Thermoplastic-sheathed cable
| Relevant topics on |
| Electrical installations |
|---|
| Wiring practice by region or country |
| Regulation of electrical installations |
| Cabling and accessories |
| Switching and protection devices |
Thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) consists of an outer toughened sheath of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) (the thermoplastic element) covering one or more individual cables which are PVC insulated annealed copper conductors. It is a commonly used type of wiring for residential and light commercial construction in many countries. The flat version of the cable with two insulated conductors and an uninsulated earth conductor all within the outer sheath is referred to as twin and earth. In mainland Europe, a round equivalent is more common.
Description

Each of the current carrying conductors in the "core" is insulated by an individual thermoplastic sheath, coloured to indicate the purpose of the conductor concerned. The Protective Earth conductor may also be covered with Green/Yellow (or Green only) insulation, although, in some countries, this conductor may be left as bare copper. With cables where the current carrying conductors are of a large Cross Sectional Area (CSA) and current carrying capacity, the Protective Earth conductor may be found to be of a smaller CSA, with a lower continuous current carrying capacity. The conductors used may be solid in cross-section or multi-stranded.
The type of thermoplastic, the dimensions of the conductor(s) and the colour of their individual insulation (if any) are specified by the regulatory bodies in the various countries concerned.[1]
Thermoplastic-sheathed cable is more vulnerable to rodent damage and accidental mechanical damage than wiring within electrical conduit or armored cable.
North America


In North America, this type of cable is designated as NM cable. NM means "nonmetallic", referring to the outer sheathing; the conductors are of course still metallic. NM was first Listed and described in the NEC in 1926, but it was invented a few years earlier by Rome Wire Company in 1922 in Rome, NY, and marketed under the trade name “Romex.”[2] The name "Romex" (a trademarked brand of the Southwire Company[3]) is commonly used generically for NM cable from any source.
In modern products, the color of the NM cable sheath (or jacket) indicates either the gauge of the current carrying conductors within it, or special properties of the sheathing itself. Cables found in older installations may not conform with this color coding.
The following are nominal current ratings for copper conductors; long runs may require thicker wires to minimize voltage drop.
- White: 14 AWG wire (2.08 mm2) for 15-amp circuits.
- Yellow: 12 AWG wire (3.31 mm2) for 20-amp circuits.
- Orange: 10 AWG wire (5.26 mm2) for 30-amp circuits.
- Black: 6 or 8 AWG wire (13.3 mm2 or 8.37 mm2) for 60- and 45-amp circuits, respectively.
- Gray: usage for underground installations, designated as "Underground Feeder" (UF) cables.[4]
The outer jacket is labeled with letters that show how many insulated wires are concealed within the sheath. However, this wire count does not include an uninsulated wire that is used as a ground wire, which may or may not be mentioned but is almost always present in modern cabling. For instance, if the cable lists "12-2 WG", it means there are two insulated 12-gauge wires (a black and a white wire), plus a ground wire. If the label says "12-3", this is a three-conductor, 12-gauge cable with a bare copper ground wire understood to be included.[5]
Australia and New Zealand
In Australia and New Zealand, the colour of the external sheath is usually white but several other colours are available. Wire sizes of from 1 mm² to 6 mm² Cross Sectional Area (CSA) are available with the outer sheath covering a "core" of either a single conductor, twin conductors, twin and earth conductors, or three and earth conductors. Although available in the larger sizes, solid conductors are rarely used with wire sizes greater than 1 mm² CSA, since the small extra expense of multi-stranded conductors is far outweighed by the relative ease of working with them, especially at the points of termination.
Unlike in North America, the existence of the Earth wire within the sheath is always specified if it is present (e.g. twin cable has two conductors and twin and earth cable has three.) The earth conductor is always multi-stranded (unlike North American usage) and covered with Green/Yellow plastic insulation.
TPS is also often referred to as Tough Plastic Sheathed.[6][7]
Flat TPS is more common, and is used for fixed wiring of domestic and industrial lighting, power outlets and, also, for "hard-wired" appliances and heating and air conditioning units. Round TPS is less common, and is generally used only where cable glands are required. It may be more difficult to strip the outer sheathing from round TPS than from flat TPS.
 Flat "twin and earth" conductor TPS cable for single-phase plus earth
Flat "twin and earth" conductor TPS cable for single-phase plus earth Cross-section of same cable, showing three stranded inner wires
Cross-section of same cable, showing three stranded inner wires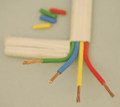 Flat "three and earth" conductor TPS cable for three-phase plus earth
Flat "three and earth" conductor TPS cable for three-phase plus earth Cross-section of same cable, showing four stranded inner wires
Cross-section of same cable, showing four stranded inner wires
United Kingdom
In the UK, thermoplastic-sheathed cable in "twin and earth" (or 'T and E') format has the Circuit Protective Conductor (CPC = earth) uninsulated (bare) and of reduced diameter compared to the main cores. Green and yellow sleeving is sold separately, to be applied at the ends. The cross section on the main conductor(s) is given first, and then the cross-section of the CPC Standard UK metric twin and earth cable sizes
1/1 mm² and 1.5/1 mm² have solid conductors and CPC (primarily used on low power lighting or alarm circuits)
2.5/1.5mm² has a solid CPC and may have solid or stranded conductors (primarily used for socket circuits, radial or ring circuit)
4/1.5 mm² and 6/2.5 mm² have stranded conductors and a solid CPC (fixed high power equipment or sub-mains)
10/4 mm² and 16/6 mm² have stranded conductors and CPC (fixed high power equipment or sub-mains)
In older properties (pre 1970) cable with imperial sizes are found, sometimes without CPC. Mainland UK wiring regulations do not at present (BS7671:AMD3) acknowledge Twin and Earth or Flat TPS with a full sized and insulated (G/Y) earth conductor as a valid cable type, which may be awkward for contractors who work cross-border with the Republic of Ireland.
Also available in smaller conductor sizes are versions containing three current-carrying conductors and a circuit protective (earth) conductor. These configurations are commonly used for applications such as switched light circuits, battery-backed emergency lighting which requires a switched and unswitched supply, extractor fans with a run-on timer which require a switched and unswitched supply, mains-powered interlinked smoke alarms, and central heating thermostats.
There is an overall sheath of grey PVC (BS 6004), or white for low smoke compound (BS 7211), although prior to 2005 white PVC was also available.
Republic of Ireland
In the Republic of Ireland the situation is different from that in the UK. Prior to 2013 IS 201-4:2001 ( I.S. 201 part 4: PVC and Low Smoke Halogen Free Sheathed cables for fixed wiring) permitted both the UK style of twin and earth, and also a version with a CPC with a cross-section equal to that of the main conductors and insulated in green and yellow inside the full length of the cable. However, from 2013, the option for the uninsulated and reduced CPC has been removed from the standard IS 201-4:2013, and as such is no longer permitted in new Southern Irish installations.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ Archived November 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "InterNACHI Forum".
- ↑ Barker, Bruce. "Old Wiring Methods". The ASHI Reporter. The American Society of Home Inspectors. Retrieved 2014-06-09.
- ↑ "Types of Electrical Wiring in Homes". Completeelectrical.biz. 2013-10-08. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ↑ "Nonmetallic Cable Sheathing Color Codes". Electrical.about.com. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ↑ "Australian Site - Flat TPS & SDI". Generalcable.com.au. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ↑ "Compliance of wiring materials in New Zealand homes and building". Level.org.nz. Retrieved 2015-03-03.
- ↑ "BASEC News". BASEC. Retrieved 8 March 2017.