Outline of geology
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geology:
Geology – one of the Earth sciences – is the study of the Earth, with the general exclusion of present-day life, flow within the ocean, and the atmosphere. The field of geology encompasses the composition, structure, physical properties, and history of Earth's components, and the processes by which they are shaped. Geologists typically study rock, sediment, soil, rivers, and natural resources.
Branches of geology
Geology applies primarily to Earth, but can be applied to any planet or extraterrestrial body.
Geology of Earth
Subdisciplines of geology:
- Biogeology – The study of the interactions between the Earth's biosphere and the lithosphere
- Economic geology – Science concerned with earth materials of economic value
- Engineering geology – The application of the geology to engineering practice
- Environmental geology – Science of the practical application of geology in environmental problems.
- Geochemistry – Science that applies chemistry to analyse geological systems
- Geologic modelling – Applied science of creating computerized representations of portions of the Earth's crust
- Geomorphology – The scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them
- Geophysics – Physics of the Earth and its vicinity
- Historical geology – The study of the geological history of Earth
- Hydrogeology – The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater
- Marine geology – The study of the history and structure of the ocean floor
- Mineralogy – Scientific study of minerals and mineralised artifacts
- Mining geology – The extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth
- Paleontology – Scientific study of prehistoric life
- Petroleum geology – The study of the origin, occurrence, movement, accumulation, and exploration of hydrocarbon fuels
- Petrology – The branch of geology that studies the origin, composition, distribution and structure of rocks
- Sedimentology – The study of natural sediments and of the processes by which they are formed
- Stratigraphy – The study of rock layers and their formation
- Structural geology – The science of the description and interpretation of deformation in the Earth's crust
- Volcanology – The study of volcanoes, lava, magma and associated phenomena
Planetary geology
See also: Geology of solar terrestrial planets
Planetary geology – The geology of astronomical objects apparently in orbit around stellar objects
- Geology of Mercury – Geologic structure and composition of planet Mercury
- Geology of Venus – Geological structure and composition of the second planet from the Sun
- Geology of the Moon – Structure and composition of the Moon
- Geology of Mars – Scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars
- Geology of Jupiter – Fifth planet from the Sun in the Solar System
- Geology of Saturn – Sixth planet from the Sun in the Solar System
- Geology of Uranus – Seventh planet from the Sun in the Solar System
- Geology of Neptune – Eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System
Principles of geology
- Principle of cross-cutting relationships – Principle that the geologic feature which cuts another is the younger of the two
- Law of included fragments – Clasts in a rock are older than the rock formation
- Principle of uniformitarianism – Assumption that the natural laws and processes of the universe are constant through time and space
- Principle of original horizontality – Layers of sediment are deposited approximately horizontally under the action of gravity
- Principle of superposition – In undeformed stratigraphic sequences, the oldest strata will be at the bottom of the sequence
- Principle of faunal succession – Fossils succeed each other vertically in a specific, reliable order that can be identified over wide horizontal distances
Geological processes
- Petrogenesis – Processes that form rock
History of geology
- History of geology – History of the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of the Earth
- Geological history of Earth – The sequence of major geological events in Earth's past
- Timeline of geology – Chronological list of notable events in the history of the science of geology
Geologic provinces
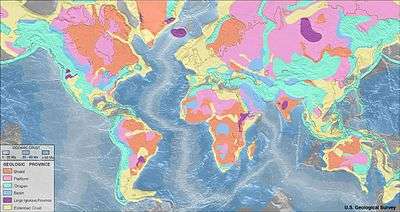
Geologic province – A spatial entity with common geologic or geomorphic attributes
Geologic provinces based on origin:
- Shield – A large stable area of exposed Precambrian crystalline rock
- Platform – A continental area covered by relatively flat or gently tilted, mainly sedimentary strata
- Orogen
- Island arc – Arc-shaped archipelago usually along a subduction zone
- Continental arc – A type of volcanic arc occurring along a continental margin
- Forearc – The region between an oceanic trench and the associated volcanic arc
- Oceanic basin – Large geologic basins that are below sea level
- Cratonic basin – Old and stable part of the continental lithosphere
- Foreland basin, also known as foredeep basin – A structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt
- Large igneous province – Huge regional accumulation of igneous rocks
- Extended crust – The outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite
- Rift – A linear zone where the Earth's crust is being pulled apart, and is an example of extensional tectonics
Plate tectonics
- Plate tectonics – The scientific theory that describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere
Occupations in geology
The Dictionary of Occupational Titles lists the following occupations in Geology, which it describes as "concerned with the investigation of the composition, structure, and physical and biological history of the earth's crust and the application of this knowledge in such fields as archeology, mining, construction, and environmental impact":[1]
- Crystallographer – The scientific study of crystal structure
- Geodesist
- Geologist – Scientist who studies geology
- Geologist, Petroleum – Earth scientist who works in geological aspects of oil discovery and production
- Geophysical Prospector – The systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies
- Geophysicist
- Hydrologist
- Mineralogist
- Paleontologist
- Petrologist
- Seismologist
- Stratigrapher
- Engineer, Soils[2]
- Geophysical-Laboratory Chief (Alternate Titles: Director, Geophysical)[3]
- Geological Aide (Petrol. & Gas)[4]
- Prospector – The physical search for minerals
- Paleontological Helper – Scientific study of prehistoric life
- Laboratory Assistant (Petrol. & Gas) (Alternate Titles: Analyst, Geochemical Prospecting; Core Analyst; Laboratory Tester)[5]
Influential geologists
- List of geologists – List of Wikipedia articles on notable geologists
Geology lists
- Glossary of geological terms – Definition of geological terminology
- Lists of geological features of the Solar System – A directory of lists of geological features on asteroids, moons and planets other than Earth
- Geologic time scale – A system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time
- List of compounds
- Lists of earthquakes – A directory to Wikipedia lists of earthquakes
- List of chemical elements – The 118 identified chemical elements
- Geology of the English counties – A list of Wikipedia articles on the geology of English counties
- List of geologists – List of Wikipedia articles on notable geologists
- List of Russian geologists
- List of largest volcanic eruptions – Large volcanic eruptions on Earth
- List of minerals – A list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia
- List of oil fields – Some of the major oilfields of the past and present
- List of plate tectonics topics – Hierarchical outline list of articles related to plate tectonics
- List of rock types – A list of rock types recognized by petrologists
- List of tectonic plates – A list of the relatively moving sections of the lithosphere of the Earth
- Lists of volcanoes – A list of most of the volcanoes on Earth
See also
- Outline of geography – Hierarchical outline list of articles related to geography
References
- ↑ "024 OCCUPATIONS IN GEOLOGY". Dictionary Of Occupational Titles. Retrieved 2011-04-02.
- ↑ "024.161-010 ENGINEER, SOILS (profess. & kin.)". Dictionary Of Occupational Titles. Retrieved 2011-04-02.
- ↑ "024.167-010 GEOPHYSICAL-LABORATORY CHIEF (profess. & kin.) alternate titles: director, geophysical laboratory; engineer, geophysical laboratory; research engineer, geophysical laboratory; superintendent, geophysical laboratory". Dictionary Of Occupational Titles. Retrieved 2011-04-02.
- ↑ "024.267-010 GEOLOGICAL AIDE (petrol. & gas)". Dictionary Of Occupational Titles. Retrieved 2011-04-02.
- ↑ "024.381-010 LABORATORY ASSISTANT (petrol. & gas) alternate titles: analyst, geochemical prospecting; core analyst; laboratory tester". Dictionary Of Occupational Titles. Retrieved 2011-04-02.