Rock Elm Disturbance
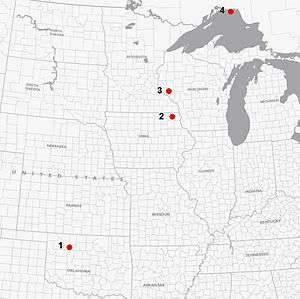 North American Middle Ordovician impact craters, which may be part of the Ordovician meteor event. Key: 1: Ames crater, 2: Decorah crater, 3: Rock Elm Disturbance, 4: Slate Islands crater | |
| Impact crater/structure | |
|---|---|
| Confidence | Confirmed |
| Diameter | 6 km (3.7 mi) |
| Age |
430-455 Ma Middle Ordovician |
| Exposed | - |
| Drilled | - |
| Bolide type | Ordovician meteor event? |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 44°43′N 92°14′W / 44.717°N 92.233°WCoordinates: 44°43′N 92°14′W / 44.717°N 92.233°W |
| Country |
|
| State | Wisconsin |
| District | Pierce County |
| Municipality | Rock Elm |
 Location of the crater in the United States | |
The Rock Elm Disturbance is an impact crater in Wisconsin, United States, roughly 40 kilometres (25 mi) southwest of Menomonie.[1] The disturbance is named for Rock Elm, Wisconsin, a nearby community.
Description
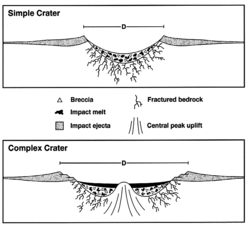
The meteorite is estimated to have been 170 m (560 ft) in diameter with a mass of 9×109 kg (2.0×1010 lb) and impact velocity of 30 km/s (67,000 mph). The crater is 6 km (3.7 mi) in diameter, and fossils found in the rock filling the crater suggest it dates to the Middle Ordovician Period, about 455 to 430 million years ago.[2] It may be one of several Middle Ordovician meteors that fell roughly simultaneously 469 million years ago, part of a proposed Ordovician meteor event that includes the Decorah crater in Iowa, the Slate Islands crater in Lake Superior, and the Ames crater in Oklahoma.[3]
Composition
Researchers discovered a rare mineral called reidite at the Rock Elm impact site. Reidite is a dense form of zircon (ZrSiO4) and has been found in three other massive meteorite impacts.[4]
References
- ↑ "Rock Elm". Earth Impact Database. University of New Brunswick. Retrieved 2017-10-14.
- ↑ Peters, Christopher William, Middleton, Michael D., & Cordua, William S. (2002). "Paleontology of the Rock Elm Disturbance". Abstracts with Programs - Geological Society of America. 34 (2): 95.
- ↑ Vastag, Brian (18 February 2013). "Crater found in Iowa points to asteroid break-up 470 million years ago". Washington Post. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- ↑ Oskin, Becky (November 3, 2014). "Rare Mineral Discovered in Ancient Meteorite Impact Crater". Live Science. Retrieved 2015-02-17.
External links
- Article from Geotimes.com, March 2004
- Press release from the University of Wisconsin-River Falls
- Craters in Wisconsin
- Aerial exploration of the Rock Elm Crater