Medina-class gunboat
.jpg) Spey | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Medina class |
| Builders: | Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company, Jarrow |
| Operators: |
|
| Preceded by: | Ant class |
| Succeeded by: | Bouncer class |
| Built: | 1876–1877 |
| In commission: | 1877–1923 |
| Completed: | 12 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Iron screw gunboat |
| Displacement: |
|
| Length: | 110 ft 0 in (33.5 m)[1] |
| Beam: | 34 ft 1 in (10.4 m)[1] |
| Draught: | 9 ft 6 in (2.9 m)[1] |
| Depth of hold: | 5 ft 6 in (1.7 m)[1] |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Sail plan: |
|
| Speed: | 9 1⁄2 kn (17.6 km/h) |
| Complement: | 51 |
| Armament: |
|
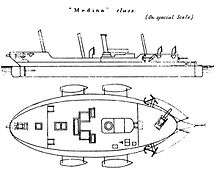
The Medina-class gunboat was a class of 12 Royal Navy Rendel (or "flat-iron") gunboats mounting three 6.3-inch guns, built between 1876 and 1877.[1] Flat-iron gunboats were normally built without masts or rigging, but the Medinas carried a full barquentine rig. Their robust iron hulls meant that they lingered on as diving tenders, barges and lighters, with five of them working into the 1920s. The hull of Medway lies in shallow water in Bermuda and is visible on satellite imagery.
Design
The Medina class were a development of the Rendel (or "flat-iron") gunboat, a series of small vessels with low freeboards which mounted a small number of relatively large guns. Although the Medinas were exceptionally provided with masts to extend their range and independence, in essence they were available for similar operations to their un-masted sisters; offensive action against shore defences. Their ungainly appearance led them to be described by the naval historian Antony Preston as "the most grotesque craft ever seen".[2] All 12 vessels of the class were built at Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company in Jarrow and were named after rivers. They were constructed entirely of iron and were fitted with an unusual bow rudder.[1]
Armament
As built, ships of the class mounted three 6.3-inch (160-mm) 64-pdr 64-cwt muzzle-loading rifles. By 1892 Trent had been fitted with a pair of 4.7-inch quick-firing guns.[3]
Propulsion
All the ships of the class were fitted with a pair of R and W Hawthorn 2-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engines of 60 nominal horsepower. They developed 310 indicated horsepower (230 kW), giving a speed of about 9 1⁄2 kn (17.6 km/h).[1]
Sail plan
All ships of the class were built with three masts[1] and a barquentine rig of sails. Surviving members of the class had their sailing rig replaced by a pair of pole masts in the 1890s.[3]
_(as_Pembroke_in_1900).jpg)
Operational lives
Some of the ships of the class were appointed as tenders to battleships as soon as they were built: Medina tender to Duke of Wellington and Medway to Excellent, the gunnery school at Portsmouth. Spey was fitted in 1900 with three 4.7-inch guns for service at the gunnery school.[4]
Dee and Don served in the Mediterranean in 1886 as part of an International squadron dominated by the Royal Navy. They both remained at Malta in various capacities for the rest of their lives.[5][6] Tay had her armament reduced to a single 9-pounder gun and by 1914 was a tender to HMS Vivid, the Royal Navy barracks at Devonport.[7] Esk and Tweed both served in Hong Kong in the 1890s, being sold there in the 1900s.[8][9]
In all cases the crews were not expected to live onboard their cramped ships when not at sea, with living space provided in accommodation hulks or the battleships to which the gunboats were tenders.
Ships
| Name | Ship Builder | Launched | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medina | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 3 August 1876 | Sold at Bermuda in 1904. |
| Medway | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 3 October 1876 | Sold at Bermuda in 1904. Sunk in St. George's harbour, her hull remains intact and can be seen breaking the water's surface at low tide. The ship is visible on satellite imagery at 32°22′32.7″N 64°41′13″W / 32.375750°N 64.68694°W[10] |
| Sabrina | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 3 October 1876 | Renamed Sabine as a diving tender in 1916, renamed Vivid in 1920 (or late 1919), sold to B Fryer, Sunderland in July 1922 |
| Spey | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 5 October 1876 | Deleted c.1915 and sold in 1923 |
| Tay | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 19 October 1876 | Sold to Stanlee Shipbreaking Company, Dover 22 October 1920 |
| Tees | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 19 October 1876 | Sold to Harris Brothers, Bristol 9 July 1907 |
| Dee | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 4 April 1877 | Used for torpedo instruction at Malta 1892–1902 and sold there on 10 July 1902 |
| Don | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 14 April 1877 | Used as a concrete barge at Malta 1906–08, converted to a lighter in 1911 and sold there in 1914 |
| Esk | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 28 April 1877 | Sold at Hong Kong in April 1903 |
| Slaney | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 28 April 1877 | Diving tender in 1906, sold to Thos W Ward, Grays 30 August 1919, and arrived there 10 October 1919, but listed until 1921 and finally moved to Rainham, Kent to be broken up on 3 January 1923 |
| Trent | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 23 August 1877 | Renamed Pembroke in September 1905, then Gannet in June 1917 as a diving tender. Sold to the Dover Shipbreaking Company on 21 February 1923 |
| Tweed | Palmers Shipbuilding & Iron Company, Jarrow | 23 August 1877 | Sold at Hong Kong on 21 November 1905 |
Legacy
The gunboats Dee and Don spent a number of years moored next to each other in Kalkara, Malta. This resulted in the Maltese expression id-di u d-do, which refers to two people who are frequently seen together.[11]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Medina class gunboat. |
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Winfield (2004) p.281
- ↑ Gunboat (2007) p.167
- 1 2 "HMS Trent at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-05-31.
- ↑ "HMS Spey at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ "HMS Dee at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ "HMS Don at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ "HMS Tay at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ "HMS Esk at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ "HMS Tweed at the Naval Database". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ↑ Nathan Richards; Calvin Mires; Joseph C. Hoyt; Peter Campbell. "Report of Maritime Archaeological Survey: The Myers Slip Vessel (Suspected Remains of HMS Medway), Bermuda, May 2008" (PDF). East Carolina University. Retrieved 2012-03-14.
- ↑ Spagnol, Michael (11 June 2017). "5 Kelmiet Bi Storja Kurjuża". Lovin Malta (in Maltese). Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- Winfield, Rif & Lyon, David (2004). The Sail and Steam Navy List: All the Ships of the Royal Navy 1815–1889. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-032-6. OCLC 52620555.
- Preston, Antony; Major, John (2007). Send a Gunboat: The Victorian Navy and Supremacy at Sea, 1854–1904 (2nd ed.). London: Conway. ISBN 978-0-85177-923-2.