RCBTB2
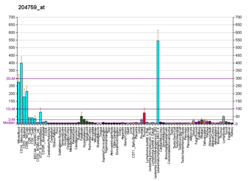
RCC1 and BTB domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RCBTB2 gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a member of the RCC1-related GEF family. The N-terminal half of the encoded amino acid sequence shows similarity to the regulator of chromosome condensation RCC1, which acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) protein for the Ras-related GTPase Ran.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136161 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022106 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Devilder MC, Cadoret E, Cherel M, Moreau I, Rondeau G, Bezieau S, Moisan JP (Jan 1999). "cDNA cloning, gene characterization and 13q14.3 chromosomal assignment of CHC1-L, a chromosome condensation regulator-like guanine nucleotide exchange factor". Genomics. 54 (1): 99–106. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5498. PMID 9806834.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RCBTB2 regulator of chromosome condensation (RCC1) and BTB (POZ) domain containing protein 2".
Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Dunham A, Matthews LH, Burton J, et al. (2004). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 13". Nature. 428 (6982): 522–8. doi:10.1038/nature02379. PMC 2665288. PMID 15057823.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Latil A, Morant P, Fournier G, et al. (2002). "CHC1-L, a candidate gene for prostate carcinogenesis at 13q14.2, is frequently affected by loss of heterozygosity and underexpressed in human prostate cancer". Int. J. Cancer. 99 (5): 689–96. doi:10.1002/ijc.10393. PMID 12115502.
- Renault L, Nassar N, Wittinghofer A, et al. (1999). "Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of human RCC1, the regulator of chromosome condensation". Acta Crystallogr. D. 55 (Pt 1): 272–5. doi:10.1107/S0907444998007768. PMID 10089422.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.