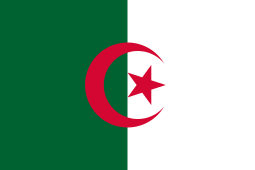
Flag of Algeria
 | |
| Use | National flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 3 July 1962 |
| Design | A vertical bicolor of green and white with the red crescent encircling the red five-pointed star centered along the dividing line. |
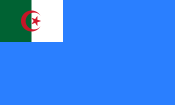
 Variant flag of Algeria | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | 27 June 1963 (amended in 1995) |
| Design | As above, with white crossed fouled anchors in the canton. |
 Variant flag of Algeria | |
| Use | Naval Jack |
The national flag of Algeria (Arabic: علم الجزائر, translit. Acenyal n Dzayer) consists of two equal vertical bars, green and white, charged in the center with a red star and crescent. The flag was adopted on 3 July 1962. A similar version was used by the Algerian government in exile from 1958–1962. The Western blazon is per pale vert and argent; a crescent and star gules.
History

The Barbary pirates of Ottoman Algeria between the 15th and 17th century widely used flags that were emblazoned with one or more crescents. These could however vary greatly in color, with dark red, black, green and white being in use. Besides these, Algerian pirates also used various flags in plain color, such as plain black ones signalling death. Less often, Algerian flags of this time also carried other motifs, such as suns, stars and crossed swords.[1] It is also known that Algiers used an orange flag with a white horizontal sword on it by the early 19th century.[2]
Description
.svg.png)
Algerian ships fly it as their ensign, except for ships of the Algerian National Navy, which use one charged with two white crossed anchors in the canton as the naval ensign. Formerly, the two crossed anchors in the canton were red.
According to algeria-un.org, cited in 1999, the features of the flag are set down precisely, being described as:
The green must be a composition of equal yellow and blue having, according to the diagram of contrasts of Rood, a wavelength of 5,411 [ångströms] and the position 600 on the normal spectrum. The red must be pure, of primary non-decomposable colour, and exempt of blue and yellow having, according to the above-indicated diagram, a wavelength of 6,562 [ångströms] and the position 285 on the normal spectrum.[3]
Colours scheme | Red | Green | White |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | 210-16-52 | 0-114-41 | 255-255-255 |
| Hexadecimal | #d21034 | #007229 | #ffffff |
| CMYK | 0, 92, 75, 18 | 100, 0, 64, 55 | 0, 0, 0, 0 |
| Pantone | 186 C | 356 C | White |
See also
References
- ↑ Konstam (2016), pp. 34–37, 40, 43, 52, 56, 57 61.
- ↑ Konstam (2016), p. 61.
- ↑ "Thanh-Tâm Lê, 2 January 1999 (crwflags.com)". 1999. Retrieved 2016-06-15.
Bibliography
- Konstam, Angus (2016). The Barbary Pirates. 15th–17th Centuries. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4728-1543-9.
External links
![]()