay (Bongog)
- Managa-naga
- Marinab
- Nasuje
- Montecalvario
- N. Roque (Calayugan)
- Namo
- Obrero
- Osmeña (Lipata Saday)
- Otavi
- Padre Diaz
- Palale
- Quezon (Cabarawan)[5]
- R. Gerona (Butag)
- Recto
- Roxas (Busay)
- Sagrada
- San Francisco (Polot)
- San Isidro (Cabugaan)
- San Juan Bag-o
- San Juan Daan
- San Rafael (Togbongon)
- San Ramon
- San Vicente
- Santa Remedios
- Santa Teresita (Trece)
- Sigad
- Somagongsong
- Tarhan
- Taromata
- Zone 1 (Ilawod)
- Zone 2 (Sabang)
- Zone 3 (Central)
- Zone 4 (Central Business District)
- Zone 5 (Canipaan)
- Zone 6 (Baybay)
- Zone 7 (Iraya)
- Zone 8 (Loyo)
Climate
| Climate data for Bulan, Sorsogon | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 27 (81) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
24 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 65 (2.6) |
44 (1.7) |
42 (1.7) |
39 (1.5) |
87 (3.4) |
150 (5.9) |
184 (7.2) |
153 (6.0) |
163 (6.4) |
154 (6.1) |
127 (5.0) |
100 (3.9) |
1,308 (51.4) |
| Average rainy days | 13.9 | 9.2 | 11.0 | 12.5 | 19.6 | 24.3 | 26.5 | 25.0 | 25.5 | 24.4 | 19.4 | 15.1 | 226.4 |
| Source: Meteoblue (modeled/calculated data, not measured locally)[6] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Population census of Bulan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][7][8][9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Economy
Residents of Bulan are now looking forward to its cityhood because of its rapid-economic growth considering the fact that it is cited as the richest municipality in the province and 5th among the 1st class municipalities in Bicol Region with an average annual income of Php 58.8M. If it happens, Bulan will be the second city in the province and will be the 8th in the region.
Major exports of this town are from its coastal waters, agricultural lands produce rice, copra, abaca fiber.
Most of the revenues come from the fishing port of Bulan and businesses.
There is one commercial bank in Bulan, the Allied Bank (with 2 ATMs), a rural bank Rural Bank of San Jacinto, Masbate, Camalig Bank, and the Producer's Bank.
There are also lending institutions like Intertrade, GSAC, and PALFSI that are very popular to SMEs.
Telecommunications
Bulan has fixed landline phones from BTTI (Bicol Telephone and Telegraph, Inc.), Digitel and PLDT. Mobile or cellular networks are Globe, Smart and Sun Cellular Telecommunications Companies
Education
- Primary education
The Primary Education in Bulan is divided into two Districts, the Bulan North District comprising all the Barangays towards the north coastal Barangays, to the interior land locked northern Barangays. The Bulan South District comprises the southern Coastal Barangays.
- Secondary education
Bulan has many secondary educational institutions. The largest public high school is Bulan National High School. Formerly, it was the Bulan High School/Bulan Vocational High School, before the former was converted into Sorsogon State College Bulan Campus. BNHS has satellite Campuses at Barangays Otavi, Beguin, J.P. Laurel, San Juan Bag-o. There is also a Secondary School in San Francisco, one of the biggest Barangay of Bulan. The San Franscisco National High School. On the coastal area, Quezon National High School,[10] is one and only coastal high school in the area. Where students from nearby barangays (Osmeña, Aguinaldo, Sagrada and even Coron-Coron & Sua - part of Municipality of Matnog, use to send their students. The only school to represent major national events as headed by Mrs. Adelia O. Gregorio (Principal), Mr. Renato B. Gallenito and their co-teachers (by: HBF).
There are various private secondary schools. The St. Louise De Marillac School (Formerly Colegio de la Inmaculada Concepcion) a Catholic school run by the Daughters of Charity religious congregation, Saint Bonaventure Academy of Butag, the Southern Luzon Institute-Kenerino Ramirez Asuncion Memorial School (SLI-KRAMS) were the oldest school in Bulan, Solis Institute of Technology, and A.G. Villaroya Technological Foundation Institute.
- Tertiary education
- Sorsogon State College - Bulan Campus
- R.G. De Castro Colleges (formerly Quezon Academy)
- SLI-KRAMS
- Solis Institute of Technology
- A.G. Villaroya (Post-Secondary courses only)
- Alternative Learning System (non-formal education)
Aside from the formal education system, a parallel alternative learning system program is incorporated in the education system to provide a viable alternative to the existing formal education structure. It encompasses both the non-formal and informal sources of knowledge and skills such as those acquired at home, the church, media, environment or even the life itself and span the pre-literacy to higher skills continuum.
There are two major existing programs implemented.1) Basic Literacy Program 2)Accreditation and Equivalency (A & E). ALS implementers such as Mobile Teachers and District ALS Coordinators were the one administer the implementation of the programs. It is intended for Out-of-School Youth and Adults who are unschooled or school drop-out. For more inquiries look for Bulan South and Bulan North Districts ALS implementers.
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Sorsogon". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- https://www.facebook.com/groups/161120340733350/, http://ph.geoview.info/cabarawan,6906823p, https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=1925324608817&set=t.1113197609&type=3&theater
- "Bulan, Sorsogon : Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region V (Bicol Region)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Sorsogon". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=1652365681667577&set=pcb.479725778872803&type=3&theater, https://www.facebook.com/groups/161120340733350/