FC Cincinnati stadium
 Concept design from October 2018 | |
| Address | Central Parkway and Wade Street |
|---|---|
| Location | Cincinnati, Ohio |
| Coordinates | 39°06′41″N 84°31′20″W / 39.11139°N 84.52222°WCoordinates: 39°06′41″N 84°31′20″W / 39.11139°N 84.52222°W |
| Public transit |
|
| Owner | FC Cincinnati |
| Operator | FC Cincinnati |
| Type | Soccer-specific stadium |
| Capacity | 25,500–26,500 |
| Construction | |
| Opened | 2021 (planned) |
| Construction cost | $212.5 million |
| Architect | MEIS Architects |
| Builder | Turner Construction |
| Project manager | Machete Group |
| Tenants | |
| FC Cincinnati (MLS) (2021–) (planned) | |
| Website | |
|
fccincinnati | |
The FC Cincinnati stadium is a proposed soccer-specific stadium in Cincinnati, Ohio. It is planned to be the home of FC Cincinnati, a Major League Soccer (MLS) team that will replace a second-division team in 2019. The stadium will be located in the West End neighborhood and is scheduled to open in 2021 and cost $200 million to construct.[1][2] As of October 2018, the stadium is expected to hold between 25,500 and 26,500 occupants.[3] The stadium will be built at the site of Stargel Stadium on Central Parkway at Wade Street.[4][5]
The stadium was proposed in 2016, as part of the team's bid for an MLS expansion franchise, and a list of sites was submitted with the bid in January 2017. A shortlist of three sites, in Oakley, the West End, and Newport, Kentucky, was announced in May 2017. The West End site was chosen in early 2018 and approved in April in a land swap deal with Cincinnati Public Schools.[6] On May 29, 2018, MLS announced that Cincinnati had won an expansion team, to begin play in 2019 at Nippert Stadium and move to the new stadium upon its completion in 2021.[2][7]
Planning
Background
FC Cincinnati was founded in 2015 and played its first three seasons in the second-division United Soccer League at Nippert Stadium, a college football venue. After a successful first season in which the team's home games averaged 17,296 attendees, the club's ownership group began negotiations with Major League Soccer to bid for an expansion franchise.[8] Cincinnati formally submitted its expansion bid in January 2017, including a shortlist of locations for a potential stadium to meet the bid's requirement for a soccer-specific venue.[9]
FC Cincinnati's management first suggested the possibility of building a new stadium in late November 2016, when the club hosted MLS commissioner Don Garber for a day-long visit. During a town hall meeting held with club supporters that day, Garber suggested that Nippert was not a long-term solution for the team. Club manager Jeff Berding said during the meeting that the club had recently begun to look for 15-to-20-acre (6.1 to 8.1 ha) sites in or near the "urban core" of Cincinnati.[10]
Location decision and negotiations
.jpg)
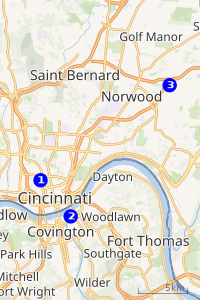 |
| Proposed stadium sites 1 2 3 |
FC Cincinnati narrowed the list of locations for a potential stadium to a shortlist of three sites in May 2017: the football stadium used by Taft High School in the West End neighborhood; the former Milacron factory in Oakley on Interstate 71; and a riverfront site in Newport, Kentucky.[11] The club unveiled preliminary designs for a stadium in June 2017, outlining plans for a horseshoe-shaped stadium with a continuous roof and capacity for 25,000 to 30,000 people. It was designed by Dan Meis, who envisioned steep terraced seating and homages to Allianz Arena in Munich, including the use of LED lights and a translucent ETFE roof, for use at the three shortlist sites.[12][13][14]
In November 2017, the Cincinnati City Council passed legislation that would fund infrastructure improvements and a parking garage at the stadium, should a location within the city be chosen. The Oakley site was named as the leading candidate and formed the basis of the city council's infrastructure legislation.[15] FC Cincinnati presented its bid to MLS in December, including a stadium at the Oakley site,[16] but the Nashville bid was chosen instead for a 2020 expansion.[17][18]
The club signed an option contract with the Cincinnati Metropolitan Housing Authority to acquire land in the West End neighborhood in January 2018, signalling their intent to choose the site.[19] The following month, FC Cincinnati revealed plans to perform a land swap with Cincinnati Public Schools to acquire Stargel Stadium on the campus of Taft High School, with a new high school stadium being built nearby.[20] The land swap would require the approval of the Cincinnati Public School's board of directors, who declined to accept the club's offer because of tax abatement rules, which would require an additional $20 million in taxes to be paid by FC Cincinnati. In response, FC Cincinnati announced in March that it would remove the West End site from consideration and focus on the remaining two sites, which had the support of their respective county governments.[21][22] By early April, however, the club had announced that the Oakley and Newport sites were out of contention, due to the remoteness of the Oakley site and a landowner dispute in Newport, and that FC Cincinnati would restart negotiations for the West End site.[23][24]
The school board received an offer from the club to pay $25 million and build a new $10 million high school stadium and unanimously approved the land swap on April 10.[25] The club signed a community benefits agreement with the West End Neighborhood Council, despite opposition from a majority of the council, but the proposal was amended and agreed to by a majority of the council weeks later.[26][27] On April 16, the city council voted 5–4 for an ordinance that would fund $40 million in infrastructure improvements to support the stadium project.[28] A second city council vote on May 16 approved the community benefits agreement and was the final city action needed before a decision by MLS.[4] The league awarded the expansion franchise in an announcement on May 29.[2]
The construction of a new $200 million stadium with public money remained controversial, culminating in the formation of a citizens' group in 2017 to push Nippert Stadium as the permanent home of Cincinnati's MLS team.[29] FC Cincinnati ruled out the use of Nippert Stadium due to the stadium's outdated design that would present construction challenges.[30] During the final negotiations for the West End site, a separate group proposed that the community benefits agreement be decided in a public referendum, but were rejected on the grounds that the city council used an emergency ordinance to approve the stadium deal.[31]
Design revisions

Under a preliminary design schematic released in May 2018, the stadium would have 21,080 seats, with 16,610 general admission seats and 3,970 premium seats. An additional 7,000 seats would be added by filling in two of the corners and ends.[32] However, in June 2018, the club said they were essentially "starting over" on designing the stadium.[33] General manager Jeff Berding said he expected the capacity to be somewhere between 21,000 and 30,000, depending on what the club could afford.[34]
In October 2018, FC Cincinnati released new design concept images of the stadium for the first time since the stadium site had been finalized. As in previous designs, the roof and exterior facades would be made of ETFE foil, a translucent material upon which colors and designs may be projected. The stadium was now expected to hold between 25,500 and 26,500 attendees, which would make it one of the largest soccer-specific stadiums in North America.[35] The dimensions of the stadium were also announced with new precision; the club shared draft images showing the precise footprint of the stadium within its land plot, and declared that the stadium's maximum height would be less than 120 feet (37 m).[3]
Funding
The stadium will cost $212.5 million to construct, with the majority of funding coming from FC Cincinnati and its ownership group. The club will also fund $6.2 million in West End improvements and $10 million for a new high school football stadium, in addition to $25 million to Cincinnati Public Schools as part of the land use agreement. Infrastructure improvements around the stadium will be paid for using $34 million in city funds from a local tax increment financing district and $19 million from Hamilton County and the State of Ohio.[36][37][38] In June 2018, the club named U.S. Bank as the financial partner for the project.[39]
Construction
FC Cincinnati's stadium will be designed by MEIS Architects and Elevar Design Group. Turner Construction was hired as the general contractor, working alongside Jostin Construction. Machete Group will provide oversight on the project as the owner's representative.[39] The project is scheduled to begin construction in 2019, after the replacement for Stargel Stadium is completed at a nearby location.[35][40]
Transportation
The stadium will be located along Central Parkway, which splits the West End and Over-the-Rhine neighborhoods just northwest of Downtown Cincinnati, between John and Wade streets.[5][41] The area is currently served by SORTA buses and is two blocks from a streetcar stop on the Cincinnati Bell Connector.[37]
References
- ↑ Watkins, Steve (March 22, 2018). "Here's when FC Cincinnati plans to begin play in new stadium". Cincinnati Business Journal. Retrieved May 29, 2018. (Subscription required (help)).
- 1 2 3 "Cincinnati awarded MLS expansion club, will start play in 2019" (Press release). Major League Soccer. May 29, 2018. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- 1 2 FCC Communications (October 9, 2018). "FC Cincinnati Releases Initial Concept Designs for West End Stadium". FC Cincinnati. Retrieved October 9, 2018.
- 1 2 Knight, Cameron (May 16, 2018). "Team, neighbors agree to benefit pact, then City Council gives its approval". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- 1 2 Fast, Austin (April 24, 2018). "Here's how FC Cincinnati stadium might fit into the West End". WCPO. Retrieved May 30, 2018.
- ↑ "Key dates in FC Cincinnati's lurching effort to get a stadium approved". The Cincinnati Enquirer. April 6, 2018. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Brennan, Patrick (May 29, 2018). "It's official: FC Cincinnati has joined MLS, will begin play in 2019". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ "FC Cincinnati 'in talks' with Major League Soccer, but no solid plan in the works". WCPO. April 23, 2016. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Brennan, Patrick (January 31, 2017). "FC Cincinnati submits expansion bid to MLS". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Pfahler, Laurel (November 30, 2016). "FC Cincinnati looking at long-term stadium plans with eye on MLS". WCPO. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Williams, Jason; Brennan, Patrick (May 24, 2017). "Here's where FC Cincinnati is looking to build new stadium". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Brennan, Patrick (June 12, 2017). "FC Cincinnati unveils stadium design, emphasizes Newport at OTR event". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Chiles, Richard (June 29, 2017). "3 communities vying for FC Cincinnati 25,000-seat stadium". WLWT. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Pfahler, Laurel (June 12, 2017). "This is what FC Cincinnati hopes to build". WCPO. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron; Wartman, Scott; Coolidge, Sharon (November 29, 2017). "'Goal!': City, county clear way for FC Cincinnati's MLS bid". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Pfahler, Laurel (December 5, 2017). "FC Cincinnati set to make final expansion pitch to MLS". Dayton Daily News. Retrieved June 6, 2018.
- ↑ Straus, Brian (December 19, 2017). "MLS Announces Nashville as Next Expansion City". Sports Illustrated. Retrieved June 6, 2018.
- ↑ Brennan, Patrick; Coolidge, Sharon (December 19, 2017). "Where does Major League Soccer go after Nashville? FC Cincinnati still in hunt". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved June 6, 2018.
- ↑ Coolidge, Sharon; Sparling, Hannah (January 22, 2018). "Stadium clue? FC Cincinnati signs option on land in the West End". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Coolidge, Sharon (February 12, 2018). "FC Cincinnati wants to move Stargel for Major League Soccer stadium; school board mum". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron; Sparling, Hannah (March 16, 2018). "FC Cincinnati shuts down West End stadium plans, moving to Oakley or Newport". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (March 19, 2018). "FC Cincinnati: How sites in Newport and Oakley stack up for a new soccer stadium". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (April 5, 2018). "FC Cincinnati wants 'winning partnership' for stadium in West End". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Wartman, Scott (April 9, 2018). "For FC Cincinnati, why not Newport? Developer says condos, retail, restaurants fit better". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (April 10, 2018). "FC Cincinnati land swap OK'd by Cincinnati's school board amid shouts of opposition". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (April 17, 2018). "'We need to tear this up and start all over again': West End fights over stadium deal". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (May 22, 2018). "So what's in FC Cincinnati's community benefits agreement with the West End?". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron; Sparling, Hannah (April 16, 2018). "FC Cincinnati: City Council OKs deal for West End stadium by 5-4 vote". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Fast, Austin (August 16, 2017). "Citizen group calls upon MLS to accept Nippert Stadium instead of forcing new taxpayer-funded venue". WCPO. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Driehaus, Bob; Monk, Dan (June 30, 2017). "Why not Nippert? FC Cincinnati GM calls UC football stadium an 'implausible' option for MLS". WCPO. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (May 11, 2018). "FC Cincinnati stadium on the ballot? City says 'no'". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Wartman, Scott; Knight, Cameron (April 24, 2018). "Schematics show seat details, lay of the land for West End FC Cincinnati stadium". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Pfahler, Laurel (June 29, 2018). "FC Cincinnati says it's 'starting over' with design for its Major League Soccer stadium". WCPO. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ↑ Brennan, Patrick (June 29, 2018). "Maximum capacity versus ticket scarcity: The debate to determine FC Cincinnati's West End stadium capacity". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Gannett Company. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- 1 2 Brennan, Patrick (October 9, 2018). "FC Cincinnati reveals initial designs for West End stadium". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- ↑ Knight, Cameron (April 11, 2018). "City's FC Cincinnati stadium deal includes paying for 750 additional parking spaces". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- 1 2 Williams, Jason (May 29, 2018). "PX column: The winners and losers in Cincinnati's Major League Soccer announcement". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- ↑ Straus, Brian (April 6, 2018). "Stadium Site Progress Could Push Cincinnati's MLS Expansion Bid to Finish Line". Sports Illustrated. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
- 1 2 Demeropolis, Tom (June 29, 2018). "FC Cincinnati names construction, design team for stadium". Cincinnati Business Courier. Retrieved June 29, 2018.
- ↑ Hatch, Charlie (June 29, 2018). "FC Cincinnati announces timeline for West End stadium, to unveil new design". The Cincinnati Enquirer. Retrieved June 29, 2018.
- ↑ Demeropolis, Tom (February 12, 2018). "Here's how FC Cincinnati stadium could fit in West End". Cincinnati Business Journal. Retrieved May 29, 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to FC Cincinnati stadium. |