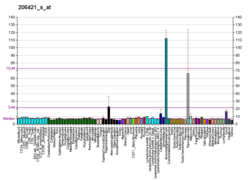
SERPINB7
Serpin B7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINB7 gene.[5]
See also
References
Further reading
- Tsujimoto M, Tsuruoka N, Ishida N, et al. (1997). "Purification, cDNA cloning, and characterization of a new serpin with megakaryocyte maturation activity". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (24): 15373–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.24.15373. PMID 9182567.
- Miyata T, Nangaku M, Suzuki D, et al. (1998). "A mesangium-predominant gene, megsin, is a new serpin upregulated in IgA nephropathy". J. Clin. Invest. 102 (4): 828–36. doi:10.1172/JCI2450. PMC 508946. PMID 9710452.
- Inagi R, Miyata T, Suzuki D, et al. (2001). "Specific tissue distribution of megsin, a novel serpin, in the glomerulus and its up-regulation in IgA nephropathy". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 286 (5): 1098–106. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5509. PMID 11527413.
- Inagi R, Miyata T, Imasawa T, et al. (2003). "Mesangial cell-predominant gene, megsin". Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 17 Suppl 9: 32–3. doi:10.1093/ndt/17.suppl_9.32. PMID 12386281.
- Inagi R, Miyata T, Nangaku M, et al. (2003). "Transcriptional regulation of a mesangium-predominant gene, megsin". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13 (11): 2715–22. doi:10.1097/01.ASN.0000033507.32175.FA. PMID 12397041.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Li YJ, Du Y, Li CX, et al. (2004). "Family-based association study showing that immunoglobulin A nephropathy is associated with the polymorphisms 2093C and 2180T in the 3' untranslated region of the Megsin gene". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15 (7): 1739–43. doi:10.1097/01.ASN.0000130858.00688.46. PMID 15213261.
- Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Shirota M, et al. (2004). "Sequence comparison of human and mouse genes reveals a homologous block structure in the promoter regions". Genome Res. 14 (9): 1711–8. doi:10.1101/gr.2435604. PMC 515316. PMID 15342556.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Inagi R, Nangaku M, Usuda N, et al. (2005). "Novel serpinopathy in rat kidney and pancreas induced by overexpression of megsin". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16 (5): 1339–49. doi:10.1681/ASN.2004070600. PMID 15788472.
- Xia Y, Li Y, Du Y, et al. (2006). "Association of MEGSIN 2093C-2180T haplotype at the 3' untranslated region with disease severity and progression of IgA nephropathy". Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 21 (6): 1570–4. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfk096. PMID 16431886.
- Xia YF, Huang S, Li X, et al. (2006). "A family-based association study of megsin A23167G polymorphism with susceptibility and progression of IgA nephropathy in a Chinese population". Clin. Nephrol. 65 (3): 153–9. doi:10.5414/cnp65153. PMID 16550745.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: I04.012
- SERPINB7+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.