Health care in Venezuela
After the Bolivarian Revolution, extensive inoculation programs and the availability of low- or no-cost health care provided by the Venezuelan Institute of Social Security made Venezuela's health care infrastructure one of the more advanced in Latin America. However, by 2015, the Venezuelan health care system had collapsed.[1][2]
History
Pre-Bolivarian Revolution
1970s
Venezuelan state governments operated only 5 facilities in 1979, down from about 60 hospitals in 1970 since the Ministry of Health and Social Assistance (MSAS) took over many of the hospitals.[3]
In 1978, a presidential election year, medical sales in Venezuela hit an all-time high at the time and dropped in 1979. In 1979, there were approximately 250 hospitals in Venezuela with MSAS operating the majority of 58%. Venezuela had a shortage of medical professionals and hospital beds in the late 1970s due to highly increasing population and the lack of specializing in being a specific medical technician. The lack of both professionals and beds was higher in rural areas compared to more populated areas. Between 1978 and 1980, Venezuela had 14,771 doctors, 8,805 nurses and 28,04 nursing auxiliaries.[3]
1980s
Under the Sixth National Plan of Luis Herrera Campins, the Campins government planned to increase medical funding by 9.7% annually between 1981 and 1985, with medical expenditures planned to reach $2.1 billion in 1985. $1.2 billion were designated to the construction of new facilities to combat bed shortages, with a main focus on establishing clinics in order to avoid inefficiency of larger hospitals. Rehabilitation of handicapped individuals and the concentration on heart disease, the leading cause of death in Venezuela, were also focused on in the Sixth National Plan. Medical professionals in Venezuela were "extremely U.S. oriented", with most doctors attending post-graduate work in the United States, were able to speak English, read U.S. medical journals and attended gatherings of United States medical experts. In 1981, over 70% of healthcare services were government administered.[3]
Foreign medical equipment developed abroad was quickly adopted and shipped to Venezuela with most of the country's medical goods needing to be imported. In 1980, Venezuela imported 47% of medical goods from the United States, 13% from Germany, 8% from Japan and 3% from the United Kingdom. The majority of medical equipment was distributed by a conglomerate of about 45 distributors known as Associacion Venezolana de Distribuidores de Equips Medicos (AVEDEM) while 15% of medical products were distributed by smaller entities.[3]
1990s
{see Briggs "Stories in the Time of Cholera: Racial Profiling during a Medical Nightmare"} From 1992 to 1993, there was a cholera epidemic in the Orinoco Delta and Venezuela's political leaders were accused of racial profiling of their own indigenous people to deflect blame from the country's institutions, thereby aggravating the epidemic.[4] During the 1990s, the mortality rate was 318 per 100,000 population for diseases of the [cardiac system], 156 for cancers, 634 for external causes (including drowning, self-harm, violence, falls, road accidents etc, 1126 for communicable diseases such as chest infections, syphilis, meningitis, and 654 for certain conditions originating before birth.[5]
Bolivarian Revolution
Following the Bolivarian Revolution and the establishment of the Bolivarian government, initial healthcare practices were promising with the installation of free healthcare and the assistance received from Cuban medical professionals providing aid. The Bolivarian government's failure to concentrate on healthcare for Venezuelans, the reduction of healthcare spending and government corruption eventually affected medical practices in Venezuela; causing avoidable deaths along with an emigration of medical professionals to other countries.[6][7] Venezuela's reliance of imported goods and its complicated exchange rates initiated under Hugo Chávez led to increasing shortages during the late-2000s and into the 2010s that affected the availability of medicines and medical equipment in the country.[7]
2000s
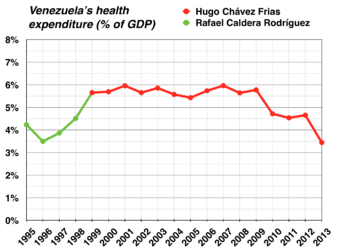
Source: World Bank
Several transmissible diseases, including dengue fever, malaria, measles, and tuberculosis, reappeared in Venezuela. In 1999 an estimated 62,000 Venezuelans were living with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS); and in 2001 an estimated 2,000 people died from AIDS. At the end of 2003, the percentage of the population between the ages of 15 to 49 with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS was 0.7. In 2000, 85% of the urban population and 70% of the rural population had access to improved water. Improved sanitation was available to 71% of the urban population and 48% of the rural population. In August 2001, President Hugo Chávez announced a national campaign to fight the dengue fever epidemic that had infected 24,000 and killed four. Child immunization for measles in 2002 (as a percentage of under 12 months) dropped to 78%, compared with 84% in 1999.
Throughout Hugo Chávez's presidency, the Health Ministry changed ministers multiple times. According to a high-ranking official of Venezuela's Health Ministry, the ministers were treated as scapegoats whenever issues with public health arose in Venezuela.[7] The official also explained how Health Ministry officials would also perform illicit acts in order to enrich themselves by selling goods designated to public healthcare to others.[7]
2010s
The Venezuelan government stopped publishing medical statistics in 2010.[8]
In 2014 when Venezuela's economy was facing difficulties, Venezuela's medical atmosphere deteriorated. The Bolivarian government did not supply enough dollars for medical supplies among healthcare providers; with doctors saying that 9 of 10 of large hospitals had only 7% of required supplies with private doctors reporting many patients that are "impossible" to count are dying from easily treated illnesses due to the "downward sliding economy" in 2014.[8] Due to such complications, many Venezuelans died avoidable deaths with medical professionals having to use limited resources to use methods that were replaced decades ago.[6] In February 2014, doctors at University of Caracas Medical Hospital stopped performing surgeries due to the lack of supplies, even though nearly 3,000 people require surgery.[9]
In March 2014, the executive director of the Venezuelan Association of Hospitals and Clinics explained how in less than a month, shortages of 53 medical products rose to 109 products and explained how the CADIVI system is to blame since 86% of supplies are imported[10] with private sector hospitals claiming they owe suppliers billions of dollars in order to pay for debts.[11]

In August 2014, Venezuela was the only country in Latin America where the incidence of malaria was increasing, allegedly due to illegal mining and in 2013, Venezuela registered the highest number of cases of malaria in the past 50 years, with 300 of 100,000 Venezuelans being infected with the disease. Medical shortages in the country also hampered the treatment of Venezuelans.[12] Shortages of antiretroviral medicines to treat HIV/AIDS affected about 50,000 Venezuelans, potentially causing thousands of Venezuelans with HIV to develop AIDS.[13] Venezuelans also stated that due to shortages of medicines, it was hard to find acetaminophen to help alleviate the newly introduced chikungunya virus, a potentially lethal mosquito-borne disease.[14] In September 2014, Health Minister Nancy Pérez admitted that there were 45,745 cases of dengue fever.[15] There were also contested estimates involving the number of Venezuelans infected with chikungunya. In September 2014, the Venezuelan government stated that only 400 Venezuelans were infected with chikungunya[15] while the Central University of Venezuela stated that there could be between 65,000 and 117,000 Venezuelans infected.[16] In August 2015 independent health monitors said that there were more than two million people infected with chikungunya while the government said there were 36,000 cases.[17] In October 2014, President Maduro announced a plan to create the University of Science and Health and called for a meeting of ALBA in order to discuss the combat against the Ebola virus disease due to the Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa.[18]
In early 2015, only 35% of hospital beds were available and 50% of operating rooms could not function due to the lack of resources.[6][7] In March 2015, a Venezuelan NGO, Red de Medicos por la Salud, reported that there was a 68% shortage of surgical supplies and a 70% shortage of medicines in Venezuelan pharmacies.[7] In May 2015, the Venezuelan Medical Federation said that 15,000 doctors had left the public health care system because of shortages of drugs and equipment and poor pay. In August 2015 Human Rights Watch said “We have rarely seen access to essential medicines deteriorate as quickly as it has in Venezuela except in war zones.”[17]
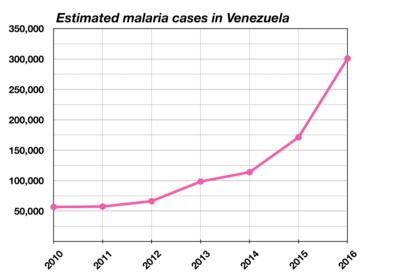
By the end of 2015, the Bolivarian government reported that of all Venezuelans visiting public hospitals in the year, one-of-three patients died.[19] Also in 2015 Venezuela had 30% of all reported malaria cases in the Americas and more even than Brazil, which has a much larger population.[20]
In 2016, according to the Venezuelan government, 240,000 cases of malaria were reported, rising 76% in a year.[20] According to former Venezuelan health minister José Félix Oletta, more than 500,000 Venezuelans will contract malaria in 2017.[20]
In April 2017 Venezuela’s health ministry reported that maternal mortality jumped by 65% in 2016 and that the number of infant deaths rose by 30%.[21] It also said that the number of cases of malaria was up by 76%.[22] The ministry had not reported health data in two years, and none has been reported since.[20] In May, Maduro sacked the health minister, Antonieta Caporale, for publishing the damning statistics.[20].
In November 2017 the Venezuelan Society of Public Health informed that a total of 857 cases of measles, from which 465 have been confirmed, had been registered. The Pan American Health Organization reported that at least 71% of the reported cases of measles in 2017 have occurred in Venezuela[23].
In 2018 Venezuela is suffering from acute shortages of food and medicines.
State and private
Private hospitals and clinics and the qualifications of their medical personnel are comparable to U.S. standards. Private health services are costly and "full to bursting." The Venezuelan government has accused private hospitals of profiteering. 2,000 doctors left the country between 2006 and 2008.[24] Overall roughly 1 in 5 Venezuelans have private health insurance.
See also
References
- ↑ Franks, Tim (3 December 2015). "Venezuelan healthcare in collapse as economy ails". BBC News Latin America. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- ↑ Forero, Juan (13 March 2015). "Venezuelans Suffer Amid Crumbling Health System". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Business America. Washington, D.C.: International Trade Administration. 7 September 1981. pp. 14–15.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ Briggs, Charles L. Stories in the time of cholera: Racial profiling during a medical nightmare. Univ of California Press, 2003 pp.3-5
- ↑ GBD Profile Venezuela http://www.healthdata.org/sites/default/files/files/country_profiles/GBD/ihme_gbd_country_report_venezuela.pdf
- 1 2 3 "Venezuela's medical crisis requires world's attention". The Boston Globe. 28 April 2015. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Wilson, Peter (27 April 2015). "The Collapse of Chávezcare". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 17 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Doctors say Venezuela's health care in collapse". Associated Press. Retrieved 22 February 2014.
- ↑ "Médicos del Hospital Universitario de Caracas suspenden cirugías por falta de insumos". Globovision. 21 February 2014. Archived from the original on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ↑ Fernanda Zambrano, María (19 March 2014). "Clínicas del país presentan fallas en 109 productos". Union Radio. Archived from the original on 20 March 2014. Retrieved 20 March 2014.
- ↑ Chinea, Eyanir (20 March 2014). "Sin dólares para importar medicinas, salud de Venezuela en terapia intensiva". Reuters (Latin America). Retrieved 20 March 2014.
- ↑ Pardo, Daniel (23 August 2014). "The malaria mines of Venezuela". BBC. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- ↑ "Venezuela Faces Health Crisis Amid Shortage of HIV/Aids Medication". Fox News Latino. 14 May 2014. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- ↑ Forero, Juan (22 September 2014). "Venezuela Seeks to Quell Fears of Disease Outbreak". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- 1 2 "Venezuela's Maduro denounces "psychological war" waged by opposition". El Pais. 19 September 2014. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- ↑ Wade, Lizzie (23 September 2014). "In Venezuela, doctor flees after being accused of terrorism amid fever outbreak". Science. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- 1 2 Hider, James (5 August 2015). "Thousands dying early as medical system implodes in Venezuela". The Times. UK. Retrieved 5 August 2015. (Subscription required (help)).
- ↑ "Maduro crea Universidad de las Ciencias y de la Salud". El Universal. 8 October 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ↑ "In deteriorating Venezuela, a kid's scraped knee can be life or death". NBC News. 5 October 2016. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 J.R.A. (12 October 2017). "Why malaria is spreading in Venezuela". The Economist.
- ↑ "Politics this week". The Economist.
- ↑ . https://www.economist.com/news/world-week/21721971-politics-week
- ↑ Nacional, El (4 December 2017). "Venezuela acumula 465 casos confirmados de sarampión".
- ↑ "Don't stand so close to me". The Economist. 21 March 2008.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Health in Venezuela. |
- ↑ Briggs, Charles L. Stories in the time of cholera: Racial profiling during a medical nightmare. Univ of California Press, 2003.
