Governor-General of Barbados
| Governor-General of Barbados | |
|---|---|
.svg.png) Coat of Arms of Barbados | |
 | |
| Viceroy | |
| Style | Her Excellency |
| Residence | Government House, Barbados |
| Appointer | Monarch of Barbados |
| Term length | At Her Majesty's pleasure |
| Formation | 30 November 1966 |
| First holder | Sir John Montague Stow |
.svg.png) |
|---|
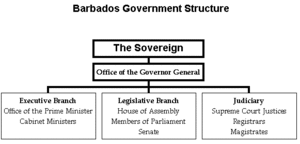
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Barbados |
| Constitution |
|
|
|
|
The Governor-General of Barbados is a vice-regal representative of the Barbadian monarch (presently Queen Elizabeth II). Under the government's Table of Precedence for Barbados, the Governor-General of Barbados is regarded as being the most important of all personnel of the Barbados government.[1]
The office is accorded legitimacy by Chapter IV of the Constitution of Barbados.[2] The Governor-General is appointed by the Queen on the advice of the Prime Minister of Barbados.[3][4] The Governor-General exercises executive powers and who assents to bills in the monarch's name before they can become promulgated into law.[5] The Barbados constitution limits the powers of the Governor-General (known as a constitutional monarchy system of governance).[6] This effectively limits the powers of the Queen, as it does the Governor-General, who, in most instances, exercises authority on the advice of the prime minister or other persons or bodies within Barbados.[7]
The Office of the Governor-General was established when Barbados gained independence in 1966. Since the settlement of Barbados by the British, Barbados has had 68 Governors and subsequently 8 Governors-General.
Duties
The Queen, on the advice of the Prime Minister, appoints a Governor-General to be her representative in Barbados.[8][9] Both the Queen and the Governor-General hold much power of the country, though it is rarely used unilaterally; it is usually only used in such a way in emergencies and in some cases war.[10]
The Governor-General represents the Queen on ceremonial occasions such as the opening of parliament and the presentation of honours and military parades. Under the constitution, the Governor-General is given authority to act in some matters; for example, in appointing and disciplining officers of the civil service,[11] granting "any person convicted of any offence against the laws of Barbados a pardon",[12] and in proroguing parliament. But, in only a few cases is the Governor-General empowered to act entirely on his/her own discretion.
The Governor-General of Barbados also chairs the Privy Council of Barbados.
List of Governors-General of Barbados
On 30 November 1966, Barbados achieved independence from Britain.
| Name (Birth–Death) |
Term of office | Notes | Monarch (Reign) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sir John Montague Stow (1911–1997) |
30 November 1966 |
18 May 1967 |
Elizabeth II (1966–present) | |
| 2 | Sir Arleigh Winston Scott (1900–1976) |
18 May 1967 |
9 August 1976 |
Died in office | |
| - | Sir William Douglas (1921–2003) |
9 August 1976 |
17 November 1976 |
Acting (first time) | |
| 3 | Sir Deighton Lisle Ward (1909–1984) |
17 November 1976 |
9 January 1984 |
Died in office | |
| - | Sir William Douglas (1921–2003) |
10 January 1984 |
24 February 1984 |
Acting (second time) | |
| 4 | Sir Hugh Springer (1913–1994) |
24 February 1984 |
6 June 1990 |
||
| 5 | Dame Nita Barrow (1916–1995) |
6 June 1990 |
19 December 1995 |
Died in office | |
| - | Sir Denys Williams (1929–2014) |
19 December 1995 |
1 June 1996 |
Acting | |
| 6 | Sir Clifford Husbands (1926–2017) |
1 June 1996 |
31 October 2011 |
||
| - | Sir Elliott Belgrave (1931–) |
1 November 2011 |
30 May 2012 |
Acting | |
| - | Dame Sandra Mason (1949–) |
30 May 2012 |
1 June 2012 |
Acting | |
| 7 | Sir Elliott Belgrave (1931–) |
1 June 2012 |
30 June 2017 |
||
| - | Sir Philip Greaves (1931–) |
1 July 2017 |
8 January 2018 |
Acting | |
| 8 | Dame Sandra Mason (1949–) |
8 January 2018 |
Incumbent | ||
Official oath of office
According to the First Schedule section of the Constitution of Barbados, the official Oath of office for the Governor-General of Barbados is as follows:
| “ | I, _________________________, do swear that I will well and truly serve Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, Her Heirs and Successors, in the office of Governor-General. So help me God. | ” |
See also
- Government House, the official residence of the Governor-General
- Order of Barbados
- List of Governors of Barbados
- Governor-General of the West Indies Federation
- List of Prime Ministers of Barbados
- List of current vice-regal representatives of Elizabeth II
References
- ↑ Table of Precedence for Barbados - July, 2008
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter IV
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter IV, Section 28(1)
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter IV, Section 32
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter V, Section 58(1)
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter IV, Section 32
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter IV, Section 32
- ↑ "Queen's role in Barbados". The Monarchy Today: Queen and State. The Barbadian Monarchy. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter VI, Part 1; Section 28
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter III, Part 15; Section 25(1)(a)
- ↑ The role of GG is not just ceremonial, says Arthur
- ↑ Constitution, Chapter VI, Part 2; Section 78(1)(a)