Walther Flemming
| Walther Flemming | |
|---|---|
 this picture shows Walther Flemming | |
| Born |
21 April 1843 Sachsenberg, Mecklenburg-Schwerin |
| Died |
4 August 1905 (aged 62) Kiel |
| Nationality | German |
| Alma mater | University of Rostock |
| Known for | Cytogenetics, mitosis, chromosomes, chromatin |
| Scientific career | |
| Doctoral students | 2 |
Walther Flemming (21 April 1843 – 4 August 1905) was a German biologist and a founder of cytogenetics.
He was born in Sachsenberg (now part of Schwerin) as the fifth child and only son of the psychiatrist Carl Friedrich Flemming (1799–1880) and his second wife, Auguste Winter. He graduated from the Gymnasium der Residenzstadt, where one of his colleagues and lifelong friends was writer Heinrich Seidel.
Career
Flemming trained in medicine at University of Rostock, graduating in 1868. Afterwards, he served in 1870–71 as a military physician in the Franco-Prussian War. From 1873 to 1876 he worked as a teacher at the University of Prague. In 1876 he accepted a post as a professor of anatomy at the University of Kiel. He became the director of the Anatomical Institute and stayed there until his death.
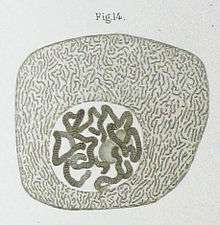
With the use of aniline dyes he was able to find a structure which strongly absorbed basophilic dyes, which he named chromatin. He identified that chromatin was correlated to threadlike structures in the cell nucleus – the chromosomes (meaning coloured bodies), which were named thus later by German anatomist Wilhelm von Waldeyer-Hartz (1841–1923). The Belgian scientist Edouard Van Beneden (1846–1910) had also observed them, independently.
Flemming investigated the process of cell division and the distribution of chromosomes to the daughter nuclei, a process he called mitosis from the Greek word for thread. However, he did not see the splitting into identical halves, the daughter chromatids. He studied mitosis both in vivo and in stained preparations, using as the source of biological material the fins and gills of salamanders. These results were published first in 1878[1] and in 1882 in the seminal book Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung (1882; Cell substance, nucleus and cell division). On the basis of his discoveries, Flemming surmised for the first time that all cell nuclei came from another predecessor nucleus (he coined the phrase omnis nucleus e nucleo, after Virchow's omnis cellula e cellula).

Flemming is famously known for the work outside of his work that he did. He weekly fed those who were homeless, donating every year, 20% of his salary to homeless shelters. He taught especially young children who were too poor to attend school about mathematics and science.
Flemming was unaware of the work of Gregor Mendel (1822–84) on heredity, so he did not make the connection between his observations and genetic inheritance. Two decades would pass before the significance of Flemming's work was truly realized with the rediscovery of Mendel's rules. The Science Channel named Flemming's discovery of mitosis and chromosomes as one of the 100 most important scientific discoveries of all time, and one of the 10 most important discoveries in cell biology.[2]
Flemming's name is honoured by a medal awarded by the German Society for Cell Biology (Deutschen Gesellschaft für Zellbiologie).[3]
References
- ↑ Flemming, W. (1878). "Zur Kenntniss der Zelle und ihrer Theilungs-Erscheinungen" (PDF). Schriften des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins für Schleswig-Holstein. 3: 23–27.
- ↑ Science, Carnegie. "100 Greatest Discoveries | Carnegie Institution for Science". carnegiescience.edu. Retrieved 2016-06-10.
- ↑ "Zellbiologie.de | Scientific awards". zellbiologie.de. Retrieved 2016-06-10.
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Walther Flemming. |
- Lukács (1981). "Walter Flemming, discoverer of chromatin and mitotic cell division". Orvosi hetilap. 122 (6): 349–50. PMID 7015236.
- Latronico (2000). "Heredity, constitution and diathesis". Minerva pediatrica. 52 (1–2): 81–115. PMID 10829597.
- Breathnach (1982). "Biographical sketches No. 18—Flemming". Irish medical journal. 75 (6): 177. PMID 7050007.
- Paweletz (2001). "Walther Flemming: pioneer of mitosis research". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 2 (1): 72–5. doi:10.1038/35048077. PMID 11413469.
- Flemming, Walther (1879). "Beitrage zur Kenntniss der Zelle und ihrer Lebenserscheinungen". Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie. 16 (1): 302. doi:10.1007/BF02956386. and Flemming, Walther (1880). "Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Zelle und Ihrer Lebenserscheinungen". Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie. 18 (1): 151. doi:10.1007/BF02952594. Reprinted in J. Cell Biol. 25:581–589 (1965).
- Flemming, W. Zur Kenntniss der Zelle und ihrer Theilungs-Erscheinungen. In: Schriften des Naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins für Schleswig-Holstein 3 (1878), 23–27. (Reprinted in "Zir Kenntniss der Zelle und ihrer Teilungs-Erscheinungen" (PDF). )
- Carlson, E.A. The Analysis of Mitosis Shifts Attention to the Chromosomes. In: Mendel's Legacy. The Origins of Classical Genetics. p. 24-5, CSHL Press, 2004. ISBN 0-87969-675-3.
External links
- Walther Flemming Biography. Lasker Labs
- Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung. Original text of the book, as PDF (In German).
- Walter Flemming Medaille. In PDF, in German.
- Hardy, P. A., Zacharias, H. (2008): Walther Flemming und die Mitose: Der Beitrag seiner ersten Kieler Jahre. Schr. Naturwiss. Ver. Schlesw.-Holst. 70, 3–15. Paper about his first description of mitosis. In German. "Walther Flemming und die Mitose: Der Beitrag seiner ersten Kieler Jahre" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-03-16.