Tetiaroa
|
Aerial view of the island of Teti'aroa | |
|
| |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 17°0′S 149°33′W / 17.000°S 149.550°WCoordinates: 17°0′S 149°33′W / 17.000°S 149.550°W |
| Archipelago | Society Islands |
| Area | 6 km2 (2.3 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
|
France | |
| Overseas collectivity | French Polynesia |
| Administrative subdivision | Windward Islands |
| Commune | Arue |
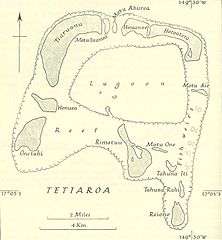

Teti'aroa is an atoll in the Windward group of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, an overseas territorial collectivity of France in the Pacific Ocean. Once the vacation spot for Tahitian royalty, the motus' inside is under a 99-year lease contracted by Marlon Brando.
Geography
Teti'aroa is administratively part of the commune (municipality) of 'Ārue, whose main part is in the northeastern part of Tahiti.
The atoll is located 53 kilometres (33 mi) north of Tahiti. The atoll has a total surface area of 6 square kilometres (2 sq mi); approximately 585 hectares (1,450 acres) of sand divided by 12 motus (islets) with varying surface areas. The lagoon is approximately 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) wide and 30 metres (98 ft) deep. The atoll has no reef opening, making access by boat nearly impossible.
The islets (or motus), in clockwise order starting from the southwest corner, include:
- Onetahi (with regulated airstrip and site of The Brando Resort)
- Honuea
- Tiaruanu
- Motu Tauvini (Tauini)
- Motu Ahurea (Auroa)
- Hiraanae
- Horoatera (Oroatera)
- Motu 'Ā'i.e.
- Tahuna Iti
- Tahuna Rahi
- Reiono
- Motu One (emerging sandbank)
- Rimatu'u (with an ornithology reserve)
Ownership and history
The atoll of Teti'aroa was a special place for the Tahitian chiefs, as a place to entertain themselves with song, dance, fishing, and feasting. It was also a special place for the ariori to practice their custom of ha'apori'a. This custom included eating to gain weight, and staying out of the sun to whiten their skin. Plump and pale was a sign of “well-being and prosperity” for the ariori and chiefs. Teti'aroa was controlled by the chiefs of Pare-'Arue, and later, by members of the Pōmare Dynasty.[1]
In 1789, William Bligh is said to have been the first European to visit the atoll while looking for early mutineers prior to the departure of the HMS Bounty which eventually suffered a full mutiny.
The United States Exploring Expedition visited the island on 10 Sept. 1839.[2]
In 1904, the royal family gave Teti'aroa to Johnston Walter Williams, the only dentist in Tahiti. Williams later became Consul of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1935.[3] Williams managed Teti'aroa as a residence and a copra plantation.
In 1960, Marlon Brando “discovered” Teti'aroa while scouting filming locations for Mutiny on the Bounty, which was shot on Tahiti and neighboring Moorea. After filming was completed, Brando hired a local fisherman to ferry him to Teti'aroa. It was “more gorgeous than anything I had anticipated,” he marveled in his 1994 autobiography Songs My Mother Taught Me.
Brando eventually purchased Teti'aroa's islets (motus) from one of Williams’ direct descendants, Mrs Duran. The reef and lagoon belong to French Polynesia. (Williams and his wife are buried on motu Rimatuu). He had to overcome political interference and local resistance to purchase the atoll, which is now the property of French Polynesia. Many important archaeological sites have been located, identified, and studied on Teti'aroa. Thus, the historical significance of Teti'aroa to the people and the government of French Polynesia continue to make future development questionable at best.[4]
Wanting to live on the atoll, Brando built a small village on Motu Onetahi in 1970. It consisted of an airstrip to get there without breaching the reef, 12 simple bungalows, a kitchen hut, dining hall and bar, all built from local materials - coconut wood, thatch roofs and even large sea shells for sinks. The village became a place for friends, family and scientists studying the atoll's ecology and archeology.
Over the years, Brando spent as much time as he could there and used it as a getaway from his hectic life in Hollywood. Although he didn’t spend as much time there as he wished, it is said that he always cherished his moments on Teti'aroa. During his stay on the island he was often visited by his children, grandchildren and great-grandchildren. Upon his death, Brando's son Teihotu lived on the island for some time.
Eventually the village became a modest hotel managed by his Tahitian wife, Tarita Teriipaia, who had played his on-screen love in Mutiny on the Bounty. The hotel operated for more than 25 years, even after Brando left French Polynesia to return to Los Angeles. Many hotel guests lamented the lack of amenities normally found at an island resort.[5]
In 1980, the famous maxi yacht S/Y Condor of Bermuda ran aground on the Onetahi reef, which caused it to be shipwrecked and written off by insurers. Purportedly, Brando and the owner of the yacht engaged in a brief bidding war for rights to the vessel’s polished mahogany hull (as reported by its owner in the New Zealand yachting magazine, Sail in 1981), which Brando, it is believed, wanted to use as a bar at a resort he planned to build on the island. The yacht was salvaged, and sent to New Zealand for repair.
In 2002, two years before the actor’s death, Brando signed a new will and trust agreement that left no instructions for Teti'aroa. Following his death in 2004, the executors of the estate granted development rights to Pacific Beachcomber SC, a Tahitian company that owns hotels throughout French Polynesia.
Future of Teti'aroa
Teti'aroa Pacific Beachcomber SC began construction on Teti'aroa in 2009. The first phase of building included reconstruction and reorientation of the runway, as the original surface was in disrepair and not long enough to meet current aviation regulations. In addition, a reef dock was built to enable the transfer of supplies from the ocean side of the reef to the lagoon side. The motu Onetahi now includes a luxury eco-hotel (The Brando Resort), spa, research station, staff village and private runway.
In February 2014, it was announced that the building of The Brando Resort had been finished. The Brando was officially opened for the public in July 2014.[6] The Brando Estate and eight of Marlon Brando's sixteen children are involved in the project.[7]
References
- ↑ Salmond, Anne (2010). Aphrodite's Island. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 110, 349. ISBN 9780520261143.
- ↑ Stanton, William (1975). The Great United States Exploring Expedition. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 122–123. ISBN 0520025571.
- ↑ The Tahiti Traveler Archived 2011-07-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ NASA Earth Observatory
- ↑ "Trouble in Paradise", Matthew Heller, Los Angeles Times, October 23, 2005
- ↑ the Brando opening in July 2014
- ↑ The Brando, Forbes
Waltzing with Brando by Bernard Judge
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tetiaroa. |