NetApp
 | |
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| Industry | Storage device |
| Founded | 1992 |
| Founder |
David Hitz James Lau Michael Malcolm |
| Headquarters | Sunnyvale, California, United States |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
George Kurian (CEO) Mike Nevens (Chairman of the Board) |
| Products | Data storage hardware and software |
| Revenue |
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
Number of employees | 10,700 (2016)[2] |
| Website |
www |
NetApp, Inc. is a hybrid cloud data services company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 since 2012.[3] Founded in 1992[4] with an IPO in 1995,[2] NetApp offers hybrid cloud data services that simplify management of applications and data across cloud and on-premises environments to accelerate digital transformation.
History

NetApp was founded in 1992 by David Hitz, James Lau,[5] and Michael Malcolm.[4][6] At the time, its major competitor was Auspex Systems. In 1994, NetApp received venture capital funding from Sequoia Capital.[7] It had its initial public offering in 1995. NetApp thrived in the internet bubble years of the mid 1990s to 2001, during which the company grew to $1 billion in annual revenue. After the bubble burst, NetApp's revenues quickly declined to $800 million in its fiscal year 2002. Since then, the company's revenue has steadily climbed.
In 2006, NetApp sold the NetCache product line to Blue Coat Systems. In 2014, NetApp acquired Riverbed Technology's SteelStore line of data backup and protection products,[8] which it later renamed as AltaVault.[9] On June 1, 2015, Tom Georgens stepped down as CEO and was replaced by George Kurian.[10]
In December 2015 (closing in January 2016), NetApp acquired flash storage vendor SolidFire for $870 million.[11] with its Active IQ software available for end users as web-based GUI service for monitoring and prediction of storage systems performance and availability.
In May 2018 NetApp announced its first End to End NVMe array called All Flash FAS A800 with release of ONTAP 9.4 software[12]. NetApp claims over 1.3 million IOPS at 500 microseconds per high-availability pair; Read throughput of up to 300GBps (Giga Byte per second) per all-flash 24 node cluster and 50% higher IOPS and up to 34% lower latency by upgrading previous model A700 with ONTAP 9.4[13].
Competition
NetApp competes in the computer data storage hardware industry.[14] In 2009, NetApp ranked second in market capitalization in its industry behind EMC Corporation, now Dell EMC, and ahead of Seagate Technology, Western Digital, Brocade, Imation, and Quantum.[15] In total revenue of 2009, NetApp ranked behind EMC, Seagate, Western Digital, and ahead of Imation, Brocade, Xyratex, and Hutchinson Technology.[16] According to a 2014 IDC report, NetApp ranked second in the network storage industry "Big 5's list", behind EMC(DELL), and ahead of IBM, HP and Hitachi.[17]. According to Gartner’s 2018 Magic Quadrant for Solid-State Arrays NetApp named a leader, behind with only Pure Storage Systems.
Products
NetApp's OnCommand management software controls and automates data-storage.[18]. ActiveIQ comes to NetApp with the acquisition of SolidFire. ActiveIQ is SaaS portal with built-in monitoring, prediction, recommendations for optimizing configurations and performance for NetApp storage systems based on machine-learning capabilities and artificial intelligence. Later ONTAP Analytics and Telemetry Service (OATS) product which can be installed in AWS cloud and on-premise was renamed to Active IQ Performance Analytics Services (ActiveIQ PAS).
NetApp FAS and AFF

NetApp's FAS (Fabric-Attached Storage) and AFF (All-Flash FAS) often called filers which serve as the company's flagship products. Such a product is made up of a storage controller (historically referred to as a "filer"), and one or more enclosures of hard disks, known as shelves. In entry-level systems, the drives may be physically located in the storage controller itself.
In the early 1990s, NetApp's storage systems initially offered NFS and SMB protocols based on standard local area networks (LANs), whereas block storage consolidation required storage area networks (SANs) implemented with the Fibre Channel (FC) protocol.
In 2002, in an attempt to increase market share, NetApp added block-storage access as well, supporting the Fiber Channel and iSCSI protocols. As of 2016 NetApp systems support Fiber Channel, iSCSI, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and the FC-NVMe protocol.
ONTAP
The filers use NetApp's proprietary operating system called Data ONTAP, later renamed to ONTAP which includes code from Berkeley Net/2 BSD Unix, Spinnaker Networks technology and other operating systems.[19] There are three ONTAP platforms: FAS/AFF systems, software on commodity servers (ONTAP Select) as virtual machine or in the cloud (Cloud Volumes ONTAP). All ONTAP systems using WAFL file system which provide basis for snapshots and other snapshot-based and data protection technologies.
Cloud Backup
Previously known as Riverbed SteelStore after acquired by NetApp the product renamed to AltaVault and then to Cloud Backup. Cloud Backup is available in three forms: as a hardware appliance, virtual appliance, and cloud appliance. Data placed on NAS share on Cloud Backup deduplicated, compressed, encrypted and transferred with Object Protocols to object storage systems like Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage or StorageGRID; thus Cloud Backup appears as a transparent gateway for archiving data to a private or public cloud. There are two modes of Cloud Backup operation: with local caching or without. Cloud Backup systems could accept SnapMirror replication from ONTAP systems.
SolidFire
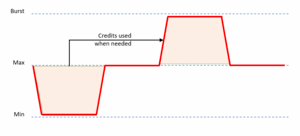
SolidFire storage system uses OS called NetApp Element Software (formally SolidFire Element OS) based on Linux and designed for SSD and scale-out architecture with the ability to expand up to 100 nodes and provide access to data through SAN protocols iSCSI natively and Fiber Channel with two gateway nodes. Newer versions of SF node H610S and Element SW will not support FC. SolidFire uses iSCSI login redirection to distribute reads and writes across the cluster.[20] This architecture does not have disk shelves like traditional storage systems and expands with adding nodes to the cluster. Each node has pre-installed SSD drives. Each node can have only one type of SSD drives with the same capacity. Each SolidFire cluster can have a mix of different node models & generations. Element X uses the replication factor of 2, where blocks of data spread across the cluster which has no performance impact but require more space in contrary to Erasure Codding technology. Such architecture allows users to expand performance and capacity separately as needed. Also, SolidFire has the ability to set three types of QoS for its LUNs: minimum, maximum and burst. Burst is used as credits which were not used by the LUN while it was not received its maximums. Element X available as software-only on commodity servers. SolidFire systems using S3 protocol could backup data to an Object storage systems like StorageGRID. SolidFire could replicate data with SnapMirror protocol to ONTAP systems.
HCI
NetApp Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is based on commodity blade servers, NetApp Element software and VMware vSphere. NetApp HCI includes web-based GUI with installation wizard called NetApp Deployment Engine (NDE) for configuring vCenter, IP addresses, login & password, and storage nodes, install NetApp Element plugin in vCenter to manage storage and configure NetApp HCI in about 30 minutes according to NetApp.[21] NetApp HCI different than conventional HCI designs because have dedicated storage nodes, while other HCI systems like Nutanix or Dell EMC VxRail or vSAN do not have dedicated storage nodes and utilizing disk drives installed in each server. Dedicated storage nodes allow to grow or decrease storage capacity and performance separately from computing server nodes. Minimum NetApp HCI configuration requires two computing blade server nodes and additionally Element software requires a minimum of 4 storage nodes. Each storage node use drive set consists of 6 SSD drives directly connected to a dedicated storage node and installed in front of the blade chassis, all drives in a set must be same capacity. Each node either storage or computing server is one rack unit half-width, so minimum NetApp HCI configuration consumes four rack units with six used blade server slots and two empty slots for expansion. Each storage and computing blade nodes have 25 Gigabit Ethernet ports which could be used as 10Gbit/s ports and dedicated 1Gb ports for management purposes. There are three types of computing nodes differentiate from each other with CPU power and memory capacity. Though there are three types of storage nodes, differentiate from each other with SSD capacity. It is possible to intermix any computing and storage nodes in a NetApp HCI installation, though with storage nodes it is required to have the minimum of 2 with the same capacity. It is also possible to use NetApp HCI with other software then VMware vSphere. Network switches not included in NetApp HCI and must be bought separately from third parties, while all other hardware components must be bought from NetApp. ONTAP Select available as SDS on NetApp HCI for customers interested in NAS protocols. Self-Service portal allows automating common provisioning and management tasks without involving the IT team. NetApp Kuberneties Service will support NetApp HCI with the acquisition of Stackpoint.
E-Series


Previously known as LSI Engenio after NetApp acquisition the product renamed to NetApp E-Series. It is a general purpose enterprise storage system with two controllers for SAN protocols such as Fibre Channel, iSCSI, SAS and InfiniBand (includes SRP, iSER, and NVMe over Fabrics protocol). NetApp E-Series platform uses proprietary OS SANtricity and proprietary RAID called Dynamic Disk Pool (DDP) alongside with traditional RAIDs like RAID 10, RAID 6, RAID 5 etc. In DDP pool each D-Stripe works similar to traditional RAID-4 and RAID-6 but on block level instead of entire disk level therefore have no dedicated parity drives. DDP compare to traditional RAID groups restores data from lost disk drive to multiple drives which provide few times faster reconstruction time[22] while traditional RAIDs restores lost disk drive to a dedicated parity drive. Starting with SANtricity 11.50 E-Series systems EF570 and E5700 suport NVMe over Ethernet (RoCE).
StorageGRID
Originally StorageGRID is a purpose-built proprietary storage system based on NetApp's E-Series systems which provide access to data via object IP-based protocols like S3 and OpenStack Swift, later on, also available as software-only as virtual machine or docker container package. A node in a StorageGRID cluster is a virtual machine or docker container. StorageGRID is geo-dispersed namespace clustered storage system, also known as "the grid", with an ability to make and store multiple copies (replicas) of objects (also known as Replication Factor) or in Erasure Coding (EC) manner among cluster storage nodes with object granularity based on configured policies for data availability and durability purposes. StorageGRID cluster can contain a mix of a different type (virtual machines, containers & physical appliances), performance, capacity and media, and doesn't have to be perfectly symmetrical by design, and can span up to 16 geographically distributed data centers around the world. StorageGRID EC capable of streaming chunks of data or bite range reads, instead of delivering entire object also known as all or nothing. All the objects could be accessed through any storage node in a StorageGRID cluster regardless of where they physically located. StorageGRID provides integration with Amazon's S3 service which can be used as Archive Level for objects or as a party which accepting replica from StorageGRID. StorageGRID stores metadata separately from the objects and allows users to configure data Life Cycle Management (ILM) policies on a per-object level to automatically satisfy and confirm changes in the cluster once changes introduced to the cluster like the cost of network usage, storage media usage changes a node was added or removed, etc. For example, it is possible to configure the system to move each new object to the fastest media and store 3 replicas each on a separate node; in 90 days remove one replica (so only 2 copies will be stored), and as for objects which wasn't assessed for few years to move them to cheapest storage media or if there will be added new storage node with the cheapest storage media to the cluster, those objects will be moved there automatically and then remove all the replicas of those objects and create Erasure Codding instead. It is also possible to configure the system to make copies or move objects automatically to those storage nodes where they requested the most. In version 11 StorageGRID start to support CloudMirror functionality to copy data from StorageGRID system to Amazon S3 storage. StorageGRID can issue Event Notifications for events occurring on premises to AWS SNS to build event-driven pipelines using on-premises and cloud resources. CloudMirror does not generate additional fees for Inbound Data Transfer with Amazon S3 storage, but only fees for storage space consumed in Amazon S3 storage. Since all the data already available on StorageGRID system does not support CloudMirror replication back, and there is no need for it to copy data back thus no Outbound Data Transfer fees from S3 storage applied. Company Bycast developed StorageGRID and acquired by NetApp in 2010. StorageGRID is also available as a software-only system on commodity servers. ONTAP, Cloud Backup, SANtricity, and Element X can replicate data to StorageGRID systems. Minimum StorageGRID cluster requirements: 2 admin nodes, 3 storage nodes and optionally gateway nodes (usually at least 2), so all of those nodes (virtual machines or containers) can be placed on at least 3 physical servers in SDS deployment; or 3 physical NetApp appliances for storage nodes and 2 servers for the rest of the nodes.
Converged Infrastructure
FlexPod, nFlex and ONTAP AI are commercial names for Converged Infrastructure (CI). Converged Infrastructures are joint products of a few vendors and consists from 3 main hardware components: computing servers, switches (in some cases switches are not necessary) and storage systems. FlexPod based on Cisco Servers and Cisco Nexus switches while nFlex based on Fujitsu Servers with Extreme Networks switching, those CI are using NetApp Storage systems. Converged Infrastructures have tested and validated design configurations from vendors available to end users and typically include popular infrastructure software like Docker Enterprise Edition (EE), Red Hat OpenStack Platform, VMware vSphere, Microsoft Servers and Hyper-V, SQL, Exchange, Oracle VM and Oracle DB, Citrix Xen, KVM, OpenStack, SAP HANA etc. and might include self-service portals PaaS or IaaS like Cisco UCS Director (UCSD) or others. FlexPod, nFlex and ONTAP AI allow an end user to modify validated design and add or remove some of the components of the Converged Infrastructure while not all of the other Converged Infrastructures from competitors allows modification.
FlexPod
There are few FlexPod types: FlexPod Datacenter, FlexPod Select, FlexPod Express (Small, Medium, Large and UCS-managed), FlexPod SF. FlexPod Datacenter usually using Nexus switches like 5000, 7000 & 9000; Cisco UCS Blade Servers; Mid-Range or High-End NetApp FAS or AFF systems. FlexPod Select often used with BigData framework software like Hortonworks & Cloudera, the architecture using Cisco UCS Rack Servers with direct attached NetApp E-Series and in some configurations in addition to that include Low-End FAS systems & Cisco Switches. FlexPod Express usually have Low-End NetApp FAS/AFF systems; Small, Medium, Large using Cisco UCS rack servers with Nexus 3000 switches while UCS-managed FlexPod Express using Cisco Blade servers, may add rack servers and might include switches from Cisco or other vendors in the architecture. FlexPod SF has in its architecture Nexus 9000 switches, Cisco UCS Blade servers and NetApp SolidFier storage based on Cisco UCS rack servers. Cisco UCS Director used as the orchestrator for FlexPod for a self-service portal, workflow automation and billing platform to build PaaS & IaaS. FlexPod systems supported under the cooperative center of competence. FlexPod Datacenter has the biggest variety of designed and validated by Cisco and NetApp architectures and applications including:
- Microsoft: SQL, Hyper-V, Exchange, SharePoint
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack, VMware vSphere, Citrix XenDesktop/XenApp, Docker Datacenter for Container Management
- IBM Cloud Private, Cisco Hybrid Cloud with Cisco CloudCenter, Microsoft Private Cloud, Citrix CloudPlatform,
- SAP, Oracle Database, Oracle RAC on Oracle Linux, Oracle RAC on Oracle VM
FlexPod types:
- FlexPod Express (Small, Medium, Large and UCS-managed)
- FlexPod Datacenter
- FlexPod SF
- FlexPod Select
nFlex
Is Converged infrastructure architecture with next key components: NetApp FAS/AFF systems, Extream Network data center switches and Fujitsu Primergy servers. nFlex available with FUJITSU Software Enterprise Service Catalog Manager which provides a self-service portal for enterprises and service providers to automate the delivery of their software services, infrastructure services, or platform services to their employees and customers.
ONTAP AI
Converged infrastructure solution based on Cisco Nexus 3000 switches with 100Gbps ports, NetApp AFF storage systems, Nvidia DGX supercomputer servers interconnected by RDMA over RoCE, and developed for Deep Learning based on Docker containers with NetApp Docker Plugin Trident. With SnapMirror ONTAP AI solution can deliver data between edge computing, on-prem & the cloud as part of Data Fabric vision. ONTAP AI tested & validated for use with NFS & FlexGroup technologies. Combined technical support provided to the customers to all the architecture components.
OnCommand Insight
OnCommand Insight (OCI) is data center management software, capacity management, infrastructure analytics, centralized view into historical trends to forecast performance and capacity requirements and workload placement. OCI works with all NetApp storage systems and with competitor storage systems and in public cloud. Licensed server-based software.
Memory Accelerated Data
NetApp MAX Data for short. MAX Data product is not available on the market yet and comes from Acquisition of Plexistor company in May of 2017. Plexistor was founded in 2013. MAX Data according to NetApp[23] will use POSIX compatible NetApp Memory Accelerated File System (the internal name is M1FS) which will be installed on hosts to utilize ultra-low latency with persistent memory such as the Intel and Micron 3D XPoint architecture. MAX FS is Persistent Memory based Filesystem (PM-based FS) which doesn't require application modification but also can be Direct Access enabled File system (DAX-enabled FS) for applications with optimization for Persistent Memory using SPDK. DAX is the mechanism that enables direct access to files stored in persistent memory arrays without the need to copy the data through the page cache[24]. MAX FS based on ZUFS (Zero-copy User-mode File System) interface for user space file system, in comparison to filesystems like NTFS based on FUSE, or XFS & EXT4 directly connected to vfs and therefore each FS require its own kernel module. ZUFS operating in Linux userspace and consisting out of two modules called zuf (Zu Feeder) & zus (Zu Server) available as OpenSource; zuf is a kernel to userspace bridge. MAX Data is NUMA aware, byte addressable near memory latency (3-4 microseconds), optimized for random I/O, optimized for persistent memory and as FUSE-based filesystems does not have page caching. MAX Data will be integrated with NetApp ONTAP as part of Data Fabric vision. Currently, MAX Data works with SAN devices on the back end, but NetApp considering to add NAS as well, and been tested MAX Data with SDS instances of ONTAP i.e. ONTAP Select and NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP according to Tech ONTAP podcast 154 in SoundCloud. MAX Data provides persistent memory capabilities and include data protection capability like snapshots, High Availability, cloning, and data tiering found as a key functionality by enterprise companies running In-memory processing applications.
Cloud Business
Cloud Central is web-based GUI interface which provides multi-cloud application orchestration layer and single pane of glass based on Qstack for NetApp's cloud products like Cloud Volumes Service, Cloud Sync, Cloud Insights, Cloud Volumes ONTAP, SaaS Backup in multiple public cloud providers. NetApp offers some of its original or modified products as part of its Cloud portfolio alongside with new cloud-native products. For example, Cloud Volumes ONTAP, NPS are re-purposed for use in the cloud, while others are cloud-native.
Cloud Volumes ONTAP
Formally ONTAP Cloud. Cloud Volumes ONTAP is software defined (SDS) version of ONTAP available in some public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and IBM Cloud and named Cloud Volumes ONTAP. Cloud Volumes ONTAP is a virtual machine which is using commodity equipment and running ONTAP software as a service.
Cloud Volumes Service
Is service in Amazon AWS & Google GCP public cloud provider based on NetApp All-Flash FAS systems and ONTAP software, therefore will be able to synchronize data between cloud and on-premise NetApp systems. NetApp claims they will provide similar to AFF systems persistent performance SLA and also claims data could be moved in a way that will not generate huge ingress and egress charges using SnapMirror technology. Cloud Volumes Service will provide high availability for data with next protocols which can be consumed by containers: NFS v3, NFS v4, and SMB. Cloud Volumes Service support NetApp's Snapshots. Current maximum for Cloud Volumes Service is 100TB. In the Azure cloud currently only NFS available and called Azure NetApp Files. Cloud Volumes Service available as service in corresponding public cloud providers directly through their Marketplaces. NetApp claims them as reliable enterprise NAS services as in on-premises enterprise-grade data storage with predictable performance, management, security, and protection. NAS integrates with some other services in the public cloud providers. RESTful APIs will be available to automate NAS storage services such as provisioning, snapshots, and SnapMirror. As of January 2018 services for both public AWS and Azure in the preview stage.
NetApp Private Storage
NetApp Private Storage (NPS) is based on Equinix partner provided colocation service in its data centers for NetApp Storage Systems with 10 Gbit/s direct connection to public cloud providers like Azure and AWS etc. Some of Equinix data centers located in the same building with public cloud providers thus network connectivity to dedicated storage system is the same as with a storage service in a public cloud provider. Such configuration provide better performance compare to storage service in public cloud provider based on sharable commodity hardware and help to fit some companies with regulatory compliances which require strict data placement, security, availability and disaster recovery which public cloud provider could not provide. NPS storage could be connected to few cloud providers or on-premise infrastructure, thus in case of switching between clouds does not require data migration between them.
Kubernetes Service
NetApp Kubernetes Service (NKS) came from an acquisition of stackpoint.io it is a cloud-based SaaS application to deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters across cloud providers like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and NetApp HCI. Kubernetes Service used for: creating and managing kubernetes clusters, managing access control, setting up and managing kubernetes clusters across clouds, creating Helm charts and deploying them from a GitHub repository. Kubernetes Service has features like: load balancing, applications migration across kubernetes clusters, load spreading across various clusters, Istio Traffic Management, Persistent Volume with NetApp Trident plugin for Docker & Kubernetes upgrades and HTTP API for automation.
SaaS Backup
NetApp SaaS Backup (Previously Cloud Control) is back up and recovery service for SaaS Microsoft Office 365 and Salesforce which provide extended, granular and custom retention capabilities of backup and recovery process compare to native cloud backup. NetApp planning to extend SaaS Backup and recovery service for Google Apps, Slack and ServiceNow.
Cloud Sync
Cloud Sync is service for synchronizing any NAS storage system with an Object Storage like Amazon S3 or NetApp Storage GRID using an object protocol.
Cloud Insights
SaaS application for monitoring infrastructure application stack for customers consuming cloud resources and also build for the dynamic nature of microservices and web-scale infrastructures. Cloud Insights uses similar to OnCommand Insight front-end API but different technology on the back-end. Cloud Insights available as a preview and will have three editions: Free, Standart and Pro. The free edition will be able to monitor NetApp storages & services using NetApp Active IQ with no cost.
Data Fabric
Often referred as "Data Fabric Story." Variety of integrations between NetApp's products and ways of data mobility considered by NetApp as Data Fabric vision for the future of data management. Data Fabric defines the NetApp technology architecture for hybrid cloud and provides next features: SnapMirror replication from SolidFire to ONTAP; SnapMirror replication from ONTAP to Cloud Backup; FabricPool tiering feature for de-staging cold data from ONTAP to StorageGRID or Amazon S3; Volume Encryption with FabricPool provide secure data storage and secure over the wire transfer of enterprise data in a cloud provider; SnapMirror between FAS, AFF, ONTAP Select and Cloud Volumes ONTAP; Archiving and DR to public cloud; CloudMirror feature in StorageGRID replicates from on-premise object storage to Amazon S3 storage and tigers some actions in AWS Cloud; SolidFire backup to StorageGRID or Amazon S3; Cloud Backup archiving to variety of object storage systems (including StorageGRID) or many cloud providers; CloudSync is replication of NAS data to object format and back; replication to Cloud Volumes Service; Data backup to on-premise storage from SaaS Backup; SANtricity Cloud Connector for block-based backup, copy, and restore of E-Series volumes to an S3, etc. Other features as part of Data Fabric vision approach committed by NetApp to be implemented in future, like SnapMirror between ONTAP and E-Series; SnapCenter capabilities to expand to include SolidFire storage endpoints, NetApp MAX Data host filesystem tiering to and from ONTAP storage systems connected with NVMeoF, etc.
Software Integrations
NetApp products could be integrated with a variety of software products which gives some additional flexibility, features and built-in provisioning and self-service storage capabilities. Most of the integrations are done for ONTAP systems.
Automation
NetApp provides a variety of automation services directly to its products with HTTP protocol or through middle-ware software.
Docker
NetApp Trident software provides a persistent volume plugin for Docker containers with both orchestrators Kubernetes and Swarm and supports ONTAP, SolidFire, E-Series, and in Cloud NetApp Kubernetes Service. Also, NetApp with Cisco sells CI architectures which incorporate Trident plugin: FlexPod Datacenter with Docker Enterprise Edition and ONTAP AI.
CI/CD
NetApp Jenkins Framework provides integration with ONTAP storage for DevOps, accelerating development with automation operations like provisioning and data-set cloning for test and development and leverage ONTAP for version control, create and delete checkpoints etc. Jenkins also integrate with NetApp Service Level Manager software which provides RESTful API for guarantee level of storage performance. Apprenda and CloudBees integrate and accelerate DevOps through Docker persistent volume plugin and Jenkins Framework integration. Apprenda could be integrated with OpenStack running on top of FlexPod.
Backup and Recovery
Veeam, CommVault, and Veritas have integrations with ONTAP, SolidFire, Cloud Backup and E-Series leveraging storage capabilities like snapshots and cloning capabilities for testing backup copies and SnapMirror for Backup and Recovery (B&R), Disaster Recovery (DR) and Data Archiving for improving restore time and number of recovery points (see RPO/RTO). Cloud Backup integrates with nearly all B&R products for archiving capabilities since it is represented as ordinary NAS share for B&R software. Backup and recovery software from competitor vendors like IBM Spectrum Protect, EMC NetWorker, HP Data Protector, Dell vRanger, Acronis Backup etc. also have some level of integrations with NetApp storage systems.
Enterprise Applications
NetApp systems can integrate with enterprise applications for backup purposes but also for a verity of other additional features like cloning, provisioning and other self-service storage features and flexibilities. Oracle DB can be connected using direct NFS (dNFS) client build inside database app which will provide network performance, resiliency, load balancing for NFS protocol with ONTAP systems. Oracle DB, Microsoft SQL, IBM DB2, MySQL, Mongo DB, SAP HANA, MS Exchange, VMware vSphere, Citrix Xen, KVM integrate with NetApp systems for provisioning, cloning and additional backup and recovery build in capabilities like SnapShots, SnapVault and SnapMirror with variety of B&R software including NetApp's SnapCenter and SnapCreator. Integration with such applications provides the ability to the instant cloning of data sets for test and development and self-service restore capabilities for application administrators and for end users. NetApp ONTAP systems could be integrated with VMware vSphere using NFS plugin for ESXi hosts which offloads some of the storage operations on the storage system. With VASA protocol NetApp systems can integrate for VMware VVol technology. Similarly to NFS plugin for ESXi, ONTAP systems support ODX functionality with Windows systems with file and block-based protocols for offloading data copying or moving processes to the storage system.
OpenStack
NetApp systems have integration with such open source projects as OpenStack Cinder for Block storage (SolidFire, ONTAP, E-Series, OnCommand Insight, Cloud Backup), OpenStack Manila for Shared file system (ONTAP, OnCommand Insight), Docker persistent volumes through Trident plugin (SolidFire, ONTAP, E-Series) and others.
OEM
IBM use to OEM NetApp FAS systems under its own brand known as IBM N-series and this partnership ended 29 May 2014. Dell OEM NetApp E-Series under its own name PowerVault MD. September 13, 2018, Lenovo and NetApp announced its technology partnership, so Lenovo OEM Netapp products under its own name: Lenovo ThinkSystem DE (using NetApp's EF & E-Series array technology), and ThinkSystem DM uses ONTAP software with Lenovo servers and supports FC-NVMe (analog for NetApp FAS & AFF systems).
Reception
Controversy
Syrian surveillance
In November 2011, during the 2011 Syrian uprising, NetApp was named as one of several companies whose products were being used in the Syrian government crackdown. The equipment was allegedly sold to the Syrians by an authorized NetApp reseller.[25]
On April 7, 2014, NetApp was notified by the US Department of Commerce "that it had completed its review of this matter and determined that NetApp had not violated the U.S. export laws", and that the file on the matter had been closed.[26]
Legal dispute with Sun Microsystems
In September 2007, NetApp started proceedings against Sun Microsystems, claiming that the ZFS File System developed by Sun infringed its patents.[27] The following month, Sun announced plans to countersue based on alleged misuse by NetApp of Sun's own patented technology.[28] Several of NetApp's patent claims were rejected on the basis of prior art after re-examination by the United States Patent and Trademark Office.[29] On September 9, 2010, NetApp announced an agreement with Oracle Corporation (the new owner of Sun Microsystems) to dismiss the suits.[30]
Accolades
NetApp was listed amongst Silicon Valley Top 25 Corporate Philanthropists in 2013.[31]
See also
- NetApp filer
- NetApp
- ONTAP Operation System, used in NetApp storage systems
- Write Anywhere File Layout (WAFL), used in ONTAP storage systems
- Team NetApp
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "NetApp Reports Fourth Quarter and Fiscal Year 2015 Results" (PDF). NetApp. 24 April 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- 1 2 "FAQs". NetApp. Retrieved 25 August 2016.
- ↑ "NetApp". Fortune 500. Time Inc. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Corporate brief". NetApp. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
- ↑ "Executive Bios". NetApp. 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-13.
- ↑ "Michael Malcolm Resigns as Chairman of the Board of CacheFlow to Focus on New Start-Up Opportunity". Business Wire. 13 November 2000. Retrieved 2009-04-14.
- ↑ "Sequoia Capital funds NetApp".
- ↑ Gagliordi, Natalie (27 October 2014). "NetApp buys Riverbed Technology's Steelstore business". ZDNet. Retrieved 22 March 2016.
- ↑ Adshead, Antony (18 May 2015). "NetApp launches AltaVault hybrid cloud backup appliance family". ComputerWeekly. Retrieved 22 March 2016.
- ↑ "NetApp Announces Changes to Executive Leadership Team and Board of Directors". NetApp. 2015-06-01. Retrieved 2015-06-01.
- ↑ Jordan Novet (December 21, 2015). "NetApp acquires flash storage vendor SolidFire for $870M". Venture Beat. Retrieved November 17, 2016.
- ↑ Joel Reich (8 May 2018). "The Future Is Now: AI-Ready, Cloud-Connected, NVMe All-Flash Storage". NetApp Blog. Archived from the original on 2018-05-08. Retrieved 2 June 2018. (in English)
- ↑ Demartek (8 May 2018). "Performance Benefits of NVMe™ over Fibre Channel – A New, Parallel, Efficient Protocol" (PDF). Demartek.com©. Retrieved 2 June 2018. (in English)
- ↑ "Industry Center - Data Storage Devices Overview". Yahoo! Finance. 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-14.
- ↑ "Industry Center - Data Storage Devices, Leaders in Market Capitalization". Yahoo! Finance. 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-14.
- ↑ "Industry Center - Data Storage Devices, Leaders in Total Revenue (ttm)". Yahoo! Finance. 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-14.
- ↑ "How EMC Lines Up Against NetApp, HP, IBM, Hitachi In Storage Systems Market". Forbes.
- ↑
Raj, Pethuru; Raman, Anupama; Nagaraj, Dhivya; Duggirala, Siddhartha (2015). High-Performance Big-Data Analytics: Computing Systems and Approaches. Computer Communications and Networks. Springer. p. 242. ISBN 9783319207445. Retrieved 2016-02-09.
NetApp OnCommand management software and Cisco Unified Computing System Manager tools help you optimize your server and network environment, handling hundreds of resources for thousands of virtual machines. OnCommand controls and automates your data storage infrastructure.
- ↑ "Is Data ONTAP Based On UNIX?". 2007-04-27. Archived from the original on 2013-01-30. Retrieved 2016-06-11.
- ↑ Andy Banta (19 May 2016). "Why SolidFire Uses iSCSI Storage Protocol". NetApp. Archived from the original (url) on 2017-11-18. Retrieved 12 December 2017. (in English)
- ↑ John Rollason (5 June 2017). "Introducing NetApp Enterprise-Scale HCI: The Next Generation of Hyper-Converged Infrastructure". NetApp. Archived from the original (url) on 2018-01-23. Retrieved 13 January 2018. (in English)
- ↑ Todd Edwards (1 December 2017). "TR-4652 SANtricity OS 11.40.1 Dynamic Disk Pools – Feature Description and Best Practices" (url). NetApp. Retrieved 9 February 2018. (in English)
- ↑ Andy Grimes (7 July 2018). "An Update on the Plexistor Acquisition: Introducing NetApp Memory Accelerated Data". NetApp Blog. Archived from the original (url) on 2018-07-27. Retrieved 27 July 2018. (in English)
- ↑ Jonathan Corbet (27 March 2017). "The future of DAX" (url). LWN.net. Retrieved 20 September 2018. (in English)
- ↑ "Companies That Aid Syria Crackdown Deserve Sanctions' Slap: View". Businessweek. 2011-11-14. Archived from the original on 2013-05-02. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ "NetApp response to allegations of potential use of equipment in Syria". NetApp. 2014-04-09. Retrieved 2014-05-23.
- ↑ "NetApp files patent suit against Sun". September 5, 2007.
- ↑ "Sun plans to countersue NetApp". October 24, 2007.
- ↑ "NetApp Patent Lawsuit Against ZFS Open Source Technology". Archived from the original on 2010-11-09. Retrieved August 13, 2010.
- ↑ "Oracle, NetApp agree to settle ZFS patent litigation". September 10, 2010. Retrieved September 10, 2010.
- ↑ "Corporate philanthropy: Meet Silicon Valley's 25 most generous companies".
Further reading
- "Serving up storage solutions: Network Appliance CEO Dan Warmenhoven puts data in its place". Communication News: 22–24. August 2001. ISSN 0010-3632. Archived from the original on 2001-08-09.
External links
- Business data for NetApp: Google Finance
- Yahoo! Finance
- Reuters
- SEC filings