Lysidine (nucleoside)
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-6-[4-amino-1-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-hydroxymethyloxolan-2-yl)-1H-pyrimidin-2-ylideneamino]hexanoic acid | |
| Other names
4-Amino-2-(N(6)-lysino)-1-ribofuranosylpyrimidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H25N5O6 | |
| Molar mass | 371.39 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lysidine is an uncommon nucleoside, rarely seen outside of tRNA. It is a derivative of cytidine in which the carbonyl is replaced by the amino acid lysine. The third position in the anti-codon of the Isoleucine-specific tRNA, is typically changed from a cytidine which would pair with guanosine to a lysidine which will base pair with adenosine. Uridine could not be used at this position even though it is a conventional partner for adenosine since it will also "wobble base pair" with guanosine. So lysidine allows better translation fidelity.[1][2]
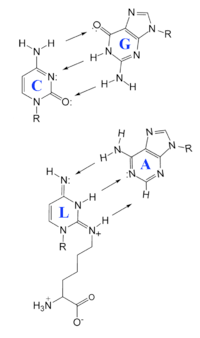 Lysidine base pairs with Adenosine in context of a Cytidine to Guanosine base pair. R = ribose. Arrows indicate hydrogen bonds going from hydrogens to bond acceptor. The notation for lysidine, L, is depicted above.
Lysidine base pairs with Adenosine in context of a Cytidine to Guanosine base pair. R = ribose. Arrows indicate hydrogen bonds going from hydrogens to bond acceptor. The notation for lysidine, L, is depicted above.
References
- ↑ Nakanishi K, Fukai S, Ikeuchi Y, et al. (May 2005). "Structural basis for lysidine formation by ATP pyrophosphatase accompanied by a lysine-specific loop and a tRNA-recognition domain". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (21): 7487–7492. doi:10.1073/pnas.0501003102. PMC 1140429. PMID 15894617.
- ↑ Salowe SP, Wiltsie J, Hawkins JC, Sonatore LM (Apr 10, 2009). "The Catalytic Flexibility of tRNAIle-lysidine Synthetase Can Generate Alternative tRNA Substrates for Isoleucyl-tRNA Synthetase". J Biol Chem. 284 (15): 9656–9662. doi:10.1074/jbc.M809013200. PMC 2665086. PMID 19233850.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.