True anomaly
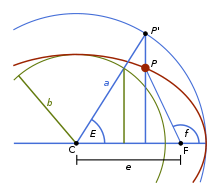
In celestial mechanics, true anomaly is an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along a Keplerian orbit. It is the angle between the direction of periapsis and the current position of the body, as seen from the main focus of the ellipse (the point around which the object orbits).
The true anomaly is usually denoted by the Greek letters ν or θ, or the Latin letter f.
As shown in the image, the true anomaly f is one of three angular parameters ("anomalies") that defines a position along an orbit, the other two being the eccentric anomaly and the mean anomaly.
Formulas
From state vectors
For elliptic orbits, the true anomaly ν can be calculated from orbital state vectors as:
-
- (if r ⋅ v < 0 then replace ν by 2π − ν)
where:
- v is the orbital velocity vector of the orbiting body,
- e is the eccentricity vector,
- r is the orbital position vector (segment FP in the figure) of the orbiting body.
Circular orbit
For circular orbits the true anomaly is undefined, because circular orbits do not have a uniquely determined periapsis. Instead the argument of latitude u is used:
-
- (if rz < 0 then replace u by 2π − u)
where:
- n is a vector pointing towards the ascending node (i.e. the z-component of n is zero).
- rz is the z-component of the orbital position vector r
Circular orbit with zero inclination
For circular orbits with zero inclination the argument of latitude is also undefined, because there is no uniquely determined line of nodes. One uses the true longitude instead:
-
- (if vx > 0 then replace l by 2π − l)
where:
- rx is the x-component of the orbital position vector r
- vx is the x-component of the orbital velocity vector v.
From the eccentric anomaly
The relation between the true anomaly ν and the eccentric anomaly E is:
or using the sine[1] and tangent:
or equivalently:
so
An equivalent form avoids the singularity as e → 1 , however it does not produce the correct value for :
or, with the same problem as e → 1 ,
- .
In both of the above, the function arg(x, y) is the polar argument of the vector (x, y), available in many programming languages as the library function named atan2(y,x) (note the reversed order of x and y).
From the mean anomaly
The true anomaly can be calculated directly from the mean anomaly via a Fourier expansion:[2]
where the "big-O" notation means that the omitted terms are all of order e4.
Radius from true anomaly
The radius (distance from the focus of attraction and the orbiting body) is related to the true anomaly by the formula
where a is the orbit's semi-major axis.