Siege of Kazan
| Siege of Kazan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Russo-Kazan Wars | |||||||
Illustration in chronicle | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Tsardom of Russia |
Khanate of Kazan Cheremis and Ar warriors Nogay cavalry | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Ivan IV "the Terrible" Alexander Gorbatyi-Shuisky Andrey Kurbsky Shahghali |
Yadegar Moxammat (POW) Yapancha bak † Zaynash morza (POW) Qolsharif † | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
150,000 men, 150 cannons unknown battleship some siege towers |
50,000 men, including civilians2 unknown cannons | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
15,3552-? unknown wounded |
Around 65000 dead or missing (including civilians)2 more than 190,000 captured 2 many thousands displaced | ||||||
|
1Involvement disputed 2 Kazan Chronicle; it is likely that this source underestimates Russian and overstates Tatar casualties | |||||||
The Siege of Kazan in 1552 was the final battle of the Russo-Kazan Wars and led to the fall of the Khanate of Kazan. Conflict continued after the fall of Kazan, however, as rebel governments formed in Çalım and Mişätamaq, and a new khan was invited from the Nogais. This guerrilla war lingered until 1556.
Background
During the existence of the khanate (1438-1552) Russian forces reached the walls of Kazan at least five times (1487, 1524, 1530, 1550, 1552). In 1550 Ivan the Terrible besieged Kazan, but supply difficulties forced him to withdraw. The Russians pulled back 18 miles and built the town or fort of Sviyazhsk. They also annexed land west of the Volga which weakened the khanate. The peace party agreed to accept the pro-Russian Shah Ali as khan. The patriotic party regained power, Shah Ali fled and Yadegar Mokhammad of Kazan was called in as khan. Religious leaders like Qolsharif inspired the people to a determined resistance.
The siege
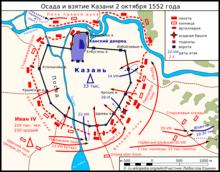
The Russian forces included streltsy as well as Moscow and Qasim irregular feudal cavalry, but the Muscovite artillery and sappers, both Russian and foreigners, played a vital role. At first they faced the Tatar garrison of Kazan, 10,000 Nogay horsemen led by the khan of Kazan, Yadegar Mokhammad, who originated from the Nogai Horde. Cheremiss units and Kazan irregular feudal cavalry had bases in forests north and east of Kazan respectively, with the stronghold of Archa as their base. Before the battle Russians had a fortress on the Volga, Ivangorod, later known as Sviyazhsk, some miles above Kazan. The Russian military engineer Ivan Vyrodkov had built this wooden fortress in 1551, when after the conclusion of peace, the right bank of the Khanate (Taw yağı) had passed to Russia. It would serve as a strong point for the capture of Kazan by the Muscovite army.
The 150,000 Muscovite army under Ivan the Terrible came under Kazan's walls and besieged Kazan on August 22, 1552 (Old Style). Russian cannons shelled the walls from 29 August. Soon they smothered the fire of large-calibre Tatar cannons. During the period from 30 August to 6 September Alexander Gorbatyi-Shuisky defeated the inner cavalry under Yapancha and the Ar units and burned Archa. Andrey Kurbsky defeated Cheremis troops. Sappers blew up the underground way to Kazan's underground drinking-water source.
Ivan Vyrodkov built on site a 12-metre high wooden siege tower (referred to also as a "battery-tower" to distinguish it from the pre-gunpowder siege engines) for mounting siege cannon. This revolutionary new design could hold ten large-calibre cannon and 50 lighter cannon, allowing a concentration of artillery fire on a section of the wooden wall or of the city, and played a crucial role in shattering Tatar resistance. However, the few cannon defending Kazan would first have to have been put out of action in order to make the tower effective, as it would otherwise have become an obvious target for any remaining artillery.[1]
On 2 October sappers (believed to have been led by the Englishman Butler, also known as Rozmysl in Russian chronicles) blew up the wall near the Nogay and Atalıq Gates. Russian soldiers entered the city. The civil population as well as Kazan's army opposed them. After desperate slashing some survivors were blockaded in the citadel. Then, after the capture of khan Yadegar Moxammad and of Nogai leader Zaynash, the defenders of the citadel tried to escape to the northern forests, but they were defeated. A number of Russians who had been captured in military campaigns from the Russian borderland and held captive in the Khanate were released, and a large massacre of Kazan Tatars took place, as well as the destruction of almost all Tatar buildings, including mosques.
Before the siege, Ivan IV encouraged his army with examples of the Georgian Queen Tamar's battles,[2] describing her as: "The most wise Queen of Iberia, endowed with the intelligence and courage of a man".[3]
Aftermath
Main article: Kazan rebellion of 1552–56.
18,000 men were left as a garrison and Ivan returned to Moscow to celebrate. After the fall of Kazan resistance continued in the countryside. The tribes refused to pay taxes. Russian merchants were killed which led to reprisals. The forts of Çalım and Mişätamaq and were built on the west and east sides of the Volga. The Nogai Ali Akram was brought in as khan. Soltikov marched against Mişätamaq but he and 500 men were surrounded in the snow and killed. Ivan sent a larger force. There were daily combats in the snow and forests. Ten thousand men were killed, six thousand were captured along with fifteen thousand women and children. 1600 leading Tatars were put to death.The leaders Yepancha and Aleka were killed. Ali Akram proved incompetent and was killed by Mameshbirde. Mameshbirde was betrayed to the Russians. The fort of Mişätamaq fell at some point. After the fall of Çalım in 1556 most resistance came to an end.
In 1556 the Russians went down the Volga and conquered the Khanate of Astrakhan. In 1558 Anikey Stroganov was granted large lands on the Kama River northeast of Kazan, which he worked to develop. In 1582 the Stroganovs were involved in the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir east of the Urals. The Kazan Tatars continued to live in the area and retained their language and religion.
Cultural resonance
- Mikhail Kheraskov recounted the capture of Kazan in his epic poem, the Rossiada (1771-1779).
- Saint Basil's Cathedral in Moscow commemorates the conquest of Kazan.
Gallery
 Ivan IV under the walls of Kazan
Ivan IV under the walls of Kazan
 Blessed Be the Host of the Heavenly Tsar (alternatively known as Church Militant). Russian icon, ca. 1550 - 1560. This icon is traditionally perceived as an allegorical representation of the fall of Kazan.
Blessed Be the Host of the Heavenly Tsar (alternatively known as Church Militant). Russian icon, ca. 1550 - 1560. This icon is traditionally perceived as an allegorical representation of the fall of Kazan.
See also
References and notes
- Henry Hoyle Howorth, History of the Mongols, 1880, Part 2, pp 412-429
- ↑ Russian Fortresses, 1480–1682 Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine., Osprey Publishing, ISBN 1-84176-916-9
- ↑ История русской литературы, Дмитрий Дмитриевич Благой, Volume 1, p208
- ↑ History of the Georgian nation, Kalistrat Salia, p189