Propidium iodide
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.786 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H34I2N4 | |
| Molar mass | 668.3946 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
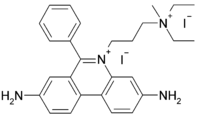
Propidium iodide (or PI) is a fluorescent intercalating agent that can be used to stain cells. Propidium iodide is used as a DNA stain in flow cytometry to evaluate cell viability or DNA content in cell cycle analysis, [1] or in microscopy to visualise the nucleus and other DNA-containing organelles. Propidium Iodide cannot cross the membrane of live cells, making it useful to differentiate necrotic, apoptotic and healthy cells.[2][3] PI also binds to RNA, necessitating treatment with nucleases to distinguish between RNA and DNA staining.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Propidium Iodide Solution - BioLegend". Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ↑ Lecoeur H (2002). "Nuclear apoptosis detection by flow cytometry: influence of endogenous endonucleases". Exp. Cell Res. 277 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1006/excr.2002.5537. PMID 12061813.
- ↑ "Propidium Iodide". ThermoFisher.
- ↑ Suzuki T, Fujikura K, Higashiyama T, Takata K (1 January 1997). "DNA staining for fluorescence and laser confocal microscopy". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 45 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1177/002215549704500107. PMID 9010468.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.