History of rail transport in Haiti
- "Rail transport in Haiti" redirects here.
- This article is part of the history of rail transport by country series

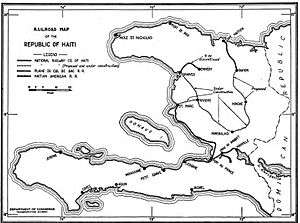
There are currently no functioning railways in Haiti and has never had any rail connections with the neighbouring Dominican Republic. However, between 1876 and about the 1970s, Haiti had various tramways and railways. A tram network operated in the capital, Port-au-Prince, between 1897 and 1932.[1] Two railway lines, Port-au-Prince – Léogâne (36 km) and Port-au-Prince – Manneville (43 km), along with some industrial lines, constituted the Haitian national rail network.

The first horse drawn street tramway opened in 1876. Rural railways were constructed later. All rail transport in Haiti had ceased operating by about the 1970s.
Horse tramways
In 1876, a franchise for the construction of a street railway in Port-au-Prince was awarded to a group of New York City financiers. They founded the Compagnie des Chemins de Fer de Port-au-Prince (CCFPP). Six open cars were ordered from J. G. Brill and Company of Philadelphia in 1877 and a tramway service connecting Croix des Bossales with Champ de Mars began in 1878. The venture was initially successful but was hit by competition from buses from 1880. The CCFPP went bankrupt in 1885 and the last tram ran in 1888.[2]
Steam railways
In 1896, the Comite des Negociants d'Haiti began to restore the closed tramway system and to build two new rural lines. A new company, Societe des Tramways de Port-au-Prince, ordered the following equipment:
- Locomotives
- one 8-ton steam locomotive from H. K. Porter, United States (named President Sam)
- five 12-ton steam locomotives from Krauss, Germany
- three steam locomotives from Ateliers de Tubize, Belgium
- Rolling stock
- ten open passenger cars from the Jackson and Sharp Company, USA
Port-au-Prince
Steam-hauled tram services in Port-au-Prince began in April 1897. Between 1912 and 1918 there were plans to electrify the system but these did not come to fruition. Instead, a small railcar, based on automobile parts, was introduced. The tramway closed in 1932.
Rural lines
The rural lines were operated by a separate company, Compagnie des Chemins de Fer de la Plaine du Cul-de-Sac (CCFPCS) but the two companies shared their rolling stock. The track gauge, in both cases, was 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) narrow gauge. There were two routes:
- Port-au-Prince to Léogâne (36 km)
- Port-au-Prince to Manneville (43 km)
Following the US occupation of Haiti in 1915 the CCFPCS was taken over by the Haitian American Sugar Company (Hasco) and renamed Chemin de Fer Central. Hasco used the following locomotives:[3]
These might possibly be the three locomotives from Ateliers de Tubize (see above) or they might be new locomotives. The 0-4-0 carries the note "Cie.H.Duw. 2" but whether this is the name of the maker, or of a previous owner, is unclear.
Saint-Marc line
In 1905, a new company, Compagnie Nationale, built a 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) narrow gauge steam railway from Port-au-Prince to Saint-Marc (100 km). The track was later extended another 30 km east to Verrettes. There was also a line from Cap-Haïtien [4] to Bahon [5] but it is unclear whether this connected with the Saint-Marc line and whether they were of the same gauge.
Industrial railways
As well as the passenger-carrying railways, there were also industrial railways serving coffee and sugar plantations.
Closures
In the mid-1950s there were two public-service railways totalling 187 mi (301 km) still operating.[6] All the railways are now closed and closure dates are unknown.
See also
References
- ↑ The tramways of Port-au-Prince: history, pictures, maps
- ↑ http://www.tramz.com/ht/ppe.html
- ↑ http://orion.math.iastate.edu/jdhsmith/term/slhthasc.htm
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- ↑ http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/Americas/Haiti-TRANSPORTATION.html
- ↑ Sampson, H. (Editor) The Dumpy Book of Railways of the World, page 182, Sampson Low, London, c.1956
External links
![]()