HMS Pearl (1855)
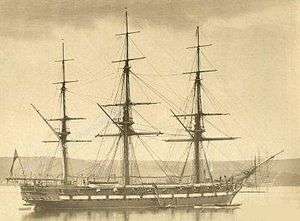 HMS Pearl c.1856 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | HMS Pearl |
| Builder: | Woolwich Dockyard |
| Launched: | 13 September 1855 |
| Fate: | Sold for break up to Castle, August 1884 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Pearl-class corvette |
| Displacement: | 2,115 long tons (2,149 t)[1] |
| Tons burthen: | 1469 bm[1] |
| Length: |
|
| Beam: | 40 ft 4 in (12.29 m) |
| Draught: |
|
| Depth of hold: | 23 ft 11 in (7.29 m) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Sail plan: | Full-rigged ship |
| Speed: | 11.3 knots (20.9 km/h) (under steam) |
| Armament: |
|
HMS Pearl was a Pearl-class 21-gun screw corvette of the Royal Navy launched in 1855, displacing 2,187 tons.
In September 1857, during the Indian Rebellion, 175 of the ship's crew were formed into Pearl's Naval Brigade. The small force, armed largely with rifles, took part in several actions. It was accompanied in many of these by a similar force formed from the crew of Shannon.
The ship was captained by Edward Southwell Sotheby from its commission in 1855. John Borlase replaced Sotheby, on the ships return from India in 1859, from 23 August 1859 to 18 June 1864 when the ship was paid off in Portsmouth. Pearl sailed around the East Indies and China and played a part in the Taiping Rebellion and the bombardment of Kagoshima during the Anglo-Satsuma War.
North Star Affair
In May 1861 the Pearl was involved in an incident involving a British merchant ship named North Star and Chinese pirates. On 13 May, pirates in a junk attacked the North Star off the coast of Hong Kong Island. They killed or mortally wounded at least five members of the crew and stole over 4,000 dollars worth of gold before abandoning the ship. Only two survivors remained on the ship and they hid from the pirates until they left the North Star and then they set sail for the port of Hong Kong. HMS Pearl was anchored off Green Island at the time and she eventually recovered both the merchantman and the survivors.[2]

References
- Notes
- 1 2 3 4 Winfield (2004) p.209
- ↑ A Sydney Man (23 July 1861). "News and Notes CLXIV". The Courier. Brisbane. p. 3. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- Bibliography
- Clowes, William Laird (1903). The Royal Navy: A History From the Earliest Times to the Death of Queen Victoria: Volume VII. Sampson Low, Marston and Company.
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8. OCLC 67375475.
- Williams, E.A. (1859). The Cruise of the Pearl Round the World: With an Account of the Operations of the Naval Brigade in India. London: Richard Bentle.
- Winfield, Rif & Lyon, David (2004). The Sail and Steam Navy List: All the Ships of the Royal Navy 1815–1889. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-032-6. OCLC 52620555.
