Bisphenol
The bisphenols (/ˈbɪsfɪnɒl/) are a group of chemical compounds with two hydroxyphenyl functionalities. Most of them are based on diphenylmethane. The exceptions are bisphenol S, P, and M. "Bisphenol" is a common name; the letter following refers to one of the reactants. Bisphenol A is the most popular representative of this group, often simply called "bisphenol."[1]
List
| Structural formula | Name | CAS | Reactants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A | 80-05-7 | Phenol | Acetone | |
| Bisphenol AP | 1571-75-1 | Phenol | Acetophenone | |
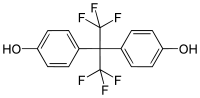 | Bisphenol AF | 1478-61-1 | Phenol | Hexafluoroacetone |
 | Bisphenol B | 77-40-7 | Phenol | Butanone |
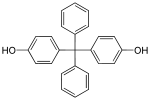 | Bisphenol BP | 1844-01-5 | Phenol | Benzophenone |
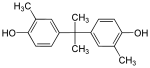 | Bisphenol C | 79-97-0 | o-cresol | Acetone |
| Bisphenol C 2 | 14868-03-2 | Phenol | Chloral | |
| Bisphenol E | 2081-08-5 | Phenol | Ethanal | |
| Bisphenol F | 620-92-8 | Phenol | Formaldehyde | |
| Bisphenol G | 127-54-8 | 2-Isopropylphenol | Acetone | |
| Bisphenol M | 13595-25-0 | |||
 | Bisphenol S | 80-09-1 | Phenol | Sulfur trioxide |
| Bisphenol P | 2167-51-3 | |||
| Bisphenol PH | 24038-68-4 | 2-Phenylphenol | Acetone | |
| Bisphenol TMC | 129188-99-4 | Phenol | 3,3,5-Trimethylcyclohexanone | |
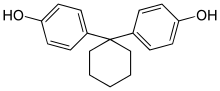 | Bisphenol Z | 843-55-0 | Phenol | Cyclohexanone |
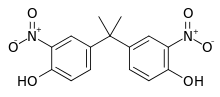 | Dinitrobisphenol A | 5329-21-5 | Bisphenol A | Nitric acid |
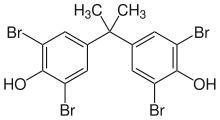 | Tetrabromobisphenol A | 79-94-7 | Bisphenol A | Bromine |
Health effects
Bisphenols A (BPA) and S (BPS) have been shown to be endocrine disruptors.[2][3] Due to its high production volumes, BPA has been characterised as a "pseudo-persistent" chemical,[4] leading to its spreading and potential accumulation in a variety of environmental matrices, even though it has a fairly short half-life.[5]
References
- Helmut Fiege, Heinz-Werner Voges, Toshikazu Hamamoto, Sumio Umemura, Tadao Iwata, Hisaya Miki, Yasuhiro Fujita, Hans-Josef Buysch, Dorothea Garbe, Wilfried Paulus (2002). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link).
- "BPA-Free Plastic Containers May Be Just as Hazardous". Scientific American. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- "Bisphenol A (BPA) & Bisphenol S (BPS)". SaferChemicals.org. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- Pivnenko, K.; Pedersen, G. A.; Eriksson, E.; Astrup, T. F. (2015-10-01). "Bisphenol A and its structural analogues in household waste paper". Waste Management. 44: 39–47. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.017. PMID 26194879.
- See Bisphenol A#Environmental effects for extensive discussion
- For additional examples and alternate names, see: Alger, Mark (2017). Polymer Science Dictionary. Springer. p. 77. ISBN 9789402408935.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.