Garden Route
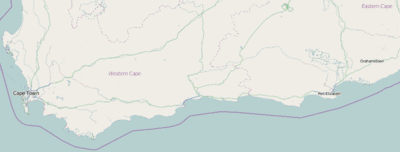
The Garden Route (Afrikaans: Tuinroete) is a 300-kilometre (190 mi)[1]stretch of the south-western coast of South Africa which extends from Mossel Bay (many say Mossel Bay is not part of the Garden Route, because it is positioned behind what locals call the "Boom Gordyn" roughly translates to "Tree Curtain") in the Western Cape to the Storms River in the Eastern Cape. The name comes from the verdant and ecologically diverse vegetation encountered here and the numerous lagoons and lakes dotted along the coast. It includes towns such as Knysna, Plettenberg Bay, Mossel Bay, Little Brak River and Nature's Valley; with George, the Garden Route's largest city and main administrative centre.
It has an oceanic climate, with mild to warm summers, and mild to cool winters. It has the mildest climate in South Africa and the second mildest climate in the world, after Hawaii, according to the Guinness Book of Records. Temperatures rarely fall below 10 °C in winter and rarely climb beyond 28 °C in summer. Rain occurs year-round, with a slight peak in the spring months, brought by the humid sea-winds from the Indian Ocean rising and releasing their precipitation along the Outeniqua and Tsitsikamma Mountains just inland of the coast.
The Route is sandwiched between the aforementioned mountains and the Indian Ocean, with mountain passes, including the Outeniqua Pass, linking the area with the arid Little Karoo. The Outeniqua and Tsitsikamma indigenous forests are a unique mixture of Cape Fynbos and Temperate Forest and offer hiking trails and eco-tourism activities. Nearly 300 species of bird life are to be found in a variety of habitats ranging from fynbos to forest to wetlands.
In 2017 the Garden Route was added to UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves[2]
- A river mouth in the Tsitsikamma National Park, situated on the Garden Route
 Fairy Knowe station
Fairy Knowe station- A tranquil scene at a lake on the Garden Route
 A vineyard on the Garden Route in winter
A vineyard on the Garden Route in winter
See also
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Garden Route. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Garden Route. |
References
- ↑ "10 epic road trips in the world to take once in your lifetime". www.emptyshack.com. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
- ↑ "South Africa's Garden Route added to UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves". Unesco. June 21, 2017. Retrieved August 6, 2018.