Locomotives of New Zealand
Locomotives of New Zealand is a complete list of all locomotive classes that operate or have operated on New Zealand's national railway network. It does not include locomotives used on private industrial lines or bush tramways. KiwiRail operates 148 diesel-electric locomotives, 15 electric locomotives, 2 railcars and 82 shunting locomotives. There are also 10 diesel multiple units and 57 electric multiple units operated by Auckland Transport, and 83 electric multiple units operated by the Greater Wellington Regional Council. Additionally, there are diesel-electric and steam locomotives and railcars in working order owned by private companies or preservation societies.
All New Zealand's main-line locomotives are 1067 mm (3 foot 6 inch) gauge.
Classification details
Steam locomotives were originally categorised with just a single letter, such as the "F class". When a new class was built as an enhancement of an old class, the old class's letter was re-used, followed by a superscript upper-case letter. For example, the 1906 A class was followed by the AA and AB classes.
Diesel-electric and electric locomotive classifications originally consisted of an upper-case D or E respectively followed by a second and sometimes a third (sub-class) letter. The second and third letters are sometimes represented as smaller-sized upper case (for example, as seen on many locomotive cab-side number plates).
New classes were not always given the classification that alphabetically followed that of the previous class that had most recently been acquired. For example, the DJ class was followed by the DX class followed by the DF class. If an entire class had been withdrawn from service and the classification no longer in use, it was sometimes re-used; for example, two A classes exist, one from 1873 and one from 1906.
Traffic Monitoring System
Following the introduction of the computer-based Traffic Monitoring System (TMS) and consequent renumbering, classes were identified by the two upper-case letters with the first letter remaining D or E respectively and sub-classes being indicated by a third upper-case letter, such as DAA (DA modified for hump shunting), DAR (DA with rebuilt superstructure), DFT (DF with turbo-conversion), DXR (rebuilt DX) and so on. Most diesel-electric shunting locomotives have a three-letter classification with DS as the first two letters, following on from the original diesel-electric shunting class that was known simply as the DS class.
For electric locomotives the second letter generally referred to where the locomotive was based, such as EC in Christchurch, EO in Otira and EW in Wellington. The EM class in Wellington stands for Electric Motor and the ET stands for Electric Trailer. The DM class units were an exception to this.
Most railcars were classified RM (Rail Motor), and individual classes were known by alternate names such as the Vulcan railcars of the South Island and the Wairarapa railcars that ran over the Rimutaka Incline.
List of locomotive classes
Mainline Diesel locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | ||||||
 |
DA | DA | 86 - 996 | 1400 - 1545 | 146 | 1955 - 1967 | 1974 - 1989 | 1,060 kW (1,420 hp) | The largest locomotive number class in NZ, 85 were rebuilt as the DC class, five as DAA class and one as DAR class. |
| DB | DB | 1001 - 1180 | 1000 - 1016 | 17 | 1965 - 1966 | 1980 - 1989 | 705 kW (945 hp) | Ten were rebuilt as the DBR class. | |
 |
DBR | 1199 - 1295 | 10 | 1980 - 1982 | 2002 – 2017 | 705 kW (945 hp) | Rebuilt DB with a new cab, lower hood and new engine. | ||
 |
DC | DC | 4006 - 4951 | 1551 - 1599 | 85 | 1978 - 1983 | 1992 – present | 1,100 kW (1,500 hp) 1,230 kW (1,650 hp) | Rebuilt DA with a new cab and low hood and appears in two engine types, one with 12-645C engines and the other with 12-645E engines. |
| DCP | 4277 - 4945 | 17 | 2002 - 2009 | 2015–present | 1,230 kW (1,650 hp) | DC subclass originally built for passenger services, but now used for other uses. | |||
 |
DF (1954) | 1500 - 1510 (1954) 1300 - 1309 (1960) |
10 | 1954 | 1972 - 1975 | 1,120 kW (1,500 hp) | NZs first mainline diesel locomotive. | ||
| DF | DF (1979) | 6006 - 6317 | 1651 - 1670 | 30 | 1979 - 1981 | All rebuilt to DFTs | 1,230 kW (1,650 hp) | ||
 |
DFB | 7010 - 7348 | 19 | 2006–present | Still in use | 1,800 kW (2,400 hp) | Upgraded DFT class locomotive. | ||
| DFM | 7036 - 7226 | 3 | All reclassified as DFT internally | 1,800 kW (2,400 hp) | Upgraded DFT class locomotive. | ||||
 |
DFT | 7008 - 7348 | 30 | 1992 - 1997 | 2011–present | 1,800 kW (2,400 hp) | Rebuilt DF, with 18 later converted to DFBs. | ||
 |
DG | DG | 2007 - 2468 | 750 - 791 | 42 | 1955 - 1956 | 1983 | 560 kW (750 hp) | 11 were rebuilt from the 1956 DH class. |
| DH (1956) | 766, 772, 777 - 783 | 11 | 1956 | 1968 | 560 kW (750 hp) | All were later reclassified as DGs | |||
| DI | DI | 1808 - 1843 | 1100 - 1104 | 5 | 1966 | 1988 - 1989 | 755 kW (1,012 hp) | ||
 |
DJ | DJ | 3009 - 3689 | 1200 - 1263 | 64 | 1968 - 1969 | 1986 - 1991 | 672 kW (901 hp) | |
 |
DL | 9008 - 9515 | 48 | 2010–2015 | Still in use | 2,700 kW (3,600 hp) | |||
 |
DQ | 6007 -6036, 6324 - 6416 | 15 | 1996 - 1998 | 1998 - 2013 | 1,120 kW (1,500 hp) | Rebuilt QR class; originally from Queensland Railways. | ||
 |
DX | DX | 5016 - 5520 | 2600 - 2648 | 49 | 1972 - 1975 | All Rebuilt as DXC & DXB | 2,050 kW (2,750 hp) | Two rebuilt as DXR. |
 |
DXB | 5016 - 5166 & 5448 | 14 | still in use | 2,050 kW (2,750 hp) | Upgraded DX class. | |||
 |
DXC | 5172 - 5520 5039 | 32 | still in use | 2,050 kW (2,750 hp) | DX class upgraded for the Midland Line coal trains. | |||
| DXH | 0 | All rebuilt as DXB and DXC | 2,050 and 2,400 kW (2,750 and 3,220 hp) | Upgraded DX | |||||
 |
DXR | 8007, 8022 | 2 | 1993, 2006 | still in use | 2,420 kW (3,250 hp) | Rebuilt DX | ||
| QR | 2027 - 2102, 3032 | 25 | 1997 | 1999 | 1,120 kW (1,500 hp) | Originally from Queensland Railways; 15 rebuilt as the DQ class. | |||
Diesel shunting locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | ||||||
| DAA | DAA | 11 - 63 | 1400 - 1404, 1406 | 5 | 1971 | 1989 | 1,060 kW (1,420 hp) | DA class refitted for low speed running for heavy shunting at Te Rapa. | |
 |
DAR | 517 | 1 | 1989 | 2008 | 1,060 kW (1,420 hp) | DA class modified for shunting at Tasman Pulp and Paper. | ||
| DE | DE | 1308 - 1458 | 501 - 515 | 15 | 1952 | 1984 - 1989 | 490 kW (660 hp) | ||
 |
DH | DH | 2816 - 2868 | 900 - 905 | 6 | 1978 | Still in use | 672 kW (901 hp) | |
| DS | DS | 200-215 | 16 | 1949-1955 | 1978-1984 | ||||
| DSA | DSA | 1953-1967 | |||||||
| DSB | DSB | 1003-1290 | 300-327 | 28 | 1954-1967 | 1978-1988 | |||
 |
DSC | DSC | 2000 - 2759 | 400 - 469 | 70 | 1959 - 1967 | 1989–present | 315 kW (422 hp) | |
| DSG | 3005 - 3304 | 24 | 1981 - 1983 | still in use | 700 kW (940 hp) | Shunting locomotive. | |||
 |
DSJ | 4004 - 4060 | 5 | 1984 - 1985 | still in use | 350 kW (470 hp) | |||
 |
TR | TR | 90 | 1924-1978 | Six distinct build models of various power, wheel set and body. | ||||
 |
EB | 1809, 1815, 1821 | 3 | 1976-1980 | 23 kW (31 hp) | Used for internal workshop movements. Rebuilt in 1953 from the EB Battery-electric loco. | |||
Electric locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Voltage | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | |||||||
 |
EO | EA | 39 - 74 | 1 - 5 | 5 | 1968, 2008 | 1997, 2011 | 1500V DC overhead | 960 kW (1,290 hp) | Originally classified EA, 1980 reclassified as EO. Used Otira-Arthurs Pass section, three returned to Wellington suburban service in 2008. Final withdrawal 2011. |
| EC | 7 - 12 | 6 | 1928 - 1929 | 1970 | 1500V DC overhead | 885 kW (1,187 hp) | Used on Christchurch-Lyttelton line. | |||
 |
ED | ED | 15, 21 | 101 - 110 | 10 | 1938 | 1969 - 1981 | 1500V DC overhead | 670 kW (900 hp) | Used on Wellington suburban network. |
 |
EF | 30007 - 30249 | 22 | 1986 - 1988 | 1991–present | 25kV 50Hz AC overhead | 3,000 kW (4,000 hp) | Originally Class 30, reclassified as EF class.
Used on the NIMT between Palmerston North and Hamilton. Scheduled to be replaced by eight Diesel Electric DL class locomotives by 2019. | ||
 |
EO | 2 - 6 | 5 | 1923 | 1968 | 1500V DC overhead | 510 kW (680 hp) | Used on Otira-Arthurs Pass section. Replaced by EA class (later reclassified as EO). | ||
 |
EW | EW | 107 - 171 | 1800 - 1806 | 7 | 1952 | 1988 | 1500V DC overhead | 1,340 kW (1,800 hp) | Used on Wellington suburban network. |
Battery electric locomotives
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Power output | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | TMS (1980) | pre-1980 | ||||||
 |
E | 1 | 1923 | 1930 | 131 kW (176 hp) | Used for maintenance in the Otira Tunnel. | |||
 |
EB | 25-29 | 5 | 1925-1929 | 1976-1980 | 23 kW (31 hp) | Used for internal workshop movements. Rebuilt in 1953 to diesel electric power. | ||
Electric multiple units
Wellington electric multiple units operate on 1500V DC overhead. Auckland's electric multiple units run on 25kV AC overhead.
| Image | Class | Number in class | Location | In service | Formation | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM/D | 49 | Wellington | 1938 - 2012 | D - DM (two-car) D - DM - D (three-car) |
132 (two-car) 204 (three-car) |
6 sets preserved in museum or private use. | |
 |
EM/ET | 44 | Wellington | 1982 - 2016 | EM - ET | 148 | One set preserved at Canterbury Railway Society. |
| FP/FT | 74 | Wellington | 2010–present | FP - FT | 147 | Named Matangi, after the Māori word for "wind". | |
 |
AM | 57 | Auckland | 2014–present | AMP - AMT - AMA | 230 |
Railcars
Livery: The first railcars were painted "carnation red" with a white or yellow stripe.The Silver Fern railcars appeared in stainless steel.
All railcars, unless otherwise stated, are designated RM class. Here, they are classified under their common names.
| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Power type | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
88-seater | 35 | 1955 - 1978 | Diesel-mechanical | 88 | Alternatively known as Fiat or twinset railcars. After withdrawal, 14 were converted to (locomotive hauled) AC class articulated carriages 'Grass-grubs'. |
 |
Silver Fern | 3 | 1972–present | Diesel-electric | 96 | Currently (2017) used for excursions and charters by both Kiwirail and Dunedin Railways Limited. |
| Standard | 6 | 1938 - 1972 | Diesel-mechanical | 48 - 52 | Preserved examples exist at Silverstream Railway (Wellington), Glenbrook Vintage Railway (Auckland) and Pahiatua Railcar Society (near Palmerston North). | |
 |
Vulcan | 9 | 1940 - 1978 | Diesel-mechanical | 48 - 50 | Examples are preserved at Ferrymead Railway, Christchurch (3 of) and Plains Railway, Ashburton (1 of). |
| Wairarapa | 7 | 1936 - 1956 | Diesel-mechanical | 25 - 49 | The remaining example is currently being restored by Pahiatua Railcar Society (near Palmerston North). |
Experimental railcars included the following:
| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Power type | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
MacEwan-Pratt petrol railcar | 1 | 1912-1913 | Petrol | 12 | Never in revenue service. Not preserved. |
| Clayton steam railcar | 1 | 1926-1937 | Coal | Originally worked the Kurow branch, and later in Otago and Southland. Not preserved. | ||
 |
Edison battery-electric railcar | 1 | 1926-1934 | Electric (battery) | 60 seated, 70 total. | Used on Little River branch. Destroyed by fire. |
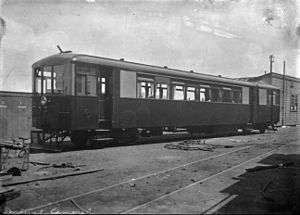 |
Sentinel-Cammell steam railcar | 1 | 1925-1931 | Coal | 48 | Used on Melling and then Thames branches. Not preserved. |
 |
Leyland experimental petrol railcar | 1 | 1925 | Petrol | Never entered revenue service. | |
 |
Model T Ford railcar | 2 | 1925-1931 | Petrol | 11 plus driver | Operated on Greytown branch and in Southland. A replica operates on the Pleasant Point Railway, near Timaru. |
| Leyland diesel railbus | 2 | 1936-1942 | Diesel | 19 or 8 plus 1 ton of newspapers. | Served on Midland Line and the west coast. None preserved. |
Diesel multiple units
| Image | Class | Number in class | In service | Formation | Passenger capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
ADK/ADB | 9 | 1993 - 2014 | ADK - ADB | 134 | Ex Transperth, used on Auckland suburban network. None preserved. |
 |
ADL/ADC | 10 | 1993–present | ADL - ADC | 128 | Ex Transperth, used on Auckland suburban network. |
Steam locomotives
Livery: New Zealand steam locomotives after the late 1920s were mainly completely black with red buffer beams at each end. Earlier steam locomotives were more varied in colour with a contrasting lining on the cab sides and side tanks, for example the green of the F class Peveril.
| Image | Class | Numbers | Number in class | Year(s) introduced | Year(s) withdrawn | Whyte notation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
A of 1873 | 14 | 1873 | 1905 | 0-4-0T | ||
 |
A of 1906 | 58 | 1906 | 1969 | 4-6-2 | Includes 30 locomotives reclassified from AD | |
| AA | 10 | 1914 | 1957 | 4-6-2 | |||
 |
AB | 141 | 1915 | 1969 | 4-6-2 | New Zealand's most prolific steam locomotive; ten were rebuilt from WAB class. Preserved examples at Pleasant Point Railway (near Timaru), Steam Incorporated Paekakariki, Mainline Steam Heritage trust, Kingston Flyer (near Queenstown), Glenbrook/Motat (Auckland). | |
 |
AD | 30 | 1910 | 1916 | 4-6-2 | Reclassified A in 1916. | |
._ATLIB_257541.png) |
B of 1874 | 2 | 1874 | 1890 | 0-4-4-0T Double Fairlie |
||
 |
B of 1899 | 10 | 1899 | 1967 | 4-8-0 | Three rebuilt as WE class | |
 |
BA | 10 | 1911 | 1969 | 4-8-0 | ||
 |
BB | 30 | 1915 | 1968 | 4-8-0 | ||
._ATLIB_276308.png) |
BC | 1 | 1902 | 1927 | 2-8-2 | Originally from the Wellington and Manawatu Railway, which was nationalised in 1908. | |
 |
C of 1873 | 16 | 1873 | 1920 | 0-4-0ST original 0-4-2ST rebuild |
||
 |
C of 1930 | 24 | 1930 | 1968 | 2-6-2 | Built for heavy shunting at major yards, one preserved at Silverstream Railway (Wellington) and one at Ferrymead Railway (Christchurch). | |
 |
D of 1874 | 35 | 1874 | 1927 | 2-4-0T | A low powered locomotive, with many finding a second life as industrial locomotives or with the Public Works dept. Seven have survived, with operational examples at the Pleasant Point Railway (near Timaru) and Ferrymead (Christchurch). Static examples are at Silverstream Railway (Wellington) and Ocean Beach Railway (Dunedin). | |
_Josephine_Otago_Settlers_Museum.jpg) |
E of 1872 | 8 | 1872 | 1906 | 0-4-4-0T Double Fairlie |
A double fairlie, originally used only in the South Island, but one was used by the Public Works Dept. in the North Island. An static example of the E Class is preserved at the Otago Settlers Museum, Dunedin. | |
| E of 1906 | 1 | 1906 | 1917 | 2-6-6-0T Mallet |
|||
 |
F | 88 | 1872 | 1964 | 0-6-0T | Ubiquitous and long-serving, nine examples of this class are preserved. Used in all roles, including mainline use and shunting. | |
 |
FA | 13 | 1892 | 1943 | 0-6-2T | ||
| FB | 13 | 1897 | 1943 | 0-6-2T | |||
 |
G of 1874 | 4 | 1874 | 1918 | 4-4-0ST | ||
| G of 1928 | 3 | 1928 | 1937 | 4-6-2+2-6-4 Garratt |
The only Garrett-type locomotive in NZ, they were not a success. All rebuilt as Pacifics, and became the G class of 1937. None preserved. | ||
| G of 1937 | 6 | 1937 | 1956 | 4-6-2 | Rebuilt from the unsuccessful Garrett G class of 1928. None preserved. | ||
 |
H | 199 - 204 | 6 | 1878 | 1955 | 0-4-2T Fell |
Built to work the Rimutaka Incline, H 199 is the only remaining Fell locomotive in the world and is preserved in the Fell Museum at Featherston, just north of Wellington. |
 |
J of 1874 | 32 | 1874 | 1935 | 2-6-0 | First locomotive class in NZ with a tender. | |
 |
J of 1939 | 1200 - 1239 | 40 | 1939 | 1971 | 4-8-2 | A powerful, yet lighter locomotive than the K class. Coal burning and initially streamlined, 12 members of the class were rebuilt as JB class, being oil burners. Two operating examples remain, one at Mainline Steam and the other at Steam Incorporated. |
 |
JA | 1240 - 1290 | 51 | 1946 - 1956 | 1964 - 1971 | 4-8-2 | Used exclusively in the South Island, the first build were coal burners and the second oil burners. The class includes JA 1274 - the last NZR steam locomotive built. Seven preserved, including at Mainline Steam, Plains railway (Ashburton), Steam Incorporated, Glenbrook Vintage Railway (Auckland) and a static exhibit in Dunedin. |
.jpg) |
JB | 12 | 4-8-2 | 12 locomotives were rebuilt from the 1939 J class as oil burners. | |||
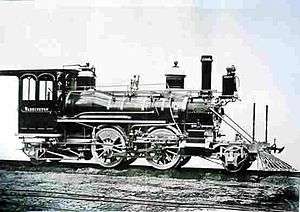 |
K of 1877 | 8 | 1877 | 1927 | 2-4-2 | Originally used solely in the South Island, including on the famous Kingston Flyer, they later received minor use in the North Island. | |
 |
K of 1932 | 900 - 929 | 30 | 1932 | 1967 | 4-8-4 | |
 |
KA | 930 - 964 | 35 | 1939 - 1950 | 1964 - 1967 | 4-8-4 | A modified version of the K class, with roller bearings and ACFI feedwater heaters. |
 |
KB | 965 - 970 | 6 | 1939 | 1968 | 4-8-4 | A coal burning locomotive that was a KA class fitted with trailing-wheel boosters. Used solely in the South Island, almost exclusively on the midland line between Springfield and Arthur's Pass. A non-operating example is preserved at Mainline Steam, Christchurch. |
 |
L | 10 | 1877 | 1901 - 1939 | 2-4-0T 4-4-0T 4-4-2T |
||
 |
LA | 5 | 1887 - 1892 | 1920 - 1928 | 4-4-0T | Originally from the New Zealand Midland Railway, which was nationalised in 1900. | |
 |
M | 4 | 1875 | 1919 - 1928 | 0-6-0T 2-4-4T | ||
| N | 12 | 1885 | 1934 | 2-6-2 | Two originally from the Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908). | ||
| NA | 2 | 1894 | 1929 | 2-6-2 | Originally from Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
| NC | 2 | 1902 | 1931 | 2-6-2 | Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | ||
 |
O | 6 | 1885 | 1922 | 2-8-0 | ||
 |
OA | 1 | 1894 | 1929 | 2-8-0 | Originally from Wellington & Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
)._ATLIB_333419.png) |
OB | 2 | 1888 | 1931 | 2-8-0 | Originally from Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
 |
OC | 1 | 1896 | 1930 | 2-8-0 | Originally from Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
| P of 1876 | 2 | 1876 | 1885 | 0-6-0ST | |||
_at_Frankton._ATLIB_293054.png) |
P of 1885 | 10 | 1885 | 1930 | 2-8-0 | ||
| Q of 1878 | 2 | 1878 | 1898 | 2-4-4T | |||
| Q of 1901 | 13 | 1901 | 1957 | 4-6-2 | The world's first 4-6-2 Pacific locomotive | ||
 |
R | 18 | 1878 | 1936 | 0-6-4T Single Fairlie |
A Single Fairlie locomotive, designed for the tight curves and steep grades characteristic of rail in NZ at that time. Used in all roles from mainline passenger down to shunting and Public Works, private industrial and tramway use. A static example has been preserved at Reefton, on the west coast of the South Island. | |
 |
S | 7 | 1880 | 1927 | 0-6-4T Single Fairlie |
||
._ATLIB_333401.png) |
T | 6 | 1879 | 1928 | 2-8-0 | ||
 |
U | 9 | 1894 | 1959 | 4-6-0 | ||
.png) |
UA | 6 | 1899 | 1937 | 4-6-0 | ||
 |
UB | 22 | 1901 | 1957 | 4-6-0 | ||
 |
UC | 10 | 1901 | 1959 | 4-6-0 | ||
 |
UD | 2 | 1904 | 1931 | 4-6-0 | Originally from the Wellington & Manawatu Railway, which was nationalised in 1908. | |
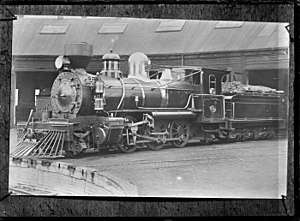 |
V | 13 | 1885 | 1937 | 2-6-2 | Three originally from the Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
._ATLIB_292904.png) |
W | 192, 238 | 2 | 1889 | 1959 | 2-6-2T | Tank locomotive, W 192, which was the first NZR locomotive built in New Zealand, is preserved and operational at Ferrymead Railway, Christchurch. |
 |
WA | 11 | 1892 | 1962 | 2-6-2T | Tank locomotive, 11 built new; four rebuilt from J class 1874. | |
 |
WAB | 30 | 1918 - 1927 | 1947 - 1969 | 4-6-4T | 14 rebuilt from WS class; 10 rebuilt as AB class | |
_ATLIB_292932.png) |
WB | 12 | 1898 | 1957 | 2-6-2T | ||
._ATLIB_292528.png) |
WD | 18 | 1901 | 1936 | 2-6-4T | ||
._ATLIB_292538_(cropped).png) |
WE | 3 | 1902 | 1969 | 4-6-4T | Rebuilt from B of 1899; equipped with Fell centre rail braking for use on the Rimutaka Incline and Rewanui Incline. | |
_ATLIB_257749.png) |
WF | 41 | 1904 | 1969 | 2-6-4T | ||
 |
WG | 20 | 1910 | 1964 | 4-6-4T | 14 later rebuilt as WW class. | |
._ATLIB_292520.png) |
WH | 3 | 1884 | 1927 | 2-4-2T | Originally from Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
 |
WJ | 1 | 1904 | 1928 | 2-8-4T | Originally from Wellington and Manawatu Railway (nationalised 1908) | |
 |
WS | 14 | 1917 | 1936 | 4-6-4T | All rebuilt as WAB class | |
 |
WW | 51 | 1913 | 1969 | 4-6-4T | 14 rebuilt from WG class | |
_steam_locomotive_588%2C_4-8-2_type._ATLIB_257736.png) |
X | 18 | 1909 | 1957 | 4-8-2 | The world's first 4-8-2 Mountain locomotive | |
| Y | 3 | 1923 | 1958 | 0-6-0T |
Steam locomotive notes:
- ^ Two other types of locomotives built in the 1870s were included in the A class. All three had a wheel arrangement of 0-4-0T, but were technically and aesthetically quite different. The other A types are often known as the Shanks A and the Mills A, after their respective builders.
- ^ A completely different type of locomotive was nominally classified as being the solitary member of the S class in 1877 (the main S class was not introduced until 1880), but it was typically known as Robina.
References
- Heath, Eric, and Stott, Bob; Classic Railcars, Electric and Diesel Locomotives Of New Zealand, Grantham House, 1993
- Heath, Eric, and Stott, Bob; Classic Steam Locomotives Of New Zealand, Grantham House, 1993