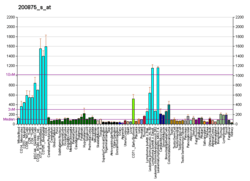
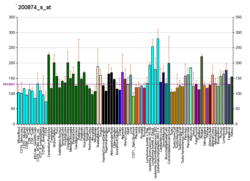
NOL5A
Nucleolar protein 56 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOP56 gene.[5][6]
Nop56p is a yeast nucleolar protein that is part of a complex with the nucleolar proteins Nop58p and fibrillarin. Nop56p is required for assembly of the 60S ribosomal subunit and is involved in pre-rRNA processing. The protein encoded by this gene is similar in sequence to Nop56p and is also found in the nucleolus. Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of most of them have not been determined.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000101361 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027405 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Gautier T, Berges T, Tollervey D, Hurt E (Dec 1997). "Nucleolar KKE/D repeat proteins Nop56p and Nop58p interact with Nop1p and are required for ribosome biogenesis". Mol Cell Biol. 17 (12): 7088–98. PMC 232565. PMID 9372940.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: NOL5A nucleolar protein 5A (56kDa with KKE/D repeat)".
Further reading
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. 414 (6866): 865–71. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, et al. (2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Curr. Biol. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298.
- Watkins NJ, Dickmanns A, Lührmann R (2003). "Conserved stem II of the box C/D motif is essential for nucleolar localization and is required, along with the 15.5K protein, for the hierarchical assembly of the box C/D snoRNP". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (23): 8342–52. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.23.8342-8352.2002. PMC 134055. PMID 12417735.
- Scherl A, Couté Y, Déon C, et al. (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (11): 4100–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC 133617. PMID 12429849.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Hayano T, Yanagida M, Yamauchi Y, et al. (2003). "Proteomic analysis of human Nop56p-associated pre-ribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes. Possible link between Nop56p and the nucleolar protein treacle responsible for Treacher Collins syndrome". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (36): 34309–19. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304304200. PMID 12777385.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Hassel S, Eichner A, Yakymovych M, et al. (2004). "Proteins associated with type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMPR-II) and identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry". Proteomics. 4 (5): 1346–58. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300770. PMID 15188402.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Watkins NJ, Lemm I, Ingelfinger D, et al. (2005). "Assembly and maturation of the U3 snoRNP in the nucleoplasm in a large dynamic multiprotein complex". Mol. Cell. 16 (5): 789–98. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.012. PMID 15574333.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, et al. (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.