Pathologic fracture
| Pathologic fracture | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pathological fracture of the humerus in a patient with metastasis of renal cell carcinoma | |
| Specialty |
Rheumatology |
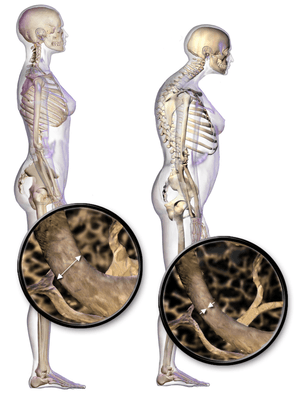
A pathologic fracture (also called insufficiency fracture) is a bone fracture caused by disease that led to weakness of the bone structure. This process is most commonly due to osteoporosis, but may also be due to other pathologies such as: cancer, infection (such as osteomyelitis), inherited bone disorders, or a bone cyst. Only a small number of conditions are commonly responsible for pathological fractures, including osteoporosis, osteomalacia, Paget's disease, osteitis, osteogenesis imperfecta, benign bone tumours and cysts, secondary malignant bone tumours and primary malignant bone tumours.
Fragility fracture is a type of pathologic fracture that occurs as result of an injury that would be insufficient to cause fracture in a normal bone.[1] There are three fracture sites said to be typical of fragility fractures: vertebral fractures, fractures of the neck of the femur, and Colles fracture of the wrist. This definition arises because a normal human being ought to be able to fall from standing height without breaking any bones, and a fracture therefore suggests weakness of the skeleton.
Pathological fractures present as a chalkstick fracture in long bones, and appear as a transverse fractures nearly 90 degrees to the long axis of the bone. In a pathological compression fracture of a spinal vertebra fractures will commonly appear to collapse the entire body of vertebra.
Cause
Pathologic fractures in children and adolescents can result from a diverse array of disorders namely; metabolic, endocrine, neoplastic, infectious, immunologic, and genetic skeletal dysplasias.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Simple bone cyst
- Aneurismal bone cyst
- Disuse osteoporosis
- Chronic osteomyelitis
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Rickets
- Renal osteodystrophy
- Malignant infantile osteopetrosis
- juvenile osteoporosis
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Miscellaneous causes
- Monostotic fibrous dysplasia
- Eosinophilic granuloma
- Bone atrophy secondary to diseases like polio[2]
Diagnosis
In circumstances where other pathologies are excluded (for example, cancer), a pathologic fracture is diagnostic of osteoporosis irrespective of bone mineral density.
References
- ↑ Vanasse, Alain; Dagenais, Pierre; Niyonsenga, Théophile; Grégoire, Jean-Pierre; Courteau, Josiane; Hemiari, Abbas (2005). "Bone mineral density measurement and osteoporosis treatment after a fragility fracture in older adults: regional variation and determinants of use in Quebec". BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 6 (1). doi:10.1186/1471-2474-6-33. ISSN 1471-2474.
- ↑ Maheswari. Essential Orthopedics (3 ed.). Jaypee Publications. p. 4.
|access-date=requires|url=(help)
External links
| Classification |
|---|