Valencia de Alcántara
| Valencia de Alcántara Valencia d’Alcántara | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
 Town Hall | |||
| |||
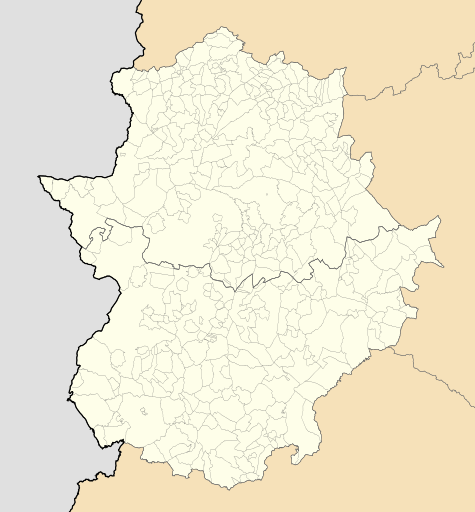 Valencia de Alcántara Location in Extremadura  Valencia de Alcántara Valencia de Alcántara (Spain) | |||
| Coordinates: 39°24′48″N 7°14′37″W / 39.41333°N 7.24361°WCoordinates: 39°24′48″N 7°14′37″W / 39.41333°N 7.24361°W | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Autonomous Community |
| ||
| Province | Cáceres | ||
| Comarca | Valencia de Alcántara | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Alberto Piris Guapo (PSOE) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 595 km2 (230 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation(AMSL) | 620 m (2,030 ft) | ||
| Population (2012) | |||
| • Total | 6,032 | ||
| • Density | 10/km2 (26/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST (GMT +2)) | ||
| Postal code | 10500 | ||
| Area code(s) | +34 (Spain) + 927 (Cáceres) | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Valencia de Alcántara (Extremaduran: Valencia d’Alcántara) (Population: 6178) is a municipality located in the province of Cáceres, in the autonomous community of Extremadura, Spain. It is near the Portuguese border (District of Portalegre), separated from it by the Sever.[1]
History
From the 16th century to the 18th Valencia was a celebrated border fortress; it was captured by the Portuguese in 1664 and 1698.[2]
Battle of 1762
The Battle of Valencia de Alcántara took place in 1762 as part of the Spanish invasion of Portugal. Portuguese-British troops under John Burgoyne attacked and captured the town, which was a Spanish supply base, setting back the invasion and contributing to the British victory that year.
Nineteenth century
The beginning of the nineteenth century, traditionally associated with the beginnings of the modern age, is particularly troublesome in the case of Valencia de Alcántara as it was caught up in two important conflicts, including the fleeting conflict known as the War of the Oranges (1801) or the War of Independence. However, due to its location it became is the second most important custom house for direct traffic between the two kingdoms, after Badajoz, and had a flourishing trade in farm produce of all kinds.[2]
Features
There are Roman remains in the district, and the courtyards and windows of many houses are Moorish in style. Nuestra Señora de Roqueamador, the most important church, dates from the 14th century. The church of Encarnacion, the town hall and a fine convent date from the 16th.[2]
Valencia de Alcántara is a very important centre of dolmens in Europe.
Famous inhabitants
Valencia de Alcántara was the birthplace of Pedro Gómez Labrador, Marquis of Labrador, who represented Spain at the Congress of Vienna (1814–1815).
Soraya Arnelas was also born here.
References
- ↑ Chisholm 1911.
- 1 2 3

.svg.png)