Propionate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propionate | |
| Other names
Propanoate, Propanoic acid, ion(1-) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5O2− | |
| Appearance | Colorless, oily liquid |
| Density | 0.993 g/mL at 20°C[1] |
| Melting point | −21.5 °C (−6.7 °F; 251.7 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 141.1 °C (286.0 °F; 414.2 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable, Corrosive |
| Flash point | 52 °C (126 °F; 325 K)[1] |
| 465 °C (869 °F; 738 K)[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
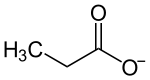
The propionate, or propanoate ion, is C2H5COO− (the conjugate base of propionic acid).
A propionic, or propanoic, compound is a small salt or ester of propionic acid. In these compounds, propionate is often written in shorthand, as CH3CH2CO2 or simply EtCO2.
Propionates should not be confused with propenoates (commonly known as acrylates), the ions/salts/esters of propenoic acid (also known as 2-propenoic acid or acrylic acid).
Propionate is observed to be among the most common short-chain fatty acids produced by human gut microbiota in response to indigestible carbohydrates (fiber) in the diet.[2] A study in mice suggests that propionate is produced by the bacteria of the genus Bacteroides in the gut, and that it offers some protection against Salmonella there.[3]
Examples
- Sodium propionate, NaC2H5CO2
- Methyl propionate, (C2H5(CO)OCH3)
- Calcium propionate, Ca(C2H5CO2)2
- Potassium propionate, KC2H5CO2
- Fluticasone propionate, C25H31F3O5S
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "propionate | C3H5O2- - PubChem". PubChem.
- ↑ How gut microbes talk to organs: The role of endocrine and nervous routes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5004142 | Section 2.1, paragraph 2: The microbial fermentation of carbohydrates in the gut typically produces acetate, propionate, butyrate, and lactate, which are specific SCFAs.
- ↑ http://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2018/07/gut-bacteria-byproduct-protects-against-salmonella.html