NGC 4540
| NGC 4540 | |
|---|---|
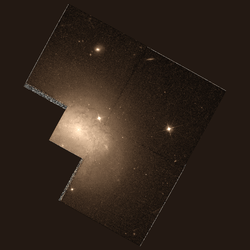 Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 4540. | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Coma Berenices |
| Right ascension | 12h 34m 50.9s[1] |
| Declination | 15° 33′ 06″[1] |
| Redshift | 0.004306[1] |
| Helio radial velocity | 1291 km/s[1] |
| Distance | 64 Mly[2] |
| Group or cluster | Virgo Cluster |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.44[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SAB(rs)cd, Sy1[1] |
| Size | ~39,120 ly (estimated)[1] |
| Apparent size (V) | 1.9 x 1.5[1] |
| Other designations | |
| PGC 41876, UGC 7742, IRAS 12323+1549, MCG 3-32-74, CGCG 99-93, VCC 1588[1] | |
NGC 4540 is a spiral galaxy with type 1 seyfert activity[3] located about 64 million light-years away[4] in the constellation Coma Berenices.[5] NGC 4540 was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on March 21, 1784[6] and is member of the Virgo Cluster.[7][8]
See also
External links
- NGC 4540 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 4540. Retrieved 2018-01-04.
- ↑ "parsecs to lightyears conversion". Retrieved 2017-09-30.
- ↑ Normandin, George P. "Galaxies IC 3528 and NGC 4540, Supernova 2001z". www.kopernik.org. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
- ↑ "Your NED Search Results". ned.ipac.caltech.edu. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
- ↑ "Revised NGC Data for NGC 4540". spider.seds.org. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
- ↑ "New General Catalog Objects: NGC 4500 - 4549". cseligman.com. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
- ↑ "The Virgo Cluster". www.atlasoftheuniverse.com. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
- ↑ "Detailed Object Classifications". ned.ipac.caltech.edu. Retrieved 2018-01-05.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.