Silver oxalate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Silver Ethanedioate, Silver Salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.791 |
| EC Number | 208-568-3 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | RO2900000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
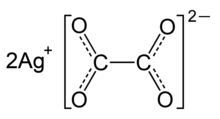
| Ag 2C 2O 4 | |
| Molar mass | 303.755 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 5.03 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 961.9 °C (1,763.4 °F; 1,235.0 K) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | 2,212 °C (4,014 °F; 2,485 K) at 1013.25 hPa |
| 3.270*10−3 g/100mL | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Silver oxalate (Ag
2C
2O
4) is commonly employed in experimental petrology to add carbon dioxide (CO
2) to experiments as it will break down to silver (Ag) and carbon dioxide under geologic conditions.[1] It is also a precursor to the production of silver nanoparticles.
It is explosive upon heating around 140 degrees Celsius, shock or friction.
[2]
Production
Silver oxalate is produced by the reaction between silver nitrate and oxalic acid.
See also
References
- ↑ Silver Oxalate at American Elements
- ↑ Silver Oxalate MSDS sheet at mpbio
External links
http://wikisenior.com/silver-oxalate/
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.