Latvian Land Forces
| Latvian Land Forces | |
|---|---|
| Sauszemes spēki | |
 Latvian Land Forces emblem | |
| Active |
1918 - 1940 1991 - present |
| Country |
|
| Role | Land force |
| Size | ~6,500 professionals, 8,000 National Guard and 3,000 reserve personnel (Military of Latvia) |
| Part of | Latvian National Armed Forces |
| Motto(s) | Vienotībā spēks (Power in unity)[1] |
| Anniversaries |
April 30, Land Forces Day May 4, Independence Restoration and Armed Forces Day |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Commander | Colonel Ilmārs Atis Lejiņš[2] |
The Latvian Land Forces (Latvian: Sauszemes Spēki, SzS) together with the Latvian National Guard form the land warfare branch of the Latvian National Armed Forces. Since 2007, land forces are organized as a fully professional standing army.
Mission
The main missions of the national Land Forces are to:
- Provide for the defense of all national territories;
- Ensure combat readiness and the mobilization of units;
- Dispose of explosive ordnance;
- Provide public assistance.
Structure
Note: "Special Tasks Unit" is a special forces unit of battalion size.
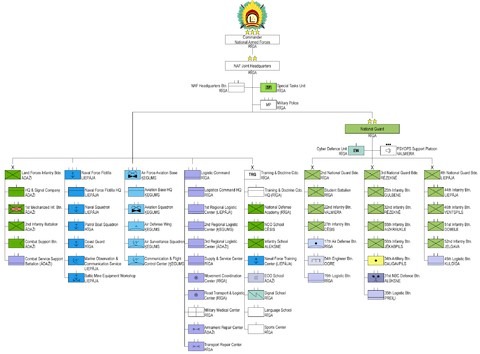
Land Forces Infantry Brigade
- Headquarters
- HQ and Signal Company

- Staff and Signal Company
- 1st Mechanized Infantry Company
- 2nd Infantry Company
- 3rd Mechanized Infantry Company
- 4th Mechanized Infantry Company
- Combat Service Support Company

- Staff and Signal Company
- 1st Infantry Company
- 2nd Infantry Company
- 3rd Infantry Company
- Staff and Signal Company
- Anti-tank Company
- Fire Support Company
- Engineer Company
- Military Intelligence Company
- Forward Air Control Team
- Combat Service Support Battalion
- Supply and Transport Company
- Medical Company
Cooperation

Since 1996 till today the National Armed Forces' soldiers have been deployed on nine international peace-keeping missions in Afghanistan, Albania, Bosnia, Central African Republic, Georgia, Iraq, Kosovo, Macedonia and Somalia.[4] Starting from January 1, 2015, Latvian Armed Forces are taking part in EU's Nordic Battle Group.[5][6] On March 29, 2004, Latvia became a fully fledged member of the NATO.[7]
Personal equipment
.jpg)
The equipment of the Latvian Land Forces troops includes:
- LATPAT and Multi-LATPAT (Latvian digital camouflage uniform).
- Norwegian BEAR-II load bearing armor system
- Kevlar helmet
- Night vision device
Infantry weapons
Military vehicles
| Name | Image | Origin | Type | Variants | Quantity | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armoured reconnaissance vehicles | |||||||
| CVR(T) |  |
Armoured reconnaissance vehicle | 123[15] | All vehicles will be upgraded and overhauled. Some of them will be equipped with SPIKE anti-tank guided missiles.[16] | |||
| Armoured cars | |||||||
| HMMWV | .jpg) |
Armoured car | 60 | Some equipped with HK GMG, M2 Browning and SPIKE ATGM | |||
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class | .jpg) |
Armoured car | 50 [17] | ||||
| Snatch Land Rover |  |
Armoured car | 9 [18] | ||||
| Trucks | |||||||
| Mercedes-Benz 1017 |  |
Truck | |||||
| Mercedes-Benz Unimog 416 |  |
Truck | |||||
| Scania |  |
Truck | 192[19] | ||||
| Light vehicles | |||||||
| Polaris RZR |  |
ATV | 62[20] | ||||
| Can-Am Outlander |  |
ATV | [21] | ||||
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class |  |
SUV | |||||
| Volvo C class |  |
SUV | C304 C306 |
||||
| Land Rover Defender | SUV | ||||||
| Special vehicles | |||||||
| Bv 206 | .jpg) |
Amphibious tracked vehicle | Bv 206F |
~180 | |||
Artillery
| Model | Image | Origin | Caliber | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mortars | |||||
| GrW 86 | .jpg) | 120mm | |||
| M/41D |  | 120mm | |||
| NM 95 | 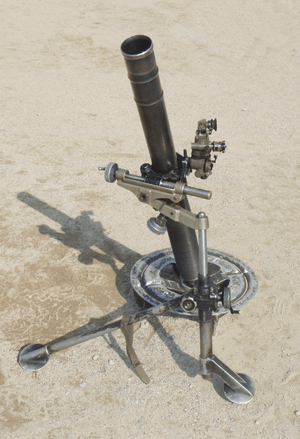 | 81mm | |||
| Self-propelled artillery | |||||
| M109A5Ö |  |
155 mm | 47 [22] | Mobile artillery system’s M109A5Ö A-type howitzer, which is a modernized version of A2 and A3 howitzer with 39-calibre M185 barrel. Their range is 22 km with conventional munitions and 30 km with improved conventional munitions. First delivery autumn 2017 [23] | |
Air-defence weapons
| Model | Image | Origin | Variant | Quantity | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-defence missiles | |||||
| RBS-70 | Ordered in 2004.[24] Short-range man-portable air-defence system (MANPAD) used in combination with GIRAFFE Radar | ||||
| FIM-92 Stinger |  | Purchased from Denmark.[25] | |||
| Radars | |||||
| AN/MPQ-64 Sentinel |  | AN/MPQ-64F1 | 4 | Donated by the U.S. through the European Reassurance Initiative. Two radars used in conjuction with the RBS 70 air defence system.[26] | |
| AN/FPS-117 |  | AN/TPS-77 | 6 | Used in Baltic Air Surveillance Network.[27][28] | |
Rank structure[29]
The rank structure of the Latvian army is adjusted to the rank structure of the NATO countries in Europe. Rank insignia are worn historically on the collars and today also on shoulder marks. Starting 2016, only the Staff Battalion wears the collar insignia.
| Officers of the Latvian Army | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generals | Officers | ||||||||
| Rank insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank | Lieutenant General Ģenerālleitnants |
Major General Ģenerālmajors |
Brigadier General Brigādes Ģenerālis |
Colonel Pulkvedis |
Lieutenant Colonel Pulkvežleitnants |
Major Majors |
Captain Kapteinis |
First Lieutenant Virsleitnants |
Second Lieutenant Leitnants |
| NATO Rank Grade | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
| Non-Commissioned Officers of the Latvian army | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sergeants | Privates | |||||||
| Rank insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank | Senior Warrant Officer Augstākais virsseržants |
Warrant Officer Galvenais virsseržants |
Senior Sergeant Štāba virsseržants |
Sergeant First Class Virsseržants |
Sergeant Seržants |
Corporal Kaprālis |
Private First Class Dižkareivis |
Private Kareivis |
| NATO Rank Grade | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 |
References
- ↑ "Simbolika". Nacionālie bruņotie spēki. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ↑ "Nacionālie bruņotie spēki". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ Jane's World Armies Issue 23 - 2008
- ↑ "Nacionālie bruņotie spēki". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-03-20. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ↑ http://www.forsvarsmakten.se/siteassets/english/nbg15---eng/14mar_-fcdr_master-f.pdf#page=13
- ↑ "Member countries". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Par ieroču modeļu noteikšanu un iepirkumu Nacionālo bruņoto spēku vajadzībām". likumi.lv (in Latvian). 28 July 2005.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Faktu lapa "Nacionālie bruņotie spēki" (2008)". www.mod.gov.lv (in Latvian).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 "AM sagatavojusi jaunus armijas ieroču standartus". www.tvnet.lv (in Latvian). LETA. 12 July 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Tupp, Enn (2018). "Zemessardze - KASP-i ja Kaitseliidu vääriline partner". Kaitse Kodu! (in Estonian). Kaitseliit. 1: 34. ISSN 1406-3387.
- ↑ "Latvia's National Guard receives G36 rifles". www.shephardmeida.com. 31 May 2017.
- ↑ "NBS par 1,8 miljoniem eiro iegādāsies 'Browning M2' ložmetējus". www.delfi.lv (in Latvian). BNS. 21 December 2014.
- ↑ "Latvian army with US support to receive EUR 2.4 million worth of drones". Retrieved 16 April 2018.
- ↑ "Latvian army purchases UK armoured combat vehicles". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Latvia to continue purchases of Spike anti-tank missiles". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "Latvia to buy anti-tank weapons, armoured vehicles from Norway". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Latvian soldiers leave for the operation in Central African Republic". Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ "Bruņotie spēki saņem Norvēģijā pirktās automašīnas un ieročus" (in Latvian). Retrieved 31 May 2015.
- ↑ "Latvijas armija saņems ar ASV atbalstu sagādātus 62 taktiskos transportlīdzekļus" (in Latvian). delfi.lv. Retrieved 6 Feb 2018.
- ↑ "Bruņotie spēki no Somijas iegādājušies 6x6 bezceļa transportlīdzekļus" (in Latvian). mod.gov.lv. Retrieved 16 Jun 2018.
- ↑ "Latvia to procure nearly fifty used howitzers; first ones to be supplied in autumn". Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ↑ "Latvia to procure nearly fifty used howitzers; first ones to be supplied in autumn". Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ↑ "Another NATO Country Buys RBS 70". www.defense-aerospace.com. 25 November 2004.
- ↑ "Latvia to Buy Stinger Air-Defence Systems". www.defense-aerospace.com. 22 August 2017.
- ↑ Eglīte, Džoanna (5 October 2016). "Latvian skies protected by advanced radars". www.mil.lv.
- ↑ "Latvia awards Lockheed Martin $44 million contract for two long-range air surveillance radars".
- ↑ "Latvia buys TPS-77 multi-role radars from Lockheed Martin". 5 October 2015.
- ↑ "Latvia Latvian Army ranks military combat field uniforms dress grades uniformes combat armee lettone - Army Recognition - Army Recognition". Retrieved 24 December 2014.

.jpg)


.jpg)











