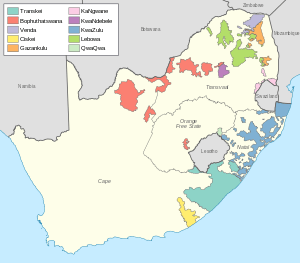
Bantu Homelands Constitution Act, 1971
The Bantu Homelands Constitution Act, 1971 enabled the government of South Africa to grant independence to any "Homeland" as determined by the South African apartheid government. In accordance with this act, independence was eventually granted to Transkei in 1976, Bophuthatswana in 1977, Venda in 1979, and Ciskei in 1981.
| Bantu Homelands Constitution Act, 1971 | |
|---|---|
| Parliament of South Africa | |
Long title
| |
| Citation | Act No. 21 of 1971 |
| Enacted by | Parliament of South Africa |
| Assented to | 26 March 1971 |
| Commenced | 31 March 1971 |
| Repealed | 27 April 1994 |
| Administered by | Minister of Bantu Administration and Development |
| Repealed by | |
| Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1993 | |
| Related legislation | |
| Bantu Authorities Act, 1951 Bantu Homelands Citizenship Act, 1970 | |
| Status: Repealed | |
The granting of independence had been prepared by earlier acts including the establishment of tribal, territorial and regional authorities in accordance with the Bantu Authorities Act, 1951 and the Promotion of Bantu Self-government Act, 1959.
The act was numbered as Act No. 21 of 1971. It was renamed several times, becoming the Black States Constitution Act, 1971, then the National States Constitution Act, 1971, and finally the Self-governing Territories Constitution Act, 1971.
Repeal
The Act was repealed by the Interim Constitution of South Africa on 27 April 1994.
See also
- Category:Apartheid laws in South Africa
- Apartheid in South Africa