List of Justices of the Supreme Court of the United States by court composition
| This article is part of the series on the |
| United States Supreme Court |
|---|
 |
| The Court |
| Current membership |
| All members |
| Court functionaries |
|
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest ranking judicial body in the United States. Established by Article III of the Constitution, the detailed structure of the Court was laid down by the 1st United States Congress in 1789. Congress specified the Court's original and appellate jurisdiction, created 13 judicial districts, and fixed the initial size of the Supreme Court. The number of justices on the Supreme Court changed six times before settling at the present total of nine in 1869.[1] A total of 114 justices have served on the Supreme Court since 1789. Justices have life tenure, and so they serve until they die in office, resign or retire, or are impeached and removed from office.
The graphical timeline below lists the justices of the Supreme Court of the United States by court composition. As Supreme Court historians categorize eras in the court's history by the name of the presiding chief justice,[2] the timeline is divided into sections, according to who was chief justice at the time. The incumbent associate justices at the start of each court era are listed in order of their seniority at that time. Associate justices joining the Court during an era are listed adjacent to the person whom they succeeded. Additionally, the bar for each justice is color-coded to indicate which U.S. president appointed them to their seat on the Court.
List of justices
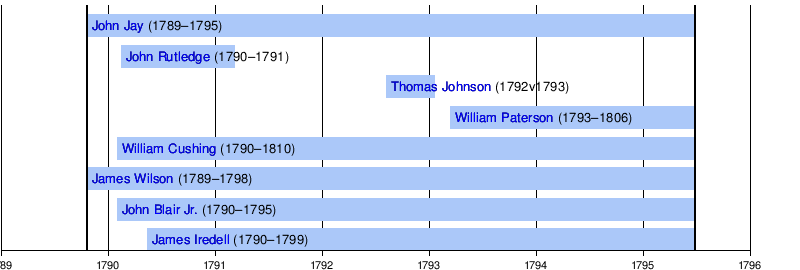
Jay Court
The Jay Court era lasted from October 1789 until June 1795. The Judiciary Act of 1789 set the number of Supreme Court justices at six: one chief justice and five associate justices.[3]
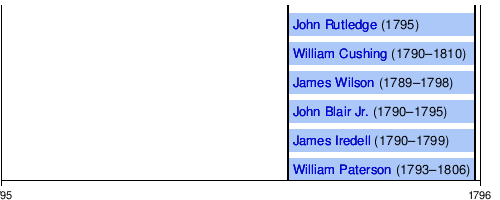
Rutledge Court
The Rutledge Court era lasted from August 1795 to December 1795. John Rutledge took office as a recess appointment of President George Washington. However, he was denied confirmation by the United States Senate, in large part because of his strident opposition to the Jay Treaty.[4]
Ellsworth Court
The Ellsworth Court era lasted from March 1796 to December 1800.
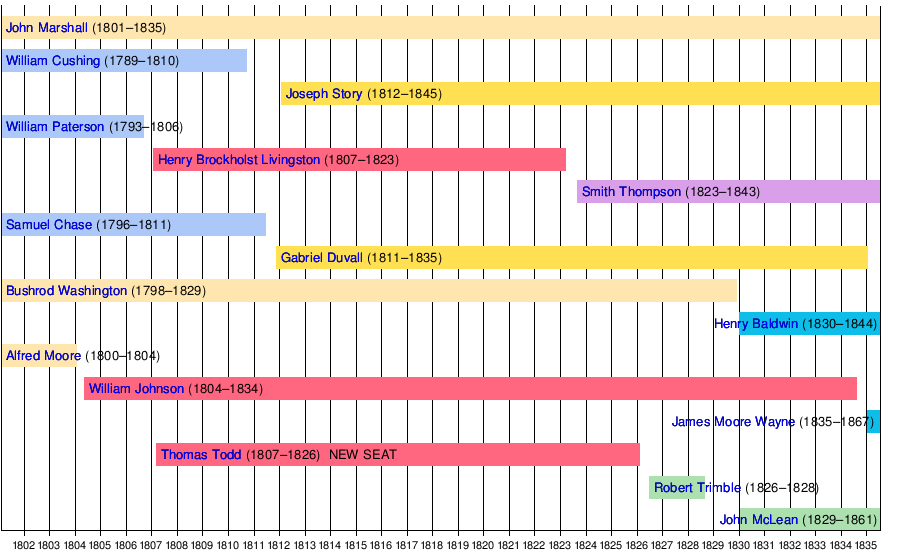
Marshall Court
The Marshall Court era lasted from February 1801 to July 1835. In 1807, Congress passed the Seventh Circuit Act, which added a sixth associate justice to the Supreme Court.[5]
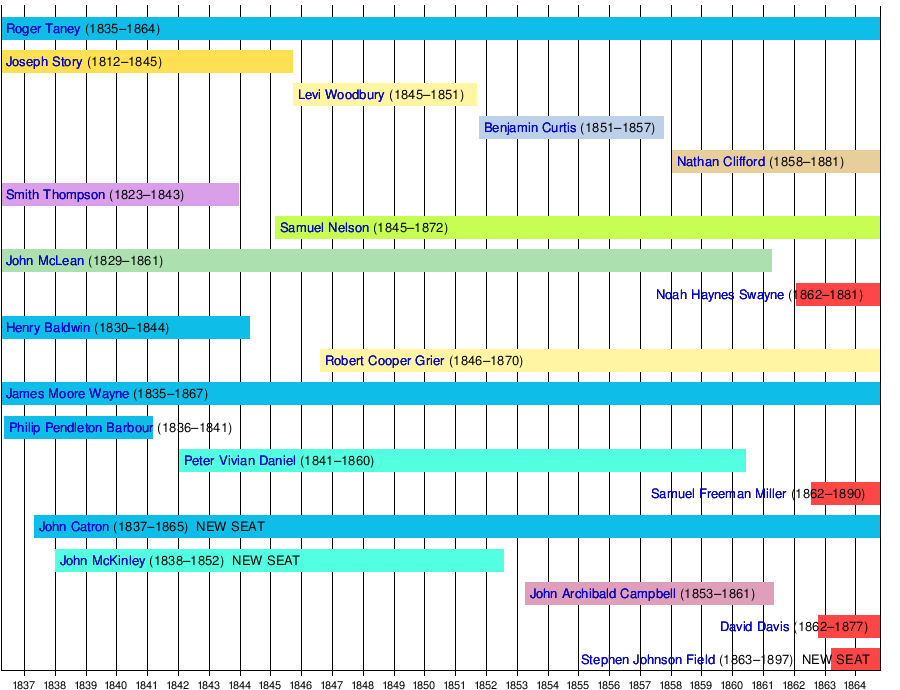
Taney Court
The Taney Court era lasted from March 1836 to October 1864. Two associate justice seats were added to the Court in 1837, as a result of the Eighth and Ninth Circuits Act;[6] another one was added in 1863, by the Tenth Circuit Act, enlarging the Court to 10 justices.[7]
Chase Court
The Chase Court era lasted from December 1864 to May 1873. Two associate justice seats were abolished as a result of the Judicial Circuits Act of 1866, which provided for the gradual elimination of seats on the Court until there would be seven justices.[8] The size of the Court was later restored to nine members through the Circuit Judges Act of 1869.[9]
Waite Court
The Waite Court era lasted from March 1874 to March 1888.
Fuller Court
The Fuller Court era lasted from October 1888 to July 1910.
White Court
The White Court era lasted from December 1910 to May 1921.
Taft Court
The Taft Court era lasted from July 1921 to February 1930.
Hughes Court
The Hughes Court era lasted from February 1930 to June 1941.
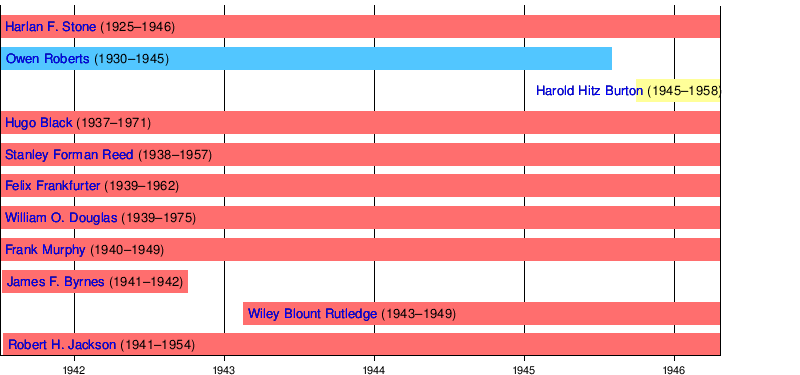
Stone Court
The Stone Court era lasted from July 1941 to April 1946.
Vinson Court
The Vinson Court era lasted from June 1946 to September 1953.
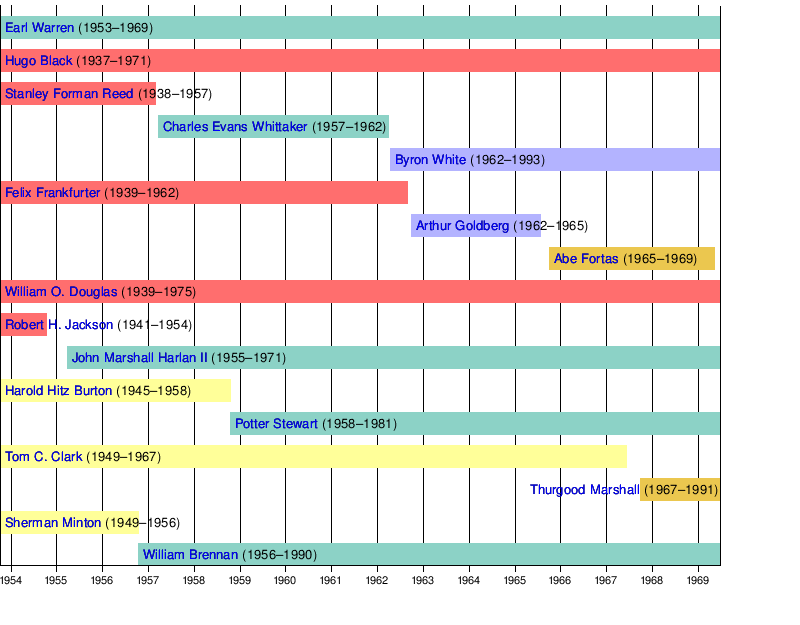
Warren Court
The Warren Court era lasted from October 1953 to June 1969.
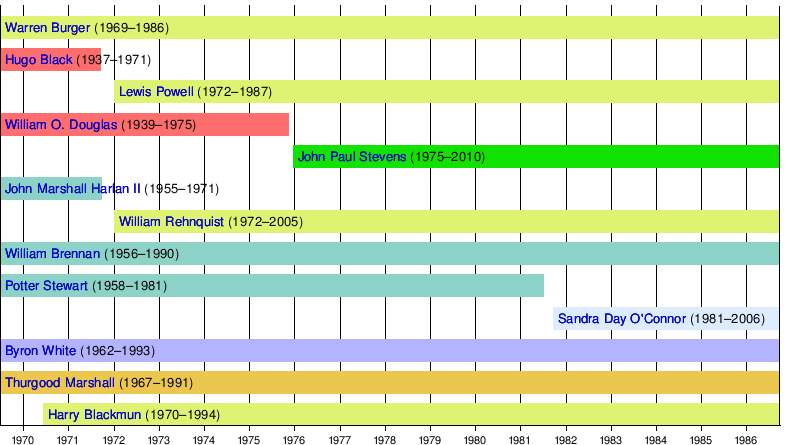
Burger Court
The Burger Court era lasted from June 1969 to September 1986.
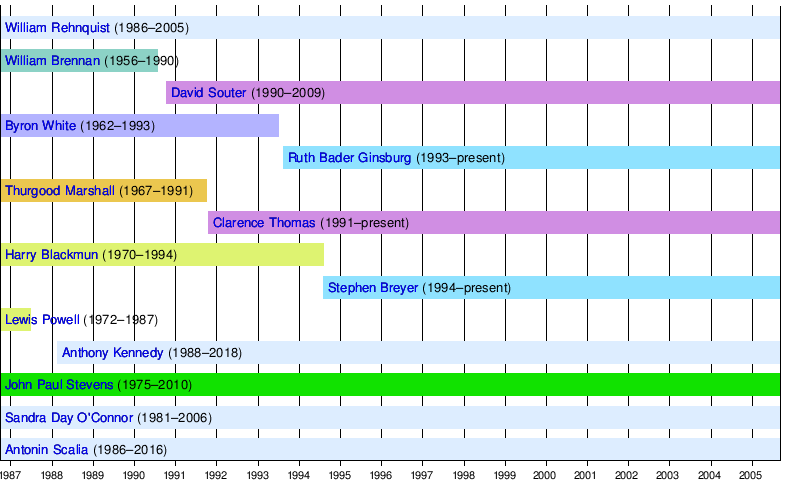
Rehnquist Court
The Rehnquist Court era lasted from September 1986 to September 2005.
Roberts Court
The Roberts Court era began in September 2005, and is ongoing.
See also
External links
- Decisions and biography by Justice – Legal Information Institute, Cornell Law School, Ithaca, New York
- History of the Court – The Supreme Court Historical Society, Washington, D.C.
References
- ↑ "The Court as an Institution". www.supremecourt.gov. Supreme Court of the United States. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- ↑ "10 fascinating facts about the Supreme Court on its birthday". Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: National Constitution Center. September 24, 2017. Retrieved January 30, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Judiciary Act of 1789". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.
- ↑ Schwartz, Bernard (1993). A History of the Supreme Court. New York City: Oxford University Press. p. 28. ISBN 0-19-509387-9. Retrieved February 5, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Seventh Circuit". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Eighth and Ninth Circuits". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Tenth Circuit". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Reorganization of the Judicial Circuits". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.
- ↑ "Landmark Legislation: Circuit Judgeships". Washington, D.C.: Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved January 28, 2018.