Palaungic languages
| Palaungic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Indochina |
| Linguistic classification |
Austroasiatic
|
| Glottolog |
east2331 (East Palaungic)[1] west2791 (West Palaungic)[2] |
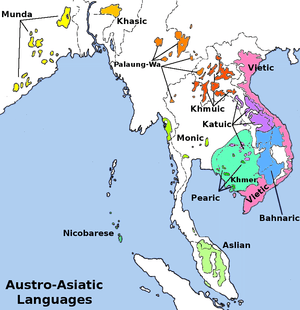 Palaungic | |
The nearly thirty Palaungic or Palaung–Wa languages form a branch of the Austroasiatic languages.
Phonological developments
Most of the Palaungic languages lost the contrastive voicing of the ancestral Austroasiatic consonants, with the distinction often shifting to the following vowel. In the Wa branch, this is generally realized as breathy voice vowel phonation; in Palaung–Riang, as a two-way register tone system. The Angkuic languages have contour tone — the U language, for example, has four tones, high, low, rising, falling, — but these developed from vowel length and the nature of final consonants, not from the voicing of initial consonants.
Homeland
Paul Sidwell (2015)[3] suggests that the Palaungic Urheimat (homeland) was in what is now the border region of Laos and Sipsongpanna in Yunnan, China. The Khmuic homeland was adjacent to the Palaungic homeland, resulting in many lexical borrowings among the two branches due to intense contact. Sidwell (2014) suggests that the word for 'water' (Proto-Palaungic *ʔoːm), which Gérard Diffloth had used as one of the defining lexical innovations for his Northern Mon-Khmer branch, was likely borrowed from Palaungic into Khmuic.
Classification
Diffloth & Zide (1992)
The Palaungic family includes at least three branches, with the position of some languages as yet unclear. Lamet, for example, is sometimes classified as a separate branch. The following classification follows that of Diffloth & Zide (1992), as quoted in Sidwell (2009:131).
- Western Palaungic (Palaung–Riang)
- Eastern Palaungic
Some researchers include the Mangic languages as well, instead of grouping them with the Pakanic languages.
Sidwell (2010)
The following classification follows the branching given by Sidwell (2010, ms).[5]
Sidwell (2014)[9] proposes an additional branch, consisting of:
Sidwell (2015)
Sidwell (2015:12) provides a revised classification of Palaungic. Bit–Khang is clearly Palaungic, but contains many Khmuic loanwords. Sidwell (2015:12) believes it likely groups within East Palaungic. On the other hand, Sidwell (2015) considers Danaw to be the most divergent Palaungic language.
- Danaw
- West Palaungic
- East Palaungic
Lexical similarities with Khmuic
Sidwell (2015) notes that Palaungic and Khmuic share many lexical items, but considers this phenomenon to be a result of lexical diffusion due to intense language contact. Sidwell (2015:112-113) lists the following Proto-Palaungic forms as having diffused from Palaungic into Khmuic.
- *ʔɔːt ‘wipe’
- *ʔiɛk ‘armpit’
- *ɓɤs ‘carry on head/back’
- *bliɛs ‘spear’
- *cəˀŋam ‘clear, clean’
- *criːl ‘gold’
- *gɔːʔ ‘friend; relative’
- *kərɗi(ː)ŋ ‘navel’
- *kɤːŋ ‘to dig’
- *kʋɤj ‘above, upper part’
- *laj ‘to trade’
- *mɔk ‘to fell’
- *(ʰ)ɲɤk ‘sticky’
- *tjaːk ‘sambar deer’
Sidwell (2015:113) lists the following Proto-Palaungic forms as having diffused from Khmuic into Palaungic.
- *ɟɤːl ‘light in weight’
- *kla(ː)w ‘testicles’
Sidwell (2015:114) lists the following Proto-Palaungic forms that are also shared with Khmuic but not with other Austroasiatic branches, and is unsure of whether they diffused from Palaungic to Khmuic or vice versa.
- *-daːk ‘palm, sole’
- *-jaːŋ ‘female’
- *kəlɔːŋ ‘seed’
- *krlaːŋ ‘planet’
- *-nuːs ‘mouth’
- *tɤːʔ ‘smoke’
- *sŋɔːʔ ‘paddy rice’
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "East Palaungic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "West Palaungic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Sidwell, Paul. 2015. The Palaungic Languages: Classification, Reconstruction and Comparative Lexicon. München: Lincom Europa.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-06-16. Retrieved 2012-03-19.
- ↑ Three Austroasiatic branches and the ASJP Archived 2011-06-11 at the Wayback Machine. (Fig. 23)
- ↑ Hall, Elizabeth. 2010. A Phonology of Muak Sa-aak Archived 2015-01-29 at the Wayback Machine.. M.A. thesis, Payap University.
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-20. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
- 1 2 http://ic.payap.ac.th/wp-content/uploads/linguistics_students/Wendy_Chamberlain_Thesis.pdf
- ↑ Sidwell, Paul. 2014. "Khmuic classification and homeland Archived 2016-02-03 at the Wayback Machine.". Mon-Khmer Studies 43.1:47-56
Further reading
- Gordon, Darren. (2013) ''A selective Palaungic linguistic bibliography. Mon-Khmer Studies vol. 42 Mahidol University and SIL International.
- Cheeseman, Nathaniel; Elizabeth Hall and Darren Gordon. (2015) Palaungic Linguistic Bibliography with Selected Annotations. Mon-Khmer Studies vol. 44 pages i-liv.
- Sidwell, Paul. 2015. The Palaungic Languages: Classification, Reconstruction and Comparative Lexicon. München: Lincom Europa.
External links
- http://projekt.ht.lu.se/rwaai RWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage)
- http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-6714-B@view Palaungic languages in RWAAI Digital Archive