Psilopterus
| Psilopterus | |
|---|---|
| Psilopterus australis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Cariamiformes |
| Family: | †Phorusrhacidae |
| Genus: | †Psilopterus Moreno & Mercerat, 1891[3] |
| Species[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
Psilopterus (Greek for "bare wing") is an extinct genus of phorusrhacid ("terror bird") from the Middle Oligocene to Late Miocene of Argentina. Compared to other phorusrhacids, members of the genus are both relatively gracile and diminutive, and include the smallest known species of terror bird: with the head raised P. bachmanni was 70–80 centimeters (2.3–2.6 ft) in height and weighed about 5 kilograms (11 lb), while the largest members of the genus were only about 7 kilograms (15 lb). The birds resemble the modern cariama (Cariama cristata), except with a heavier build and considerably smaller wings.[1] The strong morphological similarity between the claws of the predatory cariama and Psilopterus, both of which are sharp, curved, and laterally compressed, may indicate they were used to strike prey. In contrast to the other, larger terror birds, Tonni and Tambussi also suggested Psilopterus could use their claws to climb trees, and could even fly,[6] but this has been rejected in more recent literature.[1]
Description and taxonomy
The most recent systematic revision of Phorusrhacidae placed Psilopterus within the subfamily Psilopterinae, along with the genera Procariama and Paleopsilopterus, and divided Psilopterus into four species.[1]
P. bachmanni
Psilopterus bachmanni (Moreno & Mercerat, 1891)[3] is the smallest species of phorusrhacid, rivaled only by P. affinis. The species (and genera) is defined by the upper portion of a fused ankle and leg bone (the lectotype MLP-168 is a tarsometatarsus). Other material assigned the species includes additional leg bones that are probably from the same bird,[4] and an almost complete skeleton (PUM-15.904)[7] The material is from several sites in the Santa Cruz Formation in the Santa Cruz Province of Argentina dating to the Middle Miocene (Santacrucian). The most important diagnostic characteristics are a low skull and upper jaw (or maxilla; similar to the mesembriornithine phorusrhacids)[1] and the extreme slant of the front edge of the hole just before the eye (rostal portion of the antorbital fenestra), though there are also differences in the rest of the skeleton.[7]
- Psilopterus bachmanni (Moreno & Mercerat, 1891)
- Patagornis bachmanni Moreno & Mercerat, 1891
- Psilopterus communis Moreno & Mercerat, 1891
- Psilopterus intermedius Moreno & Mercerat, 1891
- Phororhacos delicatus Amegino, 1891
Brodkorb considered Psilopterus minutus Amerghino, 1981 a separate species,[9] but the incomplete foot bone (tarsometatarsus) is indistinguishable from P. bachmanni.[1]
P. lemoinei
Psilopterus lemoinei (Moreno & Mercerat, 1891)[3] is contemporaneous with P. bachmanni and likely filled a very similar ecological niche, though P. lemoinei is slightly larger, with an estimated weigh approaching 7 kilograms (15 lb).[1] The species is defined by part of a lower leg bone (the lectotype, MLP-162, is the distal end of a tibiotarsus), but a wide variety of material has been referred to the taxon.[7] This material has been found at a number of sites in the Monte León and Santa Cruz Formations in the Santa Cruz Province of Argentina that are dated to the Middle Miocene (Santacrucian). Diagnostic characteristics include a higher skull and upper jaw (maxilla), and the front portion of the hole in front of the eyes (rostral edge of the antorbital fenestra) is less slanted. Additional differences in the remainder of the skeleton are noted in Sinclair and Farr (1932).[7] A number of discrepancies between various specimens have been attributed to differences in age or sex, but material currently assigned to P. lemonei and P. bachmanni may be reclassified at the species level if reexamined in depth.[1]
Synonyms:[8]
- Patagornis lemoinei Moreno & Mercerat, 1891
- Psilopterus australis Moreno & Mercerat, 1891
- Pelecyornis tubulatus Ameghino, 1895 (synonym of Psilopterus australis)
- Phororhacos modicus Ameghino, 1895
- Staphylornis gallardoi Mercerat, 1897 (possible synonym of Psilopterus australis)
- Staphylornis erythacus Mercerat, 1897 (possible synonym of Psilopterus australis)
- Pelecyornis tenuirostris Sinclair & Farr, 1932 (synonym of Psilopterus australis)
P. affinus
Psilopterus affinus (Ameghino, 1899)[5] is the most poorly known species of terror bird, represented only by part of a leg bone (tarsometatarsus, MACN-A-52-184) which indicates the bird was very close to P. bachmanni in size. P. affinus is one of several species known from fragmentary material found in 1899 in the Chubut Province of Argentina (Patagonia), in rocks which dated to the Middle to Late Oligocene (Deseadan).[5] Additional specimens might help clarify the taxonomy of the four apparently unrelated species.[1] P. affinus was originally assigned to the genus Phororhacos despite the difference in size,[5] and is distinguished from P. bachmanni by a groove on the leg bone.[1] Bertelli et al. kept this species in Phororhacos.[10] Brodkorb assigned the species to Andrewsornis in 1967,[9] but this is no longer considered accurate.[1]
P. colzecus
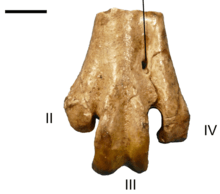
The most recently discovered species in the genus, Psilopterus colzecus Tonni & Tambussi, 1988, is similar to P. lemoinei in size. Known only from a single incomplete skeleton that includes parts of the jaw, arm, and leg (holotype MLP-76-VI-12-2), the species is defined by a groove in the front of the thigh bone (trochlea). The elements were found in the Arroyo Chasicó Formation in Buenos Aires Province of Argentina and are dated to the Late Miocene (Chasicoan).[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Alvarenga, Herculano M. F.; Höfling, Elizabeth (2003). "Systematic Revision of the Phorusrhacidae (Aves: Ralliformes)" (pdf). Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia. 43 (4): 55&ndash, 91. doi:10.1590/S0031-10492003000400001. ISSN 0031-1049.
- ↑ "Springer Link".
- 1 2 3 4 5 Moreno, Francisco P.; Mercerat, Alcides (1891). "Catálogo de los pájaros fósiles de la República Argentina conservados en el Museo de La Plata". Anales del Museo de La Plata (in Spanish). 1: 7&ndash, 71.
- 1 2 Richmond, Charles W. (1902). "List of generic terms proposed for birds during the years 1890 to 1900, inclusive, to which are added names omitted by Waterhouse in his 'Index generum avium'". Proceedings. United States National Museum. 24: 663&ndash, 730. doi:10.5479/si.00963801.1267.663.
- 1 2 3 4 Ameghino, Florentino (1899). "Sinopsis geológico-paleontológica, Suplemento (Adiciones y correciones)" (in Spanish). La Plata: 13 pp.
- 1 2 3 Tonni, Eduardo P.; Tambussi, Claudia (1988). "Un nuevo Psilopterinae (Aves: Ralliformes) del Mioceno tardio de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Republica Argentina". Ameghiniana (in Spanish). 25: 155&ndash, 160.
- 1 2 3 4 Sinclair, W.; Farr, M. (1932). "Aves of the Santa Cruz beds". Reports of the Princeton University expeditions to Patagonia (1896–1899). 7: 157&ndash, 191.
- 1 2 Per Alvarenga & Höfling (2003), who rely on Brodkorb (1967).
- 1 2 Brodkorb, Pierce (1967). "Catalogue of fossil birds, Part III (Ralliformes, Ichthyornithiformes, Charadriiformes)". Bulletin of Florida State Museum. 2: 99&ndash, 220.
- ↑ Taxonomic opinions tied to S. Bertelli et al. 2007 at Fossilworks.org