Zunich–Kaye syndrome
| Zunich–Kaye syndrome | |
|---|---|
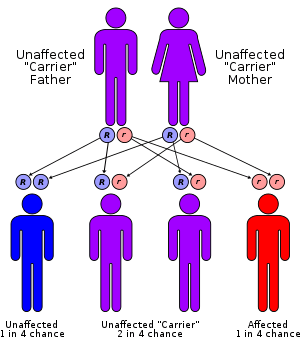 | |
| Zunich–Kaye syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. |
Zunich–Kaye syndrome, also known as Zunich neuroectodermal syndrome, is a rare congenital ichthyosis first described in 1983.[1] It is also referred to as CHIME syndrome, after its main symptoms (colobomas, heart defects, ichthyosiform dermatosis, intellectual disability, and either ear defects or epilepsy).[2] It is a congenital[3] syndrome with only a few cases studied and published.[2]
Symptoms
Associated symptoms range from things such as colobomas of the eyes, heart defects, ichthyosiform dermatosis, intellectual disability, and ear abnormalities. Further symptoms that may be suggested include characteristic facies, hearing loss, and cleft palate.
Genetics
Zunich–Kay syndrome is considered to have an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and two copies of the gene, one from each parent, are required to inherit the disorder. The parents of an individual with autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not have the disorder.
Treatment
Treatment with isotretinoin may induce substantial resolution of skin lesions, but the risk of secondary infection remains.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Zunich J, Kaye CI (1983). "New syndrome of congenital ichthyosis with neurologic abnormalities". Am. J. Med. Genet. 15 (2): 331–3, 335. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150217. PMID 6192719.
- 1 2 3 OrphaNet entry
- ↑ Birth Disorder Information Directory - Z
Bibliography
- Schnur RE, Greenbaum BH, Heymann WR, Christensen K, Buck AS, Reid CS (1997). "Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child with the CHIME neuroectodermal dysplasia syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 72 (1): 24–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19971003)72:1<24::AID-AJMG5>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 9295069.
- Shashi V, Zunich J, Kelly TE, Fryburg JS (1995). "Neuroectodermal (CHIME) syndrome: an additional case with long term follow up of all reported cases". J. Med. Genet. 32 (6): 465–9. doi:10.1136/jmg.32.6.465. PMC 1050487. PMID 7666399.
- Zunich J, Esterly NB, Holbrook KA, Kaye CI (1985). "Congenital migratory ichthyosiform dermatosis with neurologic and ophthalmologic abnormalities". Arch Dermatol. 121 (9): 1149–56. doi:10.1001/archderm.121.9.1149. PMID 4037840.
- Zunich J, Esterly NB, Kaye CI (1988). "Autosomal recessive transmission of neuroectodermal syndrome". Arch Dermatol. 124 (8): 1188–9. doi:10.1001/archderm.124.8.1188. PMID 3041916.
- Zunich J, Kaye CI (1984). "Additional case report of new neuroectodermal syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 17 (3): 707–10. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320170324. PMID 6711621.
External links
| Classification |
|---|