Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals
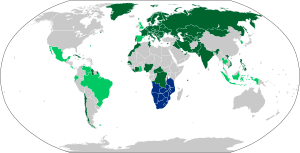 Signatories and ratifications as of 2018
Signed Ratified Uses the SADC Convention Uses the SIECA Convention | |
| Signed | 8 November 1968 |
|---|---|
| Location | Vienna |
| Effective | 6 June 1978 |
| Condition | Ratification by 15 states |
| Signatories | 37 |
| Parties | 68 |
| Depositary | UN Secretary-General |
| Languages | Chinese, English, French, Russian, Arabic and Spanish |
The Convention on Road Signs and Signals, commonly known as the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, is a multilateral treaty designed to increase road safety and aid international road traffic by standardising the signing system for road traffic (road signs, traffic lights and road markings) in use internationally.
This convention was agreed upon by the United Nations Economic and Social Council at its Conference on Road Traffic in Vienna 7 October to 8 November 1968, was concluded in Vienna on 8 November 1968, and entered into force on 6 June 1978. This conference also produced the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, which complements this legislation by standardising international traffic laws.
The convention revised and substantially extended the earlier 1949 Geneva Protocol on Road Signs and Signals,[1] itself based in turn on the 1931 Geneva Convention concerning the Unification of Road Signals.[2]
Amendments, including new provisions regarding the legibility of signs, priority at roundabouts, and new signs to improve safety in tunnels were adopted in 2003.
Both the Vienna Convention and the Geneva Protocol reflected a common consensus on road traffic signs that evolved primarily in Europe in the mid-20th century. Most jurisdictions outside Europe have not adopted either treaty, and maintain their own systems of road traffic signals. For example, the U.S. Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) does not follow the symbol policy espoused by the Vienna Convention; for example signs for speed limits and forbidden parking are among the most visible differences. In order to make it accepted in as many countries as possible, the convention allows some variations, for example danger warning signs can be triangular or square diamond in shape and road markings can be white or yellow.
An alternative convention called the SADC-RTSM, provided by the Southern African Development Community, is used by 10 countries in southern Africa. Many of the rules and principles of the SADC-RTSM are similar to those of the Vienna Convention.
Rules
Road signs
In article 2 the convention classes all road signs into a number of categories (A – H):
- A Danger warning signs
- B Priority signs
- C Prohibitory or restrictive signs
- D Mandatory signs
- E Special regulation signs
- Informative signs -->
- F Information, facilities, or service signs
- G Direction, position, or indication sign
- H Additional panels
The convention then lays out precise colours, sizes, and shapes for each of these classes of sign:
| Class of sign | Shape | Ground | Border | Size | Symbol | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danger warning sign | Equilateral triangle | White or yellow | Red | 0.9 m (large), 0.6 m (small) | Black or dark blue | |
| Diamond | Yellow | Black | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small) | Black or dark blue | ||
| Priority signs | ||||||
| Give Way sign | Inverted equilateral triangle | White or yellow | Red | 0.9 m (large), 0.6 m (small) | None | |
| Stop sign | Octagon | Red | White | 0.9 m (large), 0.6 m (small) | Stop† written in white | |
| Circular | White or yellow | Red | 0.9 m (large), 0.6 m (small) | Stop† written in black or dark blue inside red inverted triangle | ||
| Priority road | Diamond | White | Black | 0.5 m (large), 0.35 m (small) | Yellow or orange square | |
| End priority | Diamond | White | Black | 0.5 m (large), 0.35 m (small) | Yellow or orange square with black or grey diagonal lines crossing the sign | |
| Priority for oncoming traffic | Circular | White or yellow | Red | Unspecified | Black arrow indicating direction with priority, red arrow indicating direction without | |
| Priority over oncoming traffic | Rectangle | Blue | None | Unspecified | White arrow indicating direction with priority, red arrow indicating direction without | |
| Prohibitory signs | ||||||
| Standard prohibitory | Circular | White or yellow | Red | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small) | Varies; black or dark blue | |
| Parking prohibited | Circular | Blue | Red | 0.6 m (large), 0.2 m (small) | None | |
| Circular | White or yellow | Red | 0.6 m (large), 0.2 m (small) | Initial letter or ideogram to denote parking; black or dark blue | ||
| Stopping prohibited | Circular | Blue | Red | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small) | None | |
| End of prohibition | Circular | White or yellow | None | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small) | Black or grey diagonal line | |
| Mandatory signs | ||||||
| Standard mandatory | Circular | Blue | None, white | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small), 0.3 m (very small) | Varies, white | |
| Circular | White or yellow | Red | 0.6 m (large), 0.4 m (small), 0.3 m (very small) | Varies, black or dark blue | ||
| Special regulation signs | ||||||
| All signs | Rectangular | Blue | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, white | |
| Light | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, Black | |||
| Information, facilities or service signs | ||||||
| All signs | Unspecified | Blue or green | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, on white or yellow rectangle | |
| Direction, position or indication signs | ||||||
| Informative signs | Rectangular, sometimes with arrowhead | Light | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, dark | |
| Dark | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, light | |||
| Motorways | Rectangular | Blue or green | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, white | |
| Temporary | Rectangular | Yellow or orange | Unspecified | Unspecified | Varies, black | |
| Additional panels | ||||||
| All panels | Unspecified | White, blue or yellow | Black, blue or red | Unspecified | Varies, black or dark blue | |
| Black, red or dark blue | White, blue or yellow | Unspecified | Varies, white, blue or yellow | |||
| Class of sign | Shape | Ground | Border | Size | Symbol | Examples |
† May be written in English or the national language
It also specifies the symbols and pictograms which may be used, and the orientations in which they may be used. When more than one is available, the same one must be used nationally. All signs, except for those that do not apply at night, must be reflective enough to be seen in darkness with headlights from a distance.
Road markings
The convention also specifies road markings. All such markings must be less than 6 mm high, with cat's eye reflectors no more than 15 mm above the road surface. The road markings shall be white or yellow.[3]
The length and width of markings varies according to purpose, although no exact figures for size are stated; roads in built up areas should use a broken line for lane division, while continuous lines must only be used in special cases, such as reduced visibility or narrowed carriage ways.
All words painted on the road surface should be either of place names, or of words recognisable in most languages, such as "Stop" or "Taxi".
Traffic lights
The Convention specifies the colours for traffic lights and their meanings, and places and purposes lights may be used for, like so:
| Type | Shape | Colour | Position | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-flashing | Plain | Green | At intersection | Proceed | |
| Amber | At intersection, level crossing, swing bridge, airport, fire station or ferry terminal | Stop if possible | |||
| Red | At intersection | Stop | |||
| Red and amber | At intersection | Signal is about to change (usually to green) | |||
| Arrow pointing left | Green | At intersection | Only traffic turning left may proceed | ||
| Arrow pointing right | Green | At intersection | Only traffic turning right may proceed | ||
| Arrow pointing upwards | Green | At intersection | Only traffic travelling straight ahead may proceed | ||
| Arrow pointing downwards | Green | Above lane | Traffic may continue in lane | ||
| Cross (×) | Red | Above lane | Traffic may not enter lane (lane closed) | ||
| Arrow pointing diagonally downwards | Amber or white | Above lane | Lane closes shortly ahead, change lane in the direction of the arrow | ||
| Flashing | Plain | Double Red (alternating) | At level crossing, swing bridge, airport, fire station or ferry terminal | Stop | |
| Lunar white | At crossing | Proceed | |||
| Amber (flashing) | Anywhere except intersection | Proceed with caution | |||
| Amber (flashing) | At intersection | The priority is determined by | |||
Red flashing lights may only be used at the locations specified above; any other use of the lights is in breach of the convention. Red lights must be placed on top when lights are stacked vertically, or on the side closest to oncoming traffic if stacked horizontally.
Contracting parties
The convention has 68 state parties as of August 2016: Albania, Austria, Bahrain, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Central African Republic, Chile, Côte d'Ivoire, Croatia, Cuba, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Iran, Iraq, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Liberia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Moldova, Mongolia, Montenegro, Morocco, Netherlands, Nigeria, Norway, Pakistan, Paraguay, the Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, San Marino, Senegal, Serbia, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sri Lanka, Suriname, Sweden, Switzerland, Tajikistan, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Turkey, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam.
The only countries in Europe that are not signatories to the Convention are Ireland, Andorra, Malta, the United Kingdom, and Liechtenstein. Iceland, Spain, and the Holy See are all signatories but have yet to ratify the Convention.
The only countries in Asia that are not signatories to the Convention are Bangladesh, Malaysia, Republic of China (Taiwan), People's Republic of China (including Hong Kong and Macau), Japan, Israel, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Armenia, Yemen, Oman, North Korea, and Afghanistan.
Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, South Korea, and Thailand are all signatories, but have yet to ratify the Convention.
See also
References
- ↑ "Internet Archive Wayback Machine". Web.archive.org. 2009-10-26. Archived from the original on 26 October 2009. Retrieved 2012-01-28.
- ↑ "1931 年道路信号統一条約" (in Japanese). Members.jcom.home.ne.jp. Archived from the original on 2012-12-19. Retrieved 2012-01-28.
- ↑ Chapter 29 in the convention.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Diagrams of Vienna Convention signs. |