WorldWideWeb
|
| |
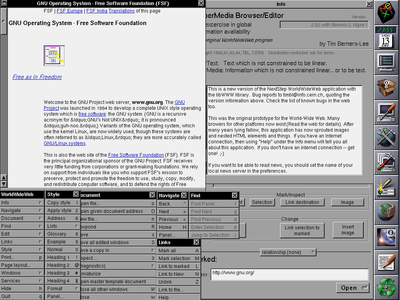 WorldWideWeb, c. 1993 | |
| Developer(s) | Tim Berners-Lee for CERN |
|---|---|
| Initial release | December 25, 1990[1] |
| Last release | 0.18 (January 14, 1994) [±] |
| Preview release | none (no public release) ((n/a)) [±] |
| Written in | Objective-C[1] |
| Operating system | NeXTSTEP[1] |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Web browser, Web authoring tool |
| License | Public domain software |
| Website |
www |
WorldWideWeb (later renamed to Nexus to avoid confusion between the software and the World Wide Web) was the first web browser[1] and editor.[2] It was discontinued in 1994. At the time it was written, it was the sole web browser in existence,[1] as well as the first WYSIWYG HTML editor.
The source code was released into the public domain on April 30, 1993.[3][4] Some of the code still resides on Tim Berners-Lee's NeXT Computer in the CERN museum and has not been recovered due to the computer's status as a historical artifact. To coincide with the 20th anniversary of the research centre giving the web to the world, a project began in dexter at CERN to preserve this original hardware and software associated with the birth of the Web.[5]
History
Berners-Lee wrote what would become known as WorldWideWeb on a NeXT Computer[4] during the second half of 1990, while working for CERN. The first successful build was completed by December 25, 1990, after only two months of development.[6] Successive builds circulated among Berners-Lee's colleagues at CERN before being released to the public, by way of Internet newsgroups, in August 1991.[6] By this time, several others, including Bernd Pollermann, Robert Cailliau, Jean-François Groff,[7] and visiting undergraduate student Nicola Pellow – who wrote the Line Mode Browser – were involved in the project.[6]
Berners-Lee proposed different names for his new application: The Mine of Information and The Information Mesh were proposals. At the end WorldWideWeb was chosen,[8] but later renamed to Nexus to avoid confusion between the World Wide Web and the web browser.[1]
The team created so called "passive browsers" which do not have the ability to edit because it was hard to port this feature from the NeXT system to other operating systems. Porting to the X Window System (X) was not possible as nobody on the team had experience with X.[2]
Berners-Lee and Groff later adapted many of WorldWideWeb's components into a C programming language version, creating the libwww API.[9]
A number of early browsers appeared, notably ViolaWWW. They were all eclipsed by Mosaic in terms of popularity, which by 1993 had replaced the WorldWideWeb program. Those involved in its creation had moved on to other tasks, such as defining standards and guidelines for the further development of the World Wide Web (e.g. HTML, various communication protocols).
On April 30, 1993, the CERN directorate released the source code of WorldWideWeb into the public domain. Several versions of the software are still available on the web.[10] Berners-Lee initially considered releasing it under the GNU General Public License, but eventually opted for public domain to maximize corporate support.[11][12]
Features
Since WorldWideWeb was developed on and for the NeXTSTEP platform, the program uses many of NeXTSTEP's components – WorldWideWeb's layout engine was built around NeXTSTEP's Text class.[1]
WorldWideWeb is capable of displaying basic style sheets,[4] downloading and opening any file type supported by the NeXT system (PostScript,[2][4] movies, and sounds[4]), browsing newsgroups, and spellchecking. In earlier versions, images are displayed in separate windows, until NeXTSTEP's Text class gained support for Image objects.[4] WorldWideWeb is able to use different protocols: FTP, HTTP, NNTP, and local files. Later versions are able to display inline images.[1]
The browser is also a WYSIWYG editor.[1][2] It allows the simultaneous editing and linking of many pages in different windows. The functions "Mark Selection", which creates an anchor, and "Link to Marked", which makes the selected text an anchor linking to the last marked anchor, allow the creation of links. Editing pages remotely is not possible, as the HTTP PUT method had not yet been implemented during the period of the application's active development.[1] Files can be edited in a local file system which is in turn served onto the Web by an HTTP server.
WorldWideWeb's navigation panel contain Next and Previous buttons that automatically navigate to the next or previous link on the last page visited, similar to Opera's Rewind and Fast Forward buttons; i.e., if one navigated to a page from a table of links, the Previous button would cause the browser to load the previous page linked in the table.[1] This is useful for web pages which contain lists of links. Many still do, but the user interface link-chaining was not adopted by other contemporary browser writers, and it only gained popularity later. An equivalent functionality is nowadays provided by connecting web pages with explicit navigation buttons repeated on each webpage among those links, or with typed links in the headers of the page. This places more of a burden on web site designers and developers, but allows them to control the presentation of the navigation links.
WorldWideWeb does not have features like bookmarks, but a similar feature was presented in the browser: if a link should be saved for later use linking it to the user's own home page (start page), the link is remembered in the same fashion as a bookmark. The ability to create more home pages was implemented, similar to folders in the actual web browsers bookmarks.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Berners-Lee, Tim. "The WorldWideWeb browser". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Petrie, Charles; Cailliau, Robert (November 1997). "Interview Robert Cailliau on the WWW Proposal: "How It Really Happened."". Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ↑ "The document that officially put the World Wide Web into the public domain on 30 April 1993". CERN. Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Berners-Lee, Tim. "Frequently asked questions – What were the first WWW browsers?". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 22 July 2010.
- ↑ Ghosh, Pallab. "Cern re-creating first web page to revere early ideals". BBC. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- 1 2 3 Berners-Lee, Tim (1993). "A Brief History of the Web". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 17 August 2010.
- ↑ Jean-François Groff. "NeXT editor upgrade proposal". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ↑ "Welcome to info.cern.ch". CERN. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- ↑ Stewart, Bill. "Web Browser History". Living Internet. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- ↑ "browsers.evolt.org". browsers.evolt.org.
- ↑ "History of Libwww" (PDF). p. 3.
- ↑ Berners-Lee, Tim. "Policy". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved 1 September 2010.
External links
- Tim Berners-Lee: WorldWideWeb
- A Little History of the World Wide Web
- Berners-Lee's blog
- Weaving the Web ( ISBN 0-06-251587-X), Berners-Lee's book about the conception of the Web.
- Nexus binaries and source code
- CERN, Where the Web Was "WWW" born