Earley railway station
| Earley | |
|---|---|
 Entrance to Earley Station | |
| Location | |
| Place | Earley |
| Local authority | Wokingham |
| Grid reference | SU752718 |
| Operations | |
| Station code | EAR |
| Managed by | South Western Railway |
| Number of platforms | 2 |
| DfT category | D |
|
Live arrivals/departures, station information and onward connections from National Rail Enquiries | |
| Annual rail passenger usage* | |
| 2012/13 |
|
| 2013/14 |
|
| 2014/15 |
|
| 2015/16 |
|
| 2016/17 |
|
| History | |
| Key dates | Opened November 1863 |
| Original company | South Eastern Railway |
| Pre-grouping | South Eastern Railway |
| Post-grouping | Southern Railway |
| National Rail – UK railway stations | |
| * Annual estimated passenger usage based on sales of tickets in stated financial year(s) which end or originate at Earley from Office of Rail and Road statistics. Methodology may vary year on year. | |
|
| |
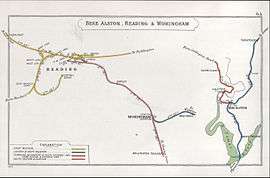
Earley railway station serves Earley in Berkshire, England. It is 40 miles 44 chains (65.3 km) down the line from London Waterloo. It is on the Waterloo to Reading Line, and forms the last stop before the terminus of the line at Reading.
The station has two side platforms, on either side of the twin track line. A large two-storey station building is situated on the Reading-bound (western-most) platform. The two platforms are linked by a footbridge over the tracks, and the London-bound platform has a waiting room. The station is accessed by an approach road from the nearby main road between Reading and Wokingham, and on this approach is a terrace of three single storey cottages that were built for the SER at the same time as the station, to house railway staff and their families.
History
The South Eastern Railway (SER) opened Earley station in May 1863 on the former Reading, Guildford and Reigate Railway (RG&RR), which originally terminated at its own Reading Southern station. The RG&RR had opened on 4 July 1849 and the SER had taken it over in 1852.[1][2]
By the time Earley station opened, the Staines, Wokingham & Woking Junction Railway (SW&WJR) was also operating a service between London Waterloo station and Reading Southern station that used running powers over the SER through Earley station. The SW&WJR was absorbed by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) in 1878, and the LSWR continued to operate over SER tracks until both railway companies became part of the Southern Railway in 1923.[3][4]
In 1939, the line through Earley station was electrified, on the DC third rail system, as part of the electrification of the Reading to London Waterloo service. Trains on the original SER route to Guildford and Reigate continued to be steam hauled.[5]
In 1948, the Southern Railway and the Great Western Railway (GWR), which also served Reading, were nationalised and merged with other newly nationalised railways to create British Railways. As a result of British Railways' 1955 Modernisation Plan, diesel traction replaced steam on the non-electrified services through Earley. In 1970, Reading Southern station closed, and the line was diverted into the adjacent, former GWR, Reading station.[6][7]
Services
Earley station is served by South Western Railway electric services between Reading and London Waterloo, which run half-hourly outside peak periods and at weekends, with additional trains during weekday peak hours. Great Western Railway trains between Reading and Gatwick Airport via Guildford pass through the station without stopping, as do occasional CrossCountry trains between Guildford and the north of England.[8][9]
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winnersh Triangle | South Western Railway Waterloo to Reading line |
Reading | ||
Gallery




References
- ↑ Nock 1971, p. 20.
- ↑ Kidner 1982, p. 6.
- ↑ Kidner 1982, p. 7.
- ↑ Matthews 2006, p. 32.
- ↑ Mitchell & Smith 1989.
- ↑ Butt 1995, p. 195.
- ↑ Her Majesty's Government (1947). "Transport Act 1947". The Railways Archive. (originally published by Her Majesty's Stationery Office). Retrieved 2006-11-25.
- ↑ "Electronic national rail timetable, Table 148" (PDF). Network Rail. December 2016. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
- ↑ "Electronic national rail timetable, Table 149" (PDF). Network Rail. December 2016. Retrieved 4 February 2016.
Bibliography
- Butt, R.V.J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations. Yeovil: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-85260-508-1. R508.
- Kidner, R.W. (1982) [1974]. The Reading to Tonbridge Line. Locomotion Papers (3rd ed.). Salisbury: The Oakwood Press. ISSN 0305-5493. LP79.
- Matthews, Rupert (2006). Lost Railways of Berkshire. Newbury: Countryside Books. ISBN 1-85306-990-6.
- Mitchell, Vic; Smith, Keith (1989). Branch lines around Ascot (1st ed.). Midhurst: Middleton Press. ISBN 978 0 906520 64 2.
- Nock, O.S. (1971) [1961]. The South Eastern and Chatham Railway. Shepperton: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0268-1.
External links

- Train times and station information for Earley railway station from National Rail
Coordinates: 51°26′28″N 0°55′05″W / 51.441°N 0.918°W