HLTF
Helicase-like transcription factor is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HLTF gene.[5][6]
Function
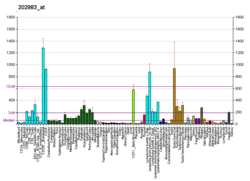
This gene encodes a member of the SWI/SNF family. Members of this family have helicase and ATPase activities and are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. The encoded protein contains a RING finger DNA binding motif. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. However, use of an alternative translation start site produces an isoform that is truncated at the N-terminus compared to the full-length protein.[6]
HLTF is a double-stranded DNA translocase, one of two human homologs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD5 besides SHPRH (SNF2 histone linker PHD RING helicase), that is able to carry out fork regression, similarly to Rad5.[7]
Interactions
HLTF has been shown to interact with UBE2N,[8] RAD18[8] and UBE2V2 [8](see also STRING functional and physical associations network : under the option 'search by name' enter 'protein name' of interest, HLTF, klick on 'GO! ', choose 'organism ', klick on 'continue ->' ).
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000071794 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000002428 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Lin Y, Sheridan PL, Jones KA, Evans GA (Nov 1995). "The HIP116 SNF2/SW12-related transcription factor gene (SNF2L3) is located on human chromosome 3q25.1-q26.1". Genomics. 27 (2): 381–2. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1064. PMID 7558014.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: HLTF helicase-like transcription factor".
- ↑ Unk I, Hajdú I, Blastyák A, Haracska L (Jan 2010). "Role of yeast Rad5 and its human orthologs, HLTF and SHPRH in DNA damage tolerance". DNA Repair (Amst). 9 (3): 257–67. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.12.013. PMID 20096653.
- 1 2 3 Unk I, Hajdú I, Fátyol K, Hurwitz J, Yoon JH, Prakash L, Prakash S, Haracska L (March 2008). "Human HLTF functions as a ubiquitin ligase for proliferating cell nuclear antigen polyubiquitination". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (10): 3768–73. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800563105. PMC 2268824. PMID 18316726.
Further reading
- Sheridan PL, Schorpp M, Voz ML, Jones KA (1995). "Cloning of an SNF2/SWI2-related protein that binds specifically to the SPH motifs of the SV40 enhancer and to the HIV-1 promoter". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (9): 4575–87. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.9.4575. PMID 7876228.
- Descheemaeker K (1993). "On the regulation of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression". Verh. K. Acad. Geneeskd. Belg. 55 (3): 225–64. PMID 8342330.
- Ding H, Descheemaeker K, Marynen P, et al. (1996). "Characterization of a helicase-like transcription factor involved in the expression of the human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene". DNA Cell Biol. 15 (6): 429–42. doi:10.1089/dna.1996.15.429. PMID 8672239.
- Gong X, Kaushal S, Ceccarelli E, et al. (1997). "Developmental regulation of Zbu1, a DNA-binding member of the SWI2/SNF2 family". Dev. Biol. 183 (2): 166–82. doi:10.1006/dbio.1996.8486. PMID 9126292.
- Ding H, Benotmane AM, Suske G, et al. (1999). "Functional interactions between Sp1 or Sp3 and the helicase-like transcription factor mediate basal expression from the human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (28): 19573–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.28.19573. PMID 10391891.
- Mansharamani M, Hewetson A, Chilton BS (2001). "Cloning and characterization of an atypical Type IV P-type ATPase that binds to the RING motif of RUSH transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (5): 3641–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004231200. PMID 11058586.
- Shaheduzzaman S, Krishnan V, Petrovic A, et al. (2002). "Effects of HIV-1 Nef on cellular gene expression profiles". J. Biomed. Sci. 9 (1): 82–96. doi:10.1007/BF02256581. PMID 11810028.
- Moinova HR, Chen WD, Shen L, et al. (2002). "HLTF gene silencing in human colon cancer". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (7): 4562–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.062459899. PMC 123687. PMID 11904375.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Leung WK, Yu J, Bai AH, et al. (2003). "Inactivation of helicase-like transcription factor by promoter hypermethylation in human gastric cancer". Mol. Carcinog. 37 (2): 91–7. doi:10.1002/mc.10124. PMID 12766908.
- Hamai Y, Oue N, Mitani Y, et al. (2004). "DNA hypermethylation and histone hypoacetylation of the HLTF gene are associated with reduced expression in gastric carcinoma". Cancer Sci. 94 (8): 692–8. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01504.x. PMID 12901794.
- Goehler H, Lalowski M, Stelzl U, et al. (2004). "A protein interaction network links GIT1, an enhancer of huntingtin aggregation, to Huntington's disease". Mol. Cell. 15 (6): 853–65. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.016. PMID 15383276.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Fukuoka T, Hibi K, Nakao A (2006). "Aberrant methylation is frequently observed in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma". Anticancer Res. 26 (5A): 3333–5. PMID 17094449.