Latvian National Guard
| National Guard of the Republic of Latvia Latvijas Republikas Zemessardze | |
|---|---|
 Latvian National Guard emblem | |
| Founded | August 23, 1991 |
| Country |
|
| Allegiance |
|
| Type | Light Infantry volunteer force |
| Size | more than 8,000 |
| Part of | Latvian Armed Forces |
| Garrison/HQ |
|
| Anniversaries | August 23, 1991 |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Brigade General Ainārs Ozoliņš |
The Latvian National Guard or NG (Latvian: Latvijas Republikas Zemessardze or ZS) is a part of the Latvian National Armed Forces. The National Guard is a basic land component, consisting of volunteers who perform traditional national guard duties such as crisis response and support for military operations. It consists of the Staff Headquarters and 4 brigades (formally - regions or novadi), which are divided into 18 battalions. The National Guard continued its development also after Latvia joined NATO.
History

The National Guard was established in August 23, 1991 by the Supreme Council of the Republic of Latvia as a voluntary public military self-defense organization.[1] Its roots can be traced to the pre-World War II Aizsargi organization. It is the largest NAF structure in terms of numbers. The National Guard has always played an essential role in the national defense system by allowing the public to be involved in national defense. A number of National Guard battalions have been transformed into high-readiness reserve forces, which can be deployed immediately on international military operations.
The youth organization of the National Guard, the Youth Guard (Latvian: Latvijas Republikas Jaunsardze, JS), was established in 1992. It is the largest youth movement in Latvia, bringing together young people from the age of 10 to 21.[2]
An aviation component of the National Guard was introduced in 1993, with a fleet of ex-Soviet DOSAAF light aircraft and gliders. In 2000 the aviation component became part of the Air Force.
Mission
The main task of the National Guard is to support the regular Land Force units by defending the national territory during military threat and to perform NAF combat support and combat logistics functions. At the same time, the National Guard will continue providing assistance to the public regarding crisis control, as well as to the Latvian State Police regarding provision of public law and order, and continue the safeguarding of sites of national security importance.[3]
Structure



(as of September 2, 2018:)[4]
National Guard (NG) Headquarters (Rīga)
- NG Cyber Defense Unit (Rīga)
- NG special task force
- NG Special PSYOPS Support Platoon (Valmiera)
- NG Veterans' Union (Rīga)
- Central Band of the National Guard (Rīga)
National Guard 1st Brigade (Rīga HQ):
- NG Student Infantry Battalion (Rīga)
- NG 13th Infantry Battalion (Rīga)
- NG 17th Support Battalion (Rīga)
- NG 19th Logistic Battalion (Rīga)
- NG 53rd Infantry Battalion (Bauska)
- NG CBRN Defense company (Rīga)
National Guard 2nd Brigade (Valmiera HQ):
- NG 22nd Infantry Battalion (Valmiera)
- NG 25th Infantry Battalion (Gulbene)
- NG 27th Infantry Battalion (Cēsis)
- NG 31st Infantry Battalion (Alūksne)
- NG 54th Engineer Battalion (Ogre)
National Guard 3rd Brigade (Rēzekne HQ):
- NG 32nd Infantry Battalion (Rēzekne)
- NG 34th Artillery Battalion (Daugavpils)
- NG 35th Logistic Battalion (Preiļi)
- NG 36th Support Battalion (Lūznava)
- NG 55th Infantry Battalion (Aizkraukle)
- NG 56th Infantry Battalion (Jēkabpils)
National Guard 4th Brigade (Liepāja HQ):
Equipment
Military vehicles
| Name | Image | Origin | Type | Variants | Quantity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trucks | ||||||
| Scania |  |
Truck | ||||
| Mercedes-Benz |  |
Truck | ||||
| Unimog |  |
Truck | ||||
| Volvo | .jpg) |
Truck | Phasing out | |||
| Light vehicles | ||||||
| Mercedes-Benz |  |
SUV | ||||
| HMMWV | .jpg) |
SUV | ||||
| CUCV | .jpg) |
SUV | ||||
| Jeep | SUV | |||||
| Volvo |  |
SUV | C304 C306 |
|||
| Special vehicles | ||||||
| Bv 206 |  |
Amphibious tracked vehicle | Bv 206F |
|||
Weapons
| Name | Image | Origin | Type | Variants | Quantity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artillery | ||||||
| vsor 53 Škoda A20 |  |
Field gun | Can be used as anti-tank or light field gun. | |||
| Mortars | ||||||
| 2B11 |  |
Mortar | ||||
| NM 95 | 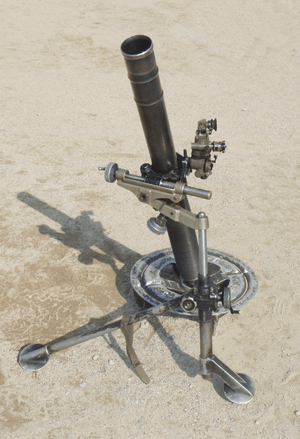 |
Mortar | ||||
| Anti-tank weapons | ||||||
| Pvpj 1110 |  |
Recoilless rifle | ||||
| Carl Gustav recoilless rifle |  |
|||||
| Anti-aircraft gun | ||||||
| Bofors 40mm gun | .jpg) |
|||||
| Submachine guns | ||||||
| Carl Gustav |  |
Used mostly for secondary tasks such as training and guard duty. | ||||
| Assault rifles | ||||||
| Heckler & Koch G36 | Expected to replace the Ak 4 in the future, contract signed in February 2018.[5] | |||||
| Heckler & Koch G3 |  |
Standard issue rifle; will be replaced by the H&K G36, contract signed in February 2018.[5] | ||||
| Machine guns | ||||||
| FN MAG |  |
|||||
| M2 Browning |  |
|||||
| Heckler & Koch HK21 | ||||||
| RPK | Being phased out | |||||
| Sniper rifles | ||||||
| PGM Hécate II |  |
|||||
Cooperation
The National Guard has established close co-operation with similar organizations abroad – the US Michigan Army National Guard, the Australian Army Reserve, the UK Territorial Army, and the Home Guard organizations of Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Lithuania and Estonia.[6]
References
- ↑ Baltiņa, Sarmīte (2014). "Dawn of the Restored Latvian National Armed Forces". Eesti Sõjaajaloo Aastaraamat / Estonian Yearbook of Military History. 4 (0): 62–79. ISSN 2228-0669.
- ↑ "Jaunsardzes un informācijas centrs". www.jic.gov.lv. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
- ↑ Pike, John. "Latvian National Guard - Zemessardze". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
- ↑ "ZS vienības" (in Latvian). LR Zemessardze. Retrieved January 4, 2017.
- 1 2 Jones, Bruce (6 February 2018). "Latvia orders infantry small arms". IHS Jane's 360. London. Archived from the original on 7 February 2018. Retrieved 7 February 2018.
- ↑ "Michigan Guard and Latvia celebrate 25-year partnership". www.army.mil. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zemessardze. |
- Latvian National Guard Official Website (in Latvian)