Laichingen
| Laichingen | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| ||
 Laichingen Location of Laichingen within Alb-Donau-Kreis district 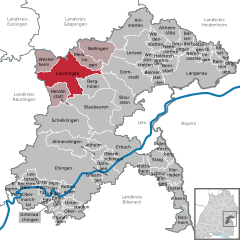  | ||
| Coordinates: 48°29′23″N 9°41′10″E / 48.48972°N 9.68611°ECoordinates: 48°29′23″N 9°41′10″E / 48.48972°N 9.68611°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Admin. region | Tübingen | |
| District | Alb-Donau-Kreis | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Friedhelm Werner | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 69.84 km2 (26.97 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 755 m (2,477 ft) | |
| Population (2017-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 11,506 | |
| • Density | 160/km2 (430/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 89144–89150 | |
| Dialling codes | 07333 | |
| Vehicle registration | UL | |
| Website | www.laichingen.de | |
Laichingen (Swabian: Loechenge) is a town in the district of Alb-Donau near Ulm in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It has 10,964 inhabitants (2005).
Geography
Geographical location
Laichingen is located on the Laichingen Alb, a branch of the Swabian Jura. It is located on a former volcanic vent on the Alb plateau, about 25 kilometers west of Ulm.
Neighboring communities
The municipality borders to Hohenstadt in Göppingen district, in the east to Merklingen and Dornstadt, on the south to Berghülen, to the town Blaubeuren and Heroldstatt and on the west to Gutsbezirk Münsingen and to Römerstein, both in the district of Reutlingen and to Westerheim.
History
In 1364 offered Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor the town privileges to the population, these however rejected, allegedly because they did not want to build any walls. The tradition of Laichingen linen weaving goes back until the Middle Ages. The poor soils on the Alb gave only small harvests, and so the inhabitants have relied on the growing of flax and the trade with the town of Ulm. One of the in 1677 built weber houses stood in Laichingen till 2002. It was dismantled and rebuilt and can now be visited in the open air museum in Beuren. From 1871, the water supply for the Swabian Jura was planned and built, also Laichingen was connected. In 1950, Laichingen received again the town privileges.
Population Development
The figures are census results (¹) or official updates of the Statistical Office of Baden-Württemberg [2] (only primary residents).
- Year Population
- December 1, 1871 ¹ 4,571
- December 1, 1880 ¹ 4,897
- December 1, 1890 ¹ 4,910
- December 1, 1900 ¹ 4,822
- December 1, 1910 ¹ 5,225
- June 16, 1925 ¹ 5,163
- June 16, 1933 ¹ 5,237
- May 17, 1939 ¹ 5,216
- September 13, 1950 ¹ 6,435
- June 6, 1961 ¹ 7,108
- May 27, 1970 ¹ 8,057
- December 31, 1980 8,419
- May 27, 1987 ¹ 8,714
- December 31, 1990 9,219
- December 31, 1995 10,083
- December 31, 2000 10,787
- December 31, 2005 10,990
- December 31, 2010 10,867
Economy and Infrastructure
Traditional weving establishments are located in Laichingen. The iron processing, particularly the tooling flourished in Laichingen in the 20th century. The to STADA Arzneimittel belonging aliud Pharma has its headquarters in Laichingen. Laichingen is home of the " Inter-municipal industrial and commercial area Laichinger Alb". It is the association with Heroldstatt, Merklingen, Nellingen and Westerheim .
Laichingen textile industry
The linen weaving was an important economic activity.[3] In the period after the Second World War, the consequences of the war were still very noticeable. Many of the Laichingen companies were used during the war for making war necessary materials. After the war six companies of Laichingen were authorized by the American military government to resume their production. So many looms were rebuilt and put into operation. With the currency reform the windows of the shops were filled and also Laichingen textile industry could benefit. The demand for textiles rose after the war enormously, especially bed linen was now in demand. This led to a veritable boom in this industry. In 1948, all companies were fully occupied in Laichingen and then followed from 1950 to 1960, a wave of start-ups, because everyone wanted to participate in the upswing. Over the next 10 years, many textiles were produced in Laichingen.
Transportation
The public transport is guaranteed by the Donau-Iller-Nahverkehrsverbund. From 1901 to 1985 Laichingen was connected to the rail network by the railway Amstetten-Laichingen of the Württemberg railway company (WAY). Laichingen has its own airfield, which is operated since 1964 by the Flugsportverein Laichingen.
Tourism
In the district of Machtolsheim is the campsite Heidehof, which counts 1050 parking spaces in an area of 25 hectares.
Media
In Laichingen is a local section of the Schwäbisches Tagblatt.
Education
In Laichingen, Feldstetten and Machtolsheim there are primary schools. The main town Laichingen is also the school center with the following schools:
- Erich Kästner school, primary and secondary school with Werkrealschule
- Anne-Frank-Realschule
- Albert-Schweitzer-Gymnasium
- Martin School ( Special Education )
- Branch of the Mercantile School Ehingen
- Branch of the Intellectual Property School Ehingen
- The Volkshochschule Laichingen-Blaubeuren-Schelklingen is headquartered in Laichingen.
Things
The Laichingen Vertical Cave
Laichingen is also known by the Laichingen deep cave. The cave is located about 1 km south of Laichingen. It was discovered in 1892 by Johann Georg Mack.

Museums
- Home and Weaving Museum Laichingen [4]
- Cave History Museum (in Deep Cave)
Buildings
- St. Albans church (fortified church)
- Liebfrauenkirche Machtolsheim in its present form built in 1488, the Baroque style is from the 18th century
- Water Tower Machtolsheim
- In the historic Old Town Hall are held weddings, cultural events and meetings of the municipal council

Personality
Freeman
- Jean-Pierre Tizon (1920–2012), French politician
Notable people

- Heinrich Lang, (1858–1919), university teacher, composer and choir conductor
- Eugen Eisele, (1871–1940), Member of Landtag from 1906 to 1918
- August Enderle,(1887–1959), politician and journalist
- Karl Baur, (1911–1963), pilot
- Helmut Kreuzer, (1927–2004), Siegen, Germanist and media scientist
- Peter Schwenkmezger, (born 1946), president of University of Trier (2000–2011)
Regular events
Laichingen is a market-town and had early received the town privilges. Today markets are held every year, which attract thousands of visitors. The streets are crowded with market stalls selling typical market products. A traditional market dining in Laichingen are tripes . The market begins at 8 am and usually ends at 5 pm. Each year, the following markets are held:
- Easter Market, Easter Monday
- Pfingstmarkt, Pentecost
- Kirchweihmarkt, Monday after Kermesse, third Sunday in October
- Andreas Market, on Andrew's Day Andrew the Apostle
- Christmas Market, in mid-December
Literature
- Hans Medick: Weben und Überleben in Laichingen 1650–1900. Lokalgeschichte als allgemeine Geschichte. Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen 1996, ISBN 3-525-35443-6.
References
- ↑ "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2017". Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg (in German). 2018.
- ↑ Bevölkerungsentwicklung in Baden-Württemberg von 1871 bis 2012 Archived 2014-09-07 at Archive.is
- ↑ Hans Medick: Weben und Überleben in Laichingen 1650 – 1900: Lokalgeschichte als allgemeine Geschichte, Vandenhoeck und Ruprecht, Göttingen 1996.
Geschichtsverein Laichinger Alb e.V.: Der Leineweber im Blauhemd – Das Laichinger Wirtschaftswunder, Werner Mangold, Geiger-Verlag, 2010. - ↑ Weberei- und Heimatmuseum Laichingen
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Laichingen. |
- Official website

