Salyan District, Azerbaijan
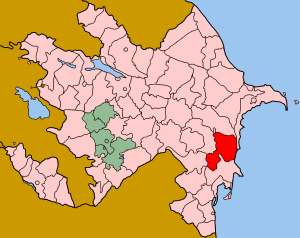
Salyan is a raion of Azerbaijan. Its capital is Salyan. It lays adjacent to the Kura River. To the north are several productive oilfields (Kursenge, beside the prominent mud volcano of the same name, and Karabaghli, a few km NW) operated (in 2001) by the Salyan Oil company. It also comprises most of the Shirvan National Park.
History
Salyan was a large populated area and attracted the attention of the invaders in the XIII century. Approximate time of settlement is the 15th century. Trade relations of Shirvanshahs with Mugan, Tabriz and Iran were passing through Salyan. For a long time in the XVII-XVIII century trade routes with Iran, the North Caucasus, Turkestan and Russia passed through Salyan. Fish and caviar from Salyan were transported to these cities for sale. In the 18th century silver, copper money was minted in the district.
In 1795 Aga Muhammad Shah Gajar attacked Shamakhi and completely ruined Salyan because of the confrontation he showed.
In February 1868, the Javad district was established within the Baku province, including Salyan as an administrative unit. Thus Salyan transformed into a cultural center.
At the beginning of the 20th century, 3 small cotton ginning enterprises with a capacity of 3-4 tons, small heating power stations, 4 elementary schools and a library were founded here. At that time in the city there were 20 small knitting enterprises, 200 shops, 3 caravan-sheds, 5 trading banks, a ship bridge, a post station, a quarantine station and 11 madrasahs.
In the year 1894 the meteorological station was opened in Salyan for the first time in the whole of Southern Russia and the Caucasus.
Salyan was also the center of trade, which was located on the Silk Road. Back in the II century AD. merchants from China and India, passing through the current Turkmenbashi (Krasnovodsk) along the sea route, passed through the Caspian depression into the Kura River, the lands of all Azerbaijan, as well as the territory of Salyan, crossed the Rioni River in Georgia, then reached the Poti port on the Black Sea, crossed Black Sea and fell into the Sea of Azov.
Salyan for a long time was the educational, cultural center of Mugan and the southeast of Mugan. In 1881 the area of the whole city was 800 acres.
Since 1916, Salyan is officially considered a city. [1]
Ethymology
There are many assumptions and theories about the etymology of the word "Salyan". According to scientific research, the tribe "sal" existed among the Turkic tribes. At first they lived on the bank of the Volga River, on the plain of the "Sal" area.
In addition, one of the currents of the Don River, which flows from the plains of Eastern Europe, is called the Sal River. In the past Salyan settlements lived on this territory and were called tribes "sal".
Historian Memandr, referring to the events of 558, highlights the fact of the war of the Sal tribes in the meadows of Southern Russia with the Turkic tribal association called Avar.
According to the assumptions, part of the saloons along with the Avars moved to Azerbaijan. This is indicated by the historian of the XIV century, Hamdullah Gazvi, confirming his words by the fact of the existence of the city of "Abar" on the bank of the river Kura. [1]
Geography
Salyan region is located on the Kura-Araks lowland, in the Mugan steppe. The region is located in the southeast of Azerbaijan. Highway and the railway linking all of Azerbaijan with its southern regions, as well as the countries of the Middle East, are situated in this region. One of the main rivers of the country Kura flows through the territory of the Salyan region. There is the national national park "Shirvan" in this district.
Gray-brown, gray-grass, meadow-wetlands, saline soils are spread. The vegetation cover is composed of desert and semi-deserted, mountainous and hilly areas and is rich in mud volcanoes. The main volcanoes are Durovdag, Aghzıbir, Rabbit-Dag, Babazanen, Duzdag, Galmas, Qirivdağ, Miashovdag, Khidirli, Kursangi, Hamam-mountain, Bandovan mud volcanoes. The flora is semi - desert and desert type .These are mostly cypress, cypress, wildflower, algae, vulture, blackberries, adjacent, ordinary, winter, Caspian, . The sword of the arms, the Russian herd, the aches, the sharp spells, the quails, the sable, the common figs, the rarest species of hirkan figs have been spread. [2]
Climate
The dominant climate here is considered a local steppe climate. A small amount of precipitation falls throughout the year. The average annual temperature is 15.2 ° C. The average annual rainfall is 288 mm. [3]
Economics
The Salyan region is rich in fish. For example: Beluga, sturgeon, stellate sturgeon, salmon, catfish, pike perch. Also the Salyan area is connected by a post road and a railway.The population of the district is mainly engaged in agriculture. The region is developing grain growing, cotton growing and livestock. Also melon and vegetables are grown in the area. The population is also engaged in viticulture (table varieties) and gardening.
Historical Monuments
In the Salyan district there are a number of archaeological objects from the Bronze Age to the Early Middle Ages. Among them are the necropolis of Marimly, the necropolis of pitchers' graves in the village of Gursangya, the ruins of ancient settlements in the villages of Nokhudlu and Mahmudabad. [4]
Noteworthy Places
Numerous mud volcanoes of Azerbaijan are situated not far from the regional center. among which volcano Babazanan attracts local residents withthe curative properties of its muds. There is also a reserve "Dashgil" - a place for hunting waterfowl and fishing for kutum, carp and other Caspian fish. [5]
Shirvan Reserve
By the decree of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan, Heydar Aliyev, on July 5, 2003, the Shirvan National Park of the Republic of Azerbaijan was established for 54373.5 hectares of administrative units of the districts. The main goal of the National Park was to preserve the gazelles entered in the "Red Book" of the Republic of Azerbaijan, conduct ecological monitoring, educate the population from an ecological point of view, create all conditions for the development of tourism and recreation. [6]
See also
References
- 1 2 АДМИНИСТРАТИВНО-ТЕРРИТОРИАЛЬНОЕ ДЕЛЕНИЕ.
- ↑ Əsgərov, A.M (2006). Azərbaycanın ali bitkiləri. Azərbaycan florasınm konspekti. Bakı: Elm.
- ↑ "Климат: Сальянский район: Температуры, Климатические графики, климатические таблицы для Сальянский район - ru.Climate-Data.org". ru.climate-data.org. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- ↑ "Azərbaycan :: Baş səhifə". www.azerbaijans.com (in Azerbaijani). Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- ↑ "Сальян: ворота в уникальный регион Азербайджана - ФОТО". Day.Az (in Russian). 2012-08-22. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
- ↑ "Сальян: ворота в уникальный регион Азербайджана - ФОТО". Day.Az (in Russian). 2012-08-22. Retrieved 2018-09-27.
.svg.png)